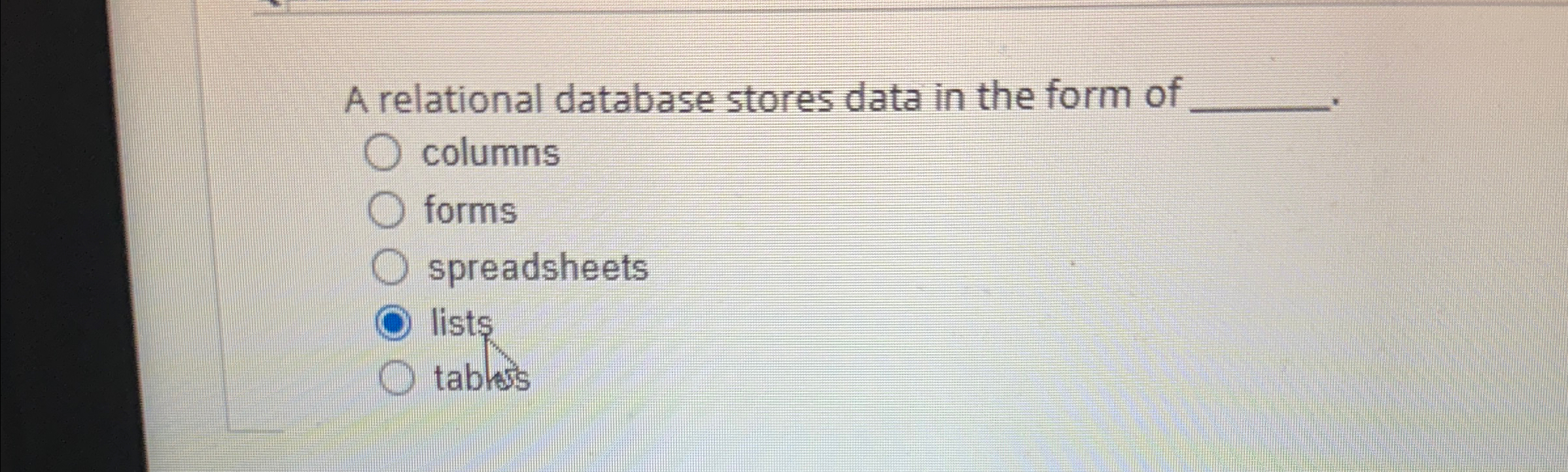
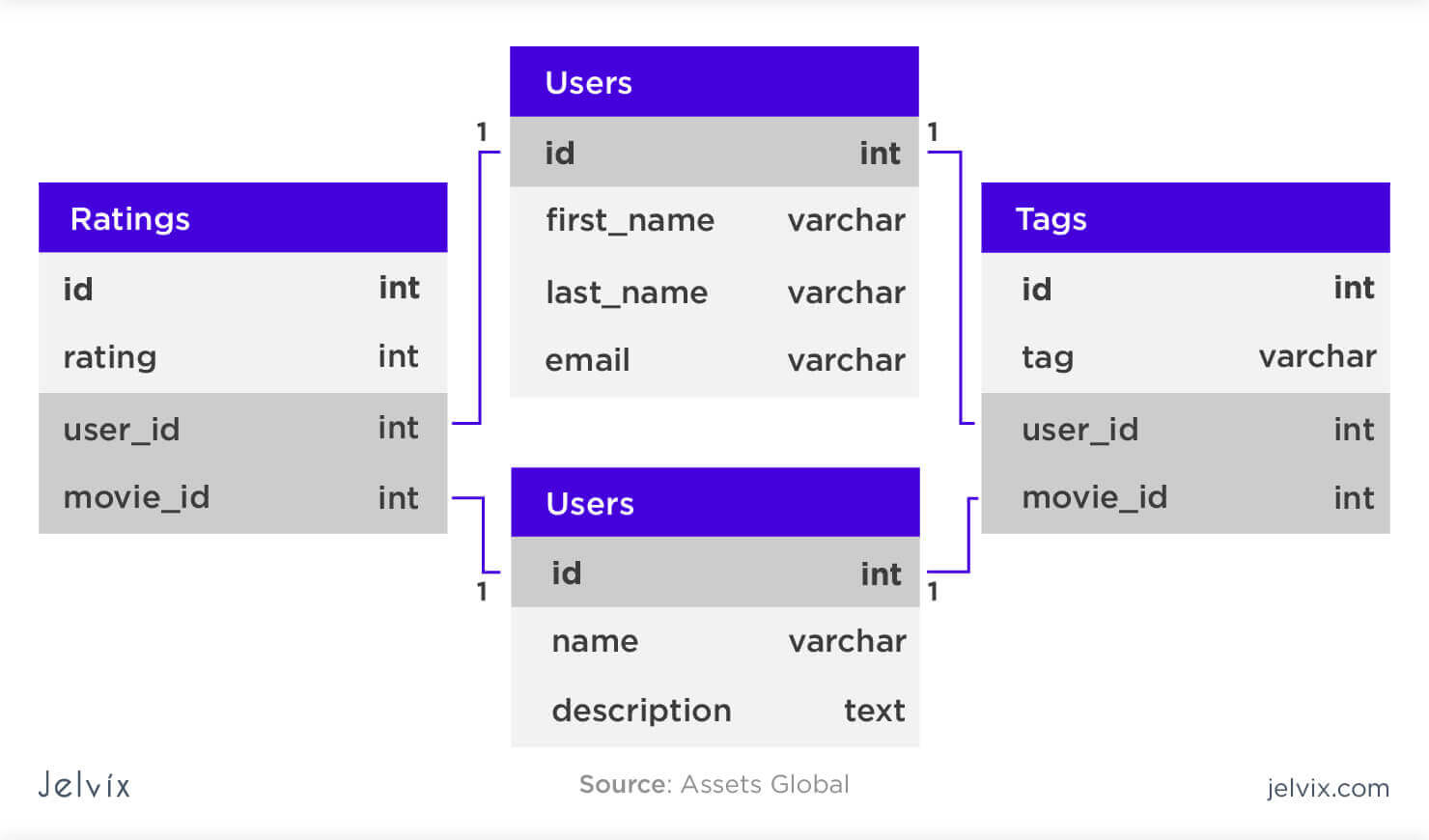
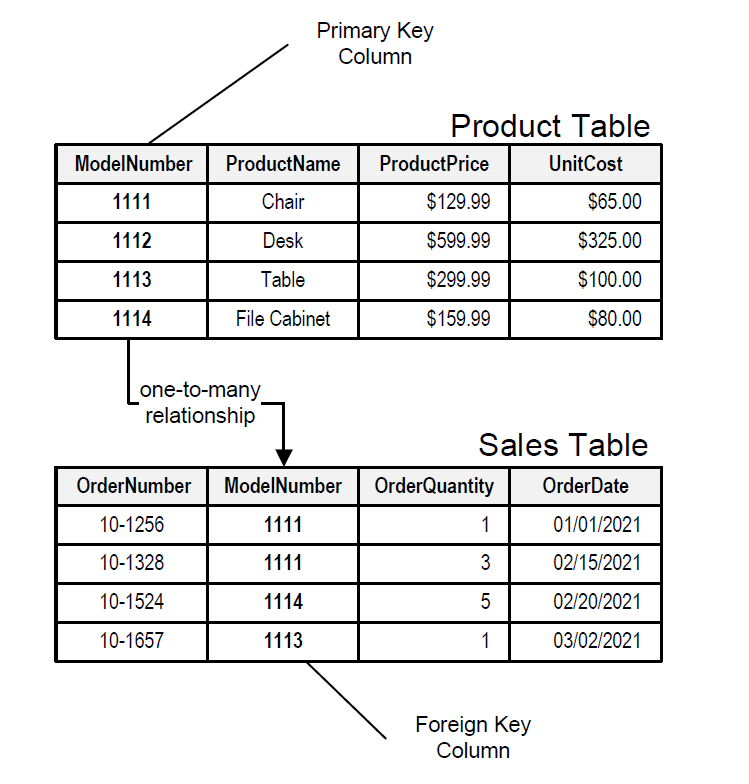
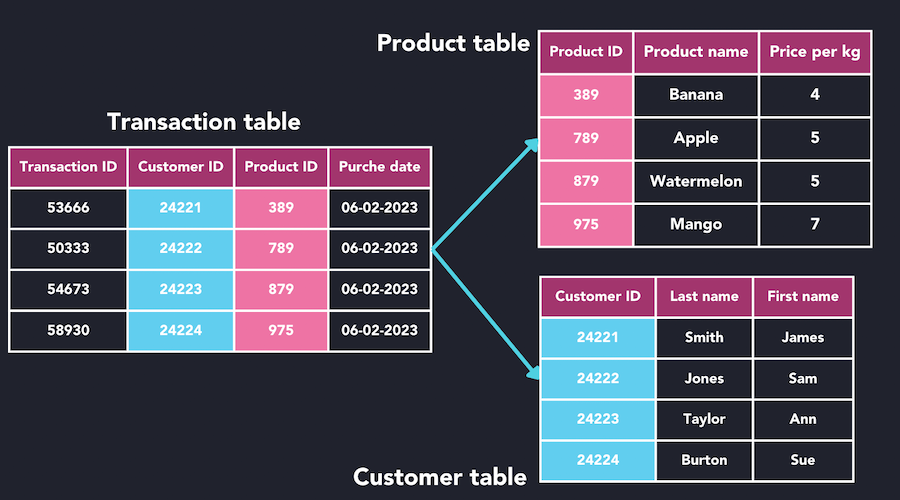
A Relational Database Stores Data In The Form Of - A relational database stores data in the form of tables. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists. T/f sql stands for structural question. Each table is made up of two. One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values. A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and.
One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values. T/f sql stands for structural question. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and. Each table is made up of two.
A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and. T/f sql stands for structural question. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. Each table is made up of two. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values. T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists.
Document Database VS Relational Database DatabaseTown
One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists. T/f sql stands for structural question. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. Each table is made up of two.
Relational Database (Model, Operations & Constraints) DatabaseTown
T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists. A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and. One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values. Each table is made up of two. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values.
Solved 1.13) A relational database stores data in the form
T/f sql stands for structural question. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. Each table is made up of two.
Solved A relational database stores data in the form of
A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and. One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values. T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values.
Difference Between Relational vs. NonRelational Database
T/f sql stands for structural question. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. Each table is made up of two. A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and.
Solved 1.13) A relational database stores data in the form
Each table is made up of two. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists. One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values. T/f sql stands for structural question.
Solved 1.13) A relational database stores data in the form
T/f sql stands for structural question. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and. Each table is made up of two. One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values.
General Database Relational Database Codecademy
Each table is made up of two. One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values. A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists.
13 Examples of Relational Database
One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and.
What Is a Relational Database?
T/f sql stands for structural question. A relational database is a type of database that organizes data into rows and. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists. One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values.
A Relational Database Is A Type Of Database That Organizes Data Into Rows And.
T/f a relational database stores data in the form of lists. One problem with storing duplicate data is the potential for inconsistent values. A relational database stores data in the form of tables. One problem with storing duplicated data is the potential for inconsistent values.
Each Table Is Made Up Of Two.
T/f sql stands for structural question.