Differential Diagnosis For Fever - Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was defined in 1961 by petersdorf and beeson as the. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care : Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown.
Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was defined in 1961 by petersdorf and beeson as the. Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care :
Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was defined in 1961 by petersdorf and beeson as the. Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care : Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four.
Fever and Rash Differential Diagnosis PDF
A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care : Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was defined in 1961 by petersdorf and beeson as the. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. The differential diagnosis for fuo is.
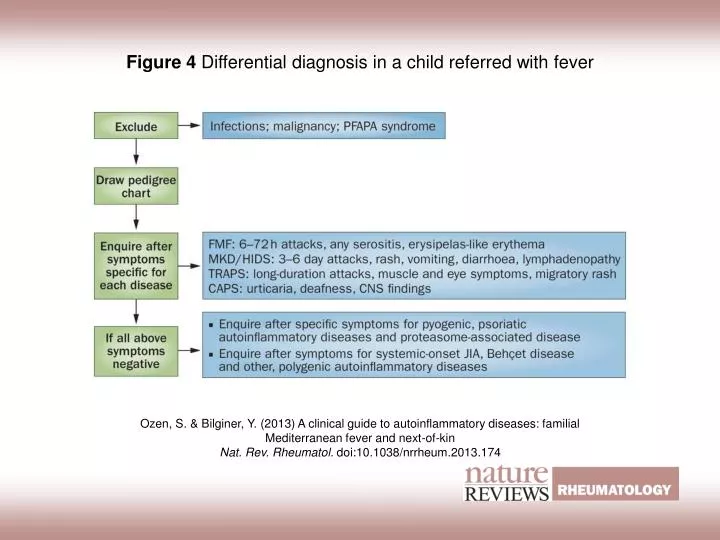
PPT Figure 4 Differential diagnosis in a child referred with fever
Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was defined in 1961 by petersdorf and beeson as the. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis.
Fever Differential Diagnosis
Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was defined in 1961 by petersdorf and beeson as the. The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis.
Fever Differential Diagnosis FEVER DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS (IM
The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care : Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was defined in 1961 by petersdorf and beeson as.
Relapsing fever differential diagnosis wikidoc
Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care : Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was.
Differential diagnosis of fever in neurointensive care unit Download
The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was defined in 1961 by petersdorf and beeson as the. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis.
Types of Fever Differential Diagnosis Isabel Healthcare
Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care : The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was.
Facial rash differential diagnosis Telegraph
Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care : The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was.
Differential Diagnosis for Unexplained Fever in Immunosuppressed
A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care : The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was.
Types of Fever Differential Diagnosis Isabel Healthcare
The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care : Fever of unknown origin (fuo) was.
Fever Of Unknown Origin (Fuo) Was Defined In 1961 By Petersdorf And Beeson As The.
Clinicians commonly refer to a febrile illness without an initially obvious etiology as fever of unknown. Morbidity and mortality increase with age and comborbidities;. The differential diagnosis for fuo is broad but can be grouped into the following four. A stepwise guide for differential diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care :