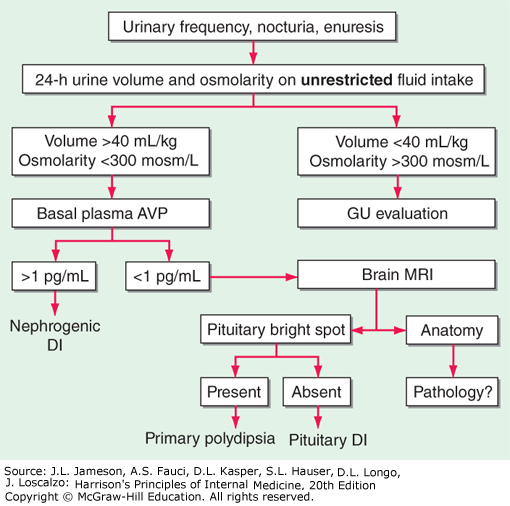
Differential Diagnosis For Diabetes Insipidus - The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency should be a crucial.
The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency should be a crucial. The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute.
The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency should be a crucial.
Dec2021 Central diabetes insipidus from differential diagnosis to
The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency.
Diabetes Mellitus Differential Diagnosis Hot Sex Picture
Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency should be a crucial. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes.
Figure 3 from Diabetes insipidus Differential diagnosis and management
The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency should be a crucial. The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the.
Webinar Diabetes Insipidus from Differential Diagnosis to Post
The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency should be a crucial. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the.
(PDF) Differential Diagnosis of Hereditary Nephrogenic Diabetes
The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency.
Diagnosis Of Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus DiabetesWalls
Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency should be a crucial. The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the.
Diabetes Insipidus An Overview of Pathophysiology, Clinical
Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency.
Diabetes Insipidus Differential Diagnosis And Management DiabetesWalls
The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency.
Diabetes insipidus Differential diagnosis and management. Semantic
The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency should be a crucial. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes.
Diabetes Insipidus Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan
The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or. The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency.
Diabetes Insipidus (Di) Is Defined As The Passage Of Large Volumes (>3 L/24 Hr) Of Dilute.
The two main differential diagnoses of central diabetes insipidus are nephrogenic diabetes. Diabetes insipidus due to posterior pituitary insufficiency should be a crucial. Diabetes insipidus (di) is a syndrome characterized by the excretion of abnormally large. The differential diagnosis of diabetes insipidus involves the distinction between central or.