Bernoulli's Equation Differential Equation - A bernoulli equation has this form: In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. When n = 1 the. It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. To find the solution, change the dependent variable. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation.
A bernoulli equation has this form: Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is. When n = 1 the. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: To find the solution, change the dependent variable.
A bernoulli equation has this form: Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). To find the solution, change the dependent variable. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. When n = 1 the. How to solve this special first order differential equation. It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a.
SOLUTION Differential equation bernoulli s equations with solved
To find the solution, change the dependent variable. In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: Dy dx.
Differential Equation Calculator
A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). To find the solution, change the dependent variable. How to solve this special first order differential equation. A bernoulli equation has this form:
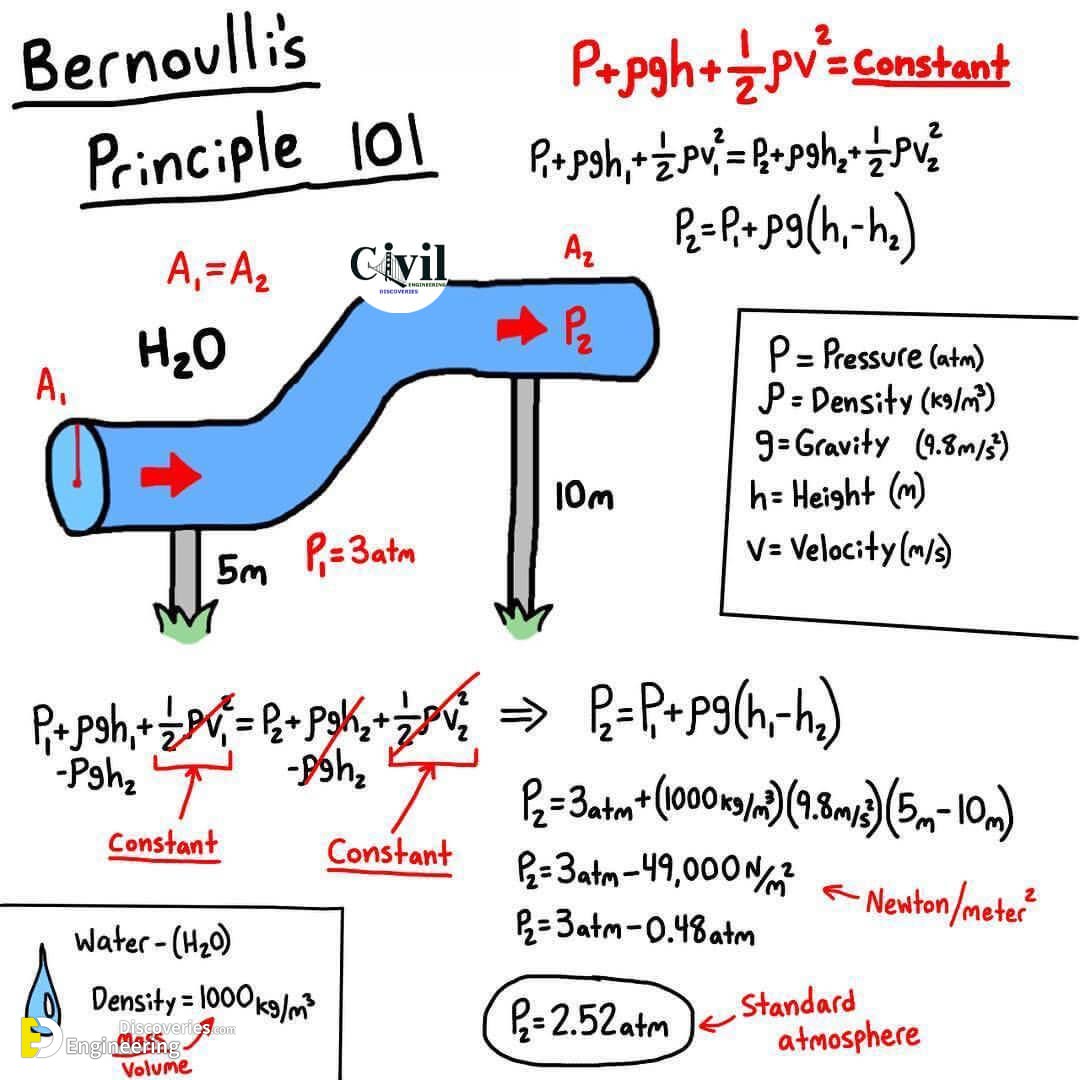
Understanding Bernoulli's Equation Engineering Discoveries
In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. When n = 1 the. When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. Bernoulli.
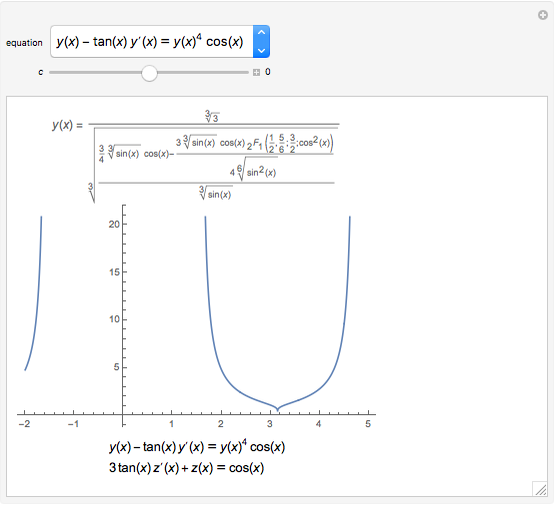
Bernoulli's Differential Equation Wolfram Demonstrations Project
To find the solution, change the dependent variable. How to solve this special first order differential equation. It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. When n = 1 the. Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear).
SOLUTION Differential equation the bernoulli equation Studypool
Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. To find the solution, change the dependent variable..
What is Bernoulli's Equation Bernoulli's Principle Definition
In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is.
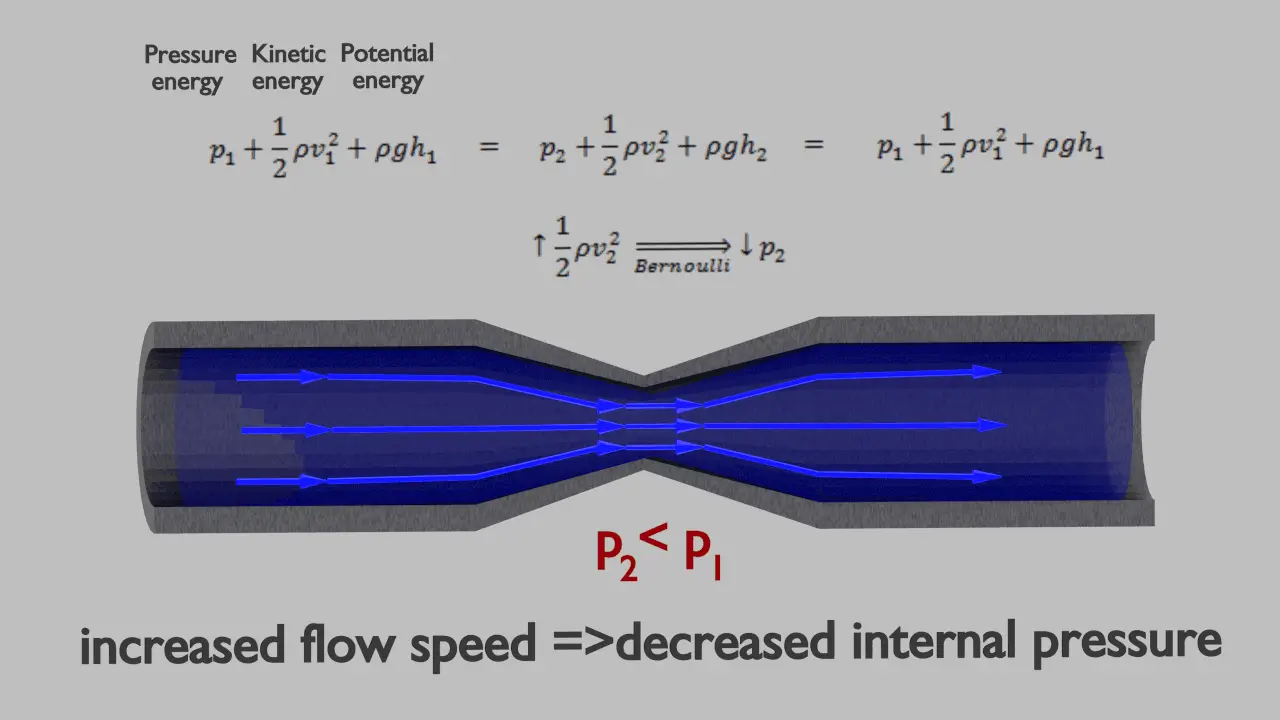
The Bernoulli's Equation in Different Conditions Download Scientific
Bernoulli differential equation is one of the topics that fall under calculus and differential equations. It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. In mathematics,.
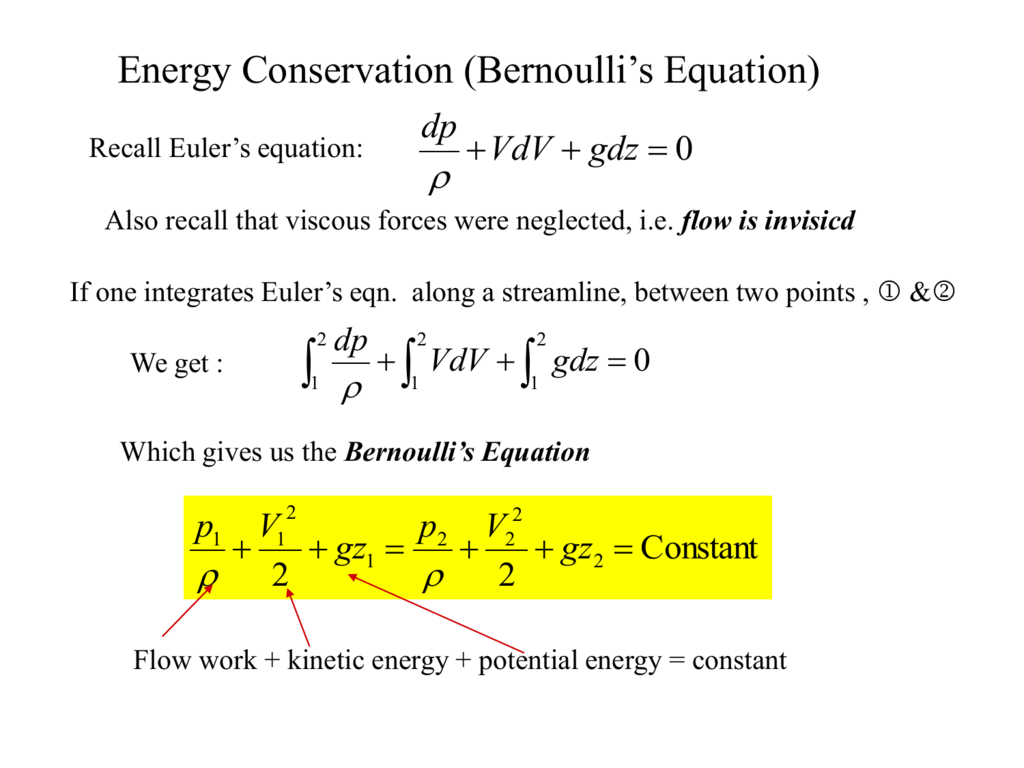
Energy Conservation (Bernoulli's Equation)
When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: To find the solution, change the dependent variable. How to solve this special first order differential equation. In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the.
Bernoulli’s differential equation Yawin
A bernoulli equation has this form: When n = 0 the equation can be solved as a first order linear differential equation. When n = 1 the. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n.
Differential Equation Calculator
Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear). It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. A bernoulli equation has this form: When n = 1 the. In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p.
Bernoulli Differential Equation Is One Of The Topics That Fall Under Calculus And Differential Equations.
How to solve this special first order differential equation. To find the solution, change the dependent variable. It is a nonlinear differential equation of a specific kind that can be. Dy dx +p(x)y = q(x)yn, where n 6= 1 (the equation is thus nonlinear).
When N = 0 The Equation Can Be Solved As A First Order Linear Differential Equation.
When n = 1 the. In this section we are going to take a look at differential equations in the form, where p(x) p (x) and q(x) q (x) are continuous functions on the interval we’re working on and n n is a. A bernoulli differential equation can be written in the following standard form: In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation is called a bernoulli differential equation if it is of the form y ′ + p ( x ) y = q ( x ) y n , {\displaystyle y'+p(x)y=q(x)y^{n},} where n {\displaystyle n} is.