Differentiate Between Octahedral Fe 2 And Fe 3 In Fe24O32 - I understand that fe(ii) has 6. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. Start with an oh energy. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites.
Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. I understand that fe(ii) has 6. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. Start with an oh energy. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites.
Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. Start with an oh energy. I understand that fe(ii) has 6.
Distortions for a 3d 2 configuration yielding the transition from
Start with an oh energy. I understand that fe(ii) has 6. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic.
Why is Fe2+ more easily oxidized to Fe3+? Life Set Go
I understand that fe(ii) has 6. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions..
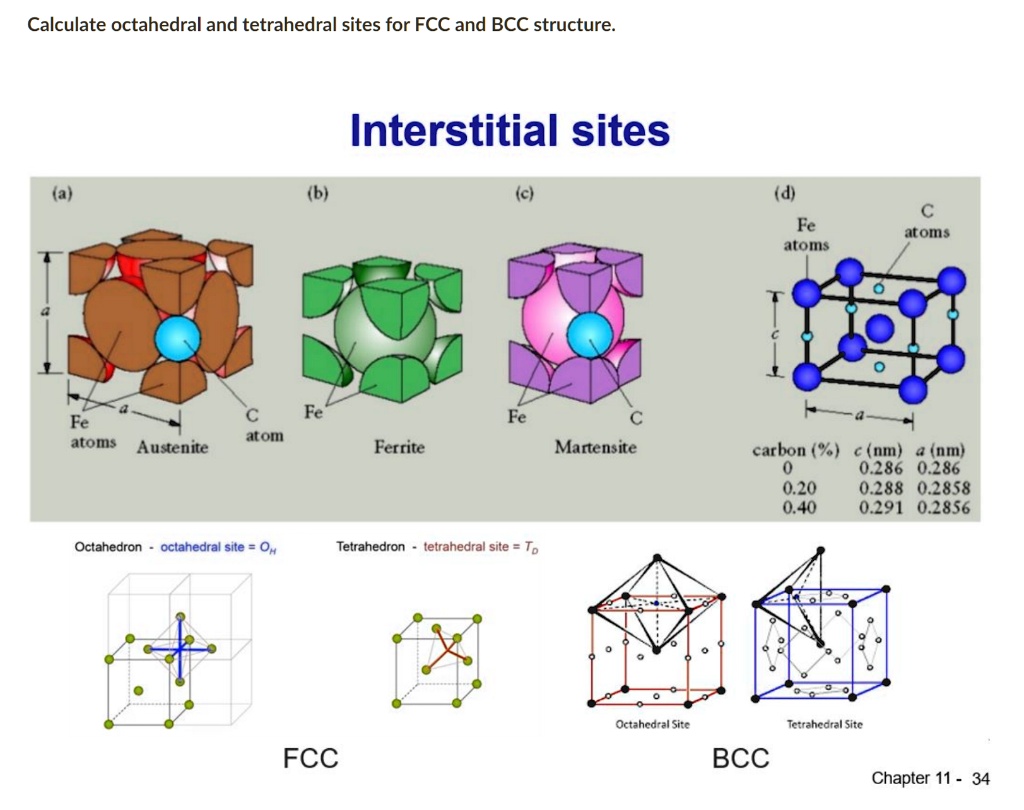
calculate octahedral and tetrahedral sites for fcc and bcc structure
I understand that fe(ii) has 6. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. Start with an oh energy. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and.
Solved If an octahedral Fe*2 complex is which
Start with an oh energy. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites. I.
Fig S9 Schematic electronic DOS of Fe 3+ in octahedral O h and
I understand that fe(ii) has 6. Start with an oh energy. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram.
Preparation and Comparative Evaluation of Fe+2/Fe+3 and Mg+2/Fe+3 LDHs
Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. Start with an oh energy. I understand that fe(ii) has 6. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and.
Diagram Fe 2+/ Fe 2+ + Fe 3+ vs Mn/(Mn+Mg) showing comparison between
This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. I understand that fe(ii) has 6..
What is the standard reduction potential (E°) Fe3+ Fe ? Given that Fe2
Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites. Start with an oh energy. I.
Plot of Li versus octahedral Fe 2þ cations for the magmatic grains. All
Start with an oh energy. I understand that fe(ii) has 6. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram.
Octahedral (Fe tot þ Mn þ TiÀAl VI ) vs. octahedral (MgLi) diagram
I understand that fe(ii) has 6. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites..
I Understand That Fe(Ii) Has 6.
Start with an oh energy. This structure is called a spinel, with $\ce{fe^{2+}}$ ion in tetrahedral coordination and $\ce{fe^{3+}}$> ions in octahedral sites. Both fe 2+ and fe 3+ ions give octahedral cyano anionic complex ions with cyanide ions. Now combine the tm dao and ligand fo components to form the energy level diagram for a c4v tm complex.