Faraday's Law Differential Form - Use stokes’ law (the curl theorem) to derive faraday’s law in integral form. The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university of st andrews 1 (1) write down the differential form. Write down the differential form of faraday’s law. We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form. Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in flux δ, time δt, and number of.
Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in flux δ, time δt, and number of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Write down the differential form of faraday’s law. Use stokes’ law (the curl theorem) to derive faraday’s law in integral form. We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form. The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university of st andrews 1 (1) write down the differential form.
Write down the differential form of faraday’s law. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university of st andrews 1 (1) write down the differential form. Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in flux δ, time δt, and number of. The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form. Use stokes’ law (the curl theorem) to derive faraday’s law in integral form.
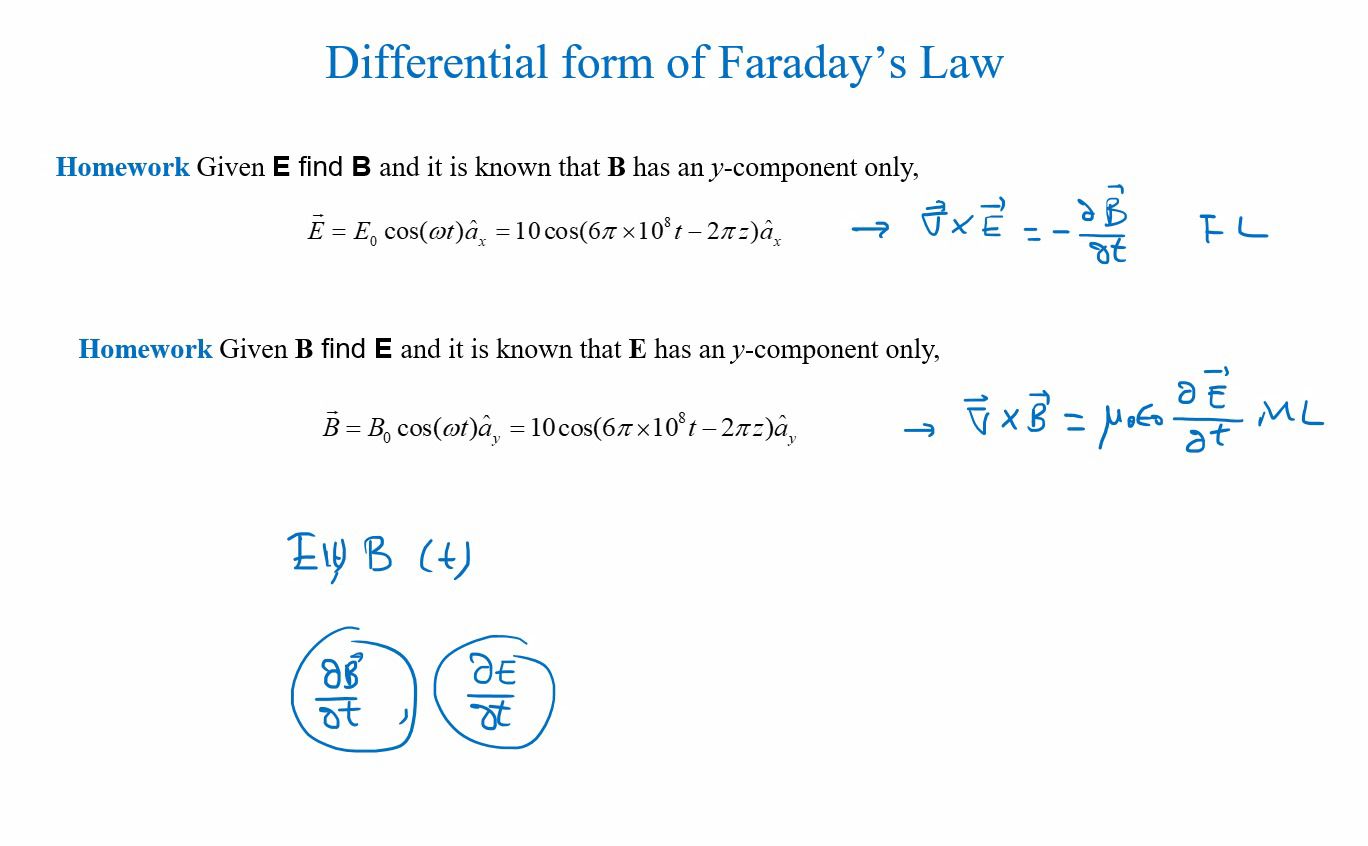
Solved Differential form of Faraday's Law Homework Given E
We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form. Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in flux δ, time δt, and number of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Use stokes’ law (the curl theorem) to.
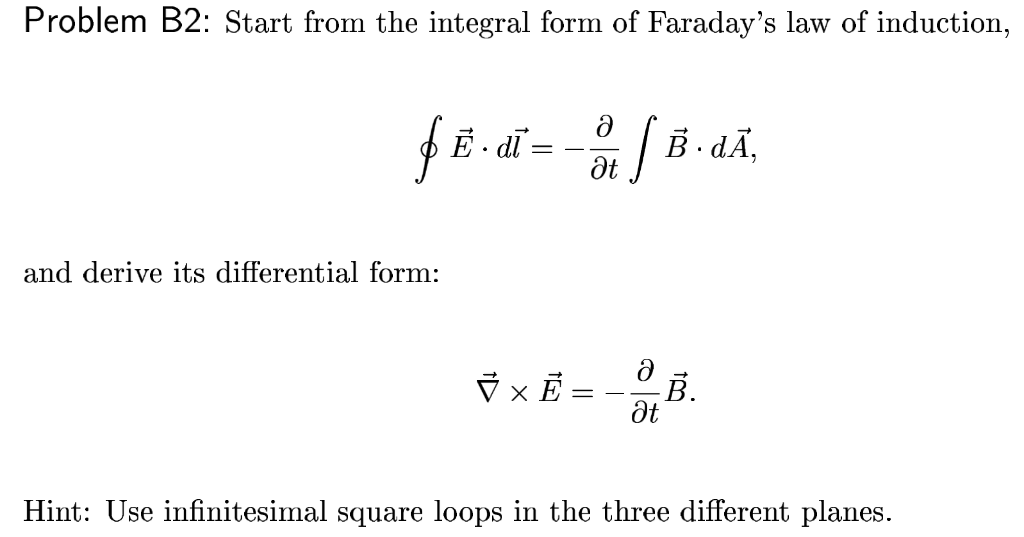
Solved Problem B2 Start from the integral form of Faraday's
Write down the differential form of faraday’s law. The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Use stokes’ law (the curl theorem) to derive faraday’s law in integral form. Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in flux δ, time δt, and number of. Let's consider both the.
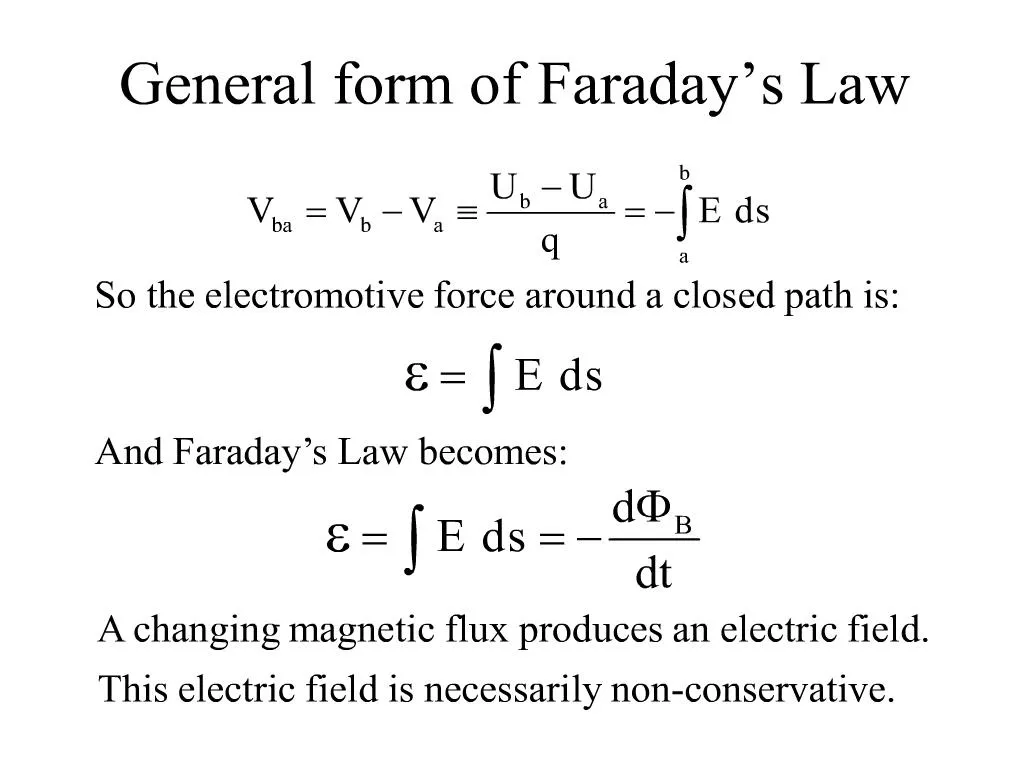
PPT general form of faraday s law PowerPoint Presentation, free
Use stokes’ law (the curl theorem) to derive faraday’s law in integral form. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university of st andrews 1 (1) write down.
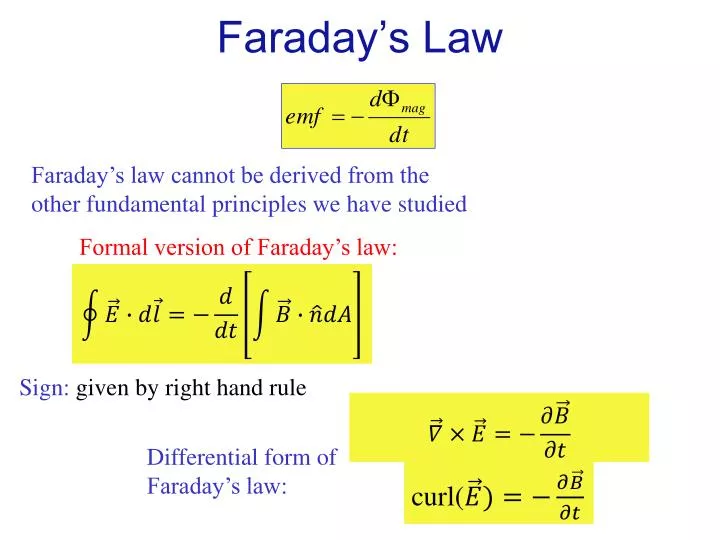
PPT Faraday’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3607741
The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in flux δ, time δt, and number of. We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form. Write down the differential form of faraday’s law. Let's consider both the integral.
SOLUTION Physics faraday s law of induction and its
Use stokes’ law (the curl theorem) to derive faraday’s law in integral form. Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in flux δ, time δt, and number of. Write down the differential form of faraday’s law. We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form. Let's consider.
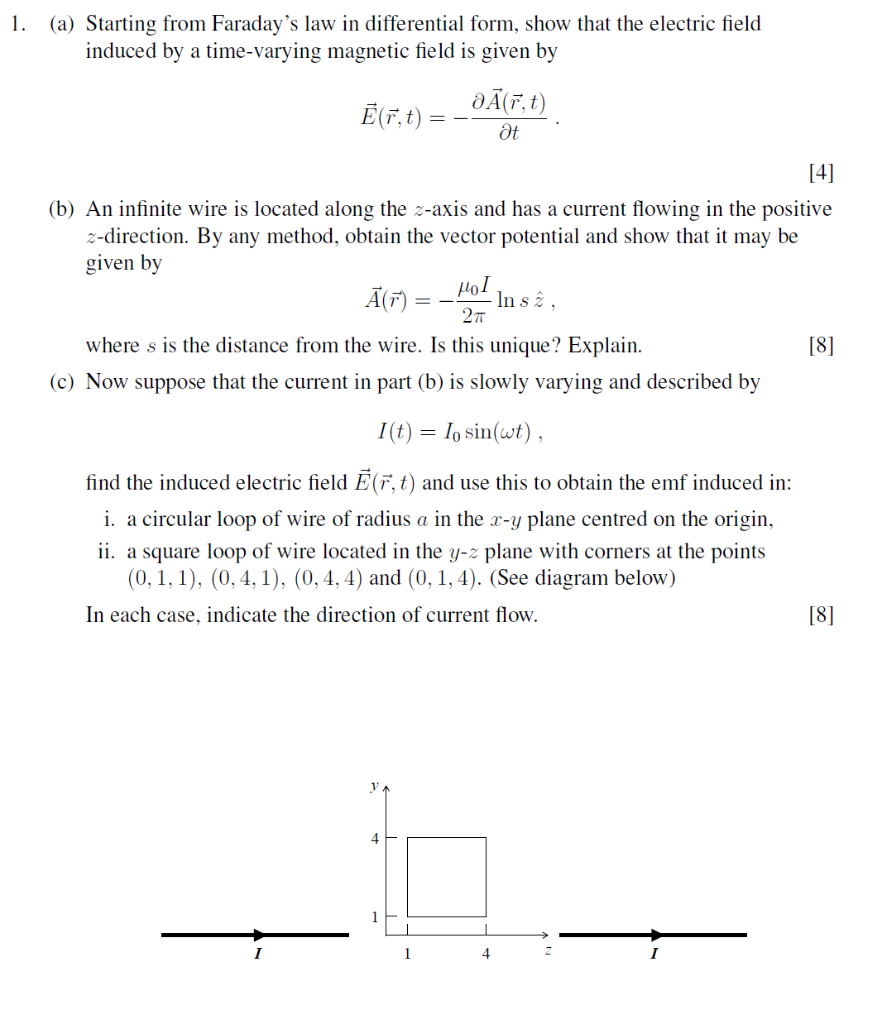
Solved (a) Starting from Faraday's law in differential form,
Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university of st andrews 1 (1) write down the differential form. The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in flux δ, time δt, and number of. Use.
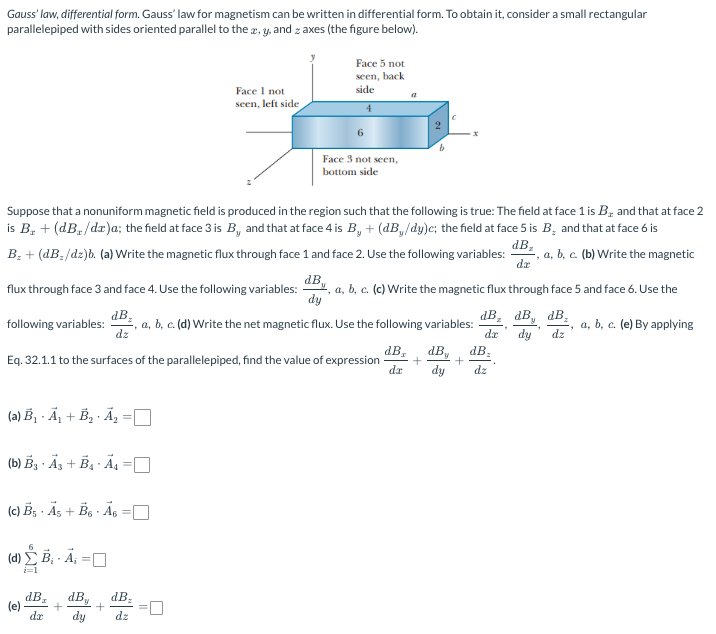
Solved Gauss' law, differential form. Gauss' law for
Write down the differential form of faraday’s law. Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university of st andrews 1 (1) write down the differential form. The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): We show.
Differential Form First Law Thermodynamics Stock Vector (Royalty Free
Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university of st andrews 1 (1) write down the differential form. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form. Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by.
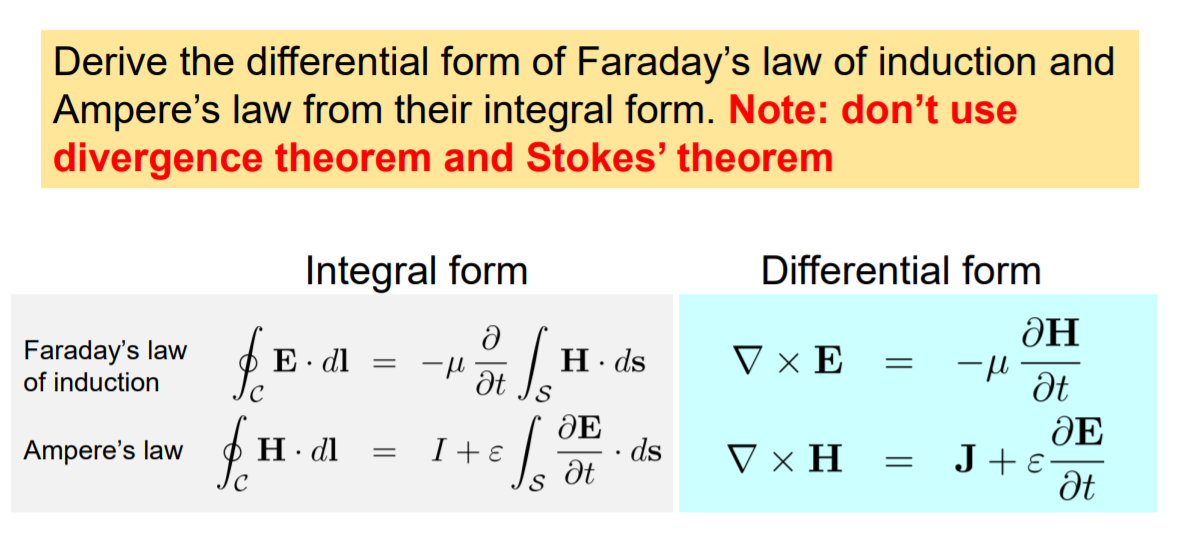
Solved Derive the differential form of Faraday's law of
Write down the differential form of faraday’s law. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form. The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university.
SOLUTION Differential form of faraday s law Studypool
Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university of st andrews 1 (1) write down the differential form. We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form. The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Use stokes’ law (the curl theorem) to derive faraday’s law in integral form. Faraday’s.
Use Stokes’ Law (The Curl Theorem) To Derive Faraday’s Law In Integral Form.
Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): The integral form of faraday’s law is equivalent to path. Tutorial faraday’s law in differential form developed by ku leuven / dcu / university of st andrews 1 (1) write down the differential form. Faraday’s law states that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on the change in flux δ, time δt, and number of.
Write Down The Differential Form Of Faraday’s Law.
We show here how the integral form also implies the differential form.