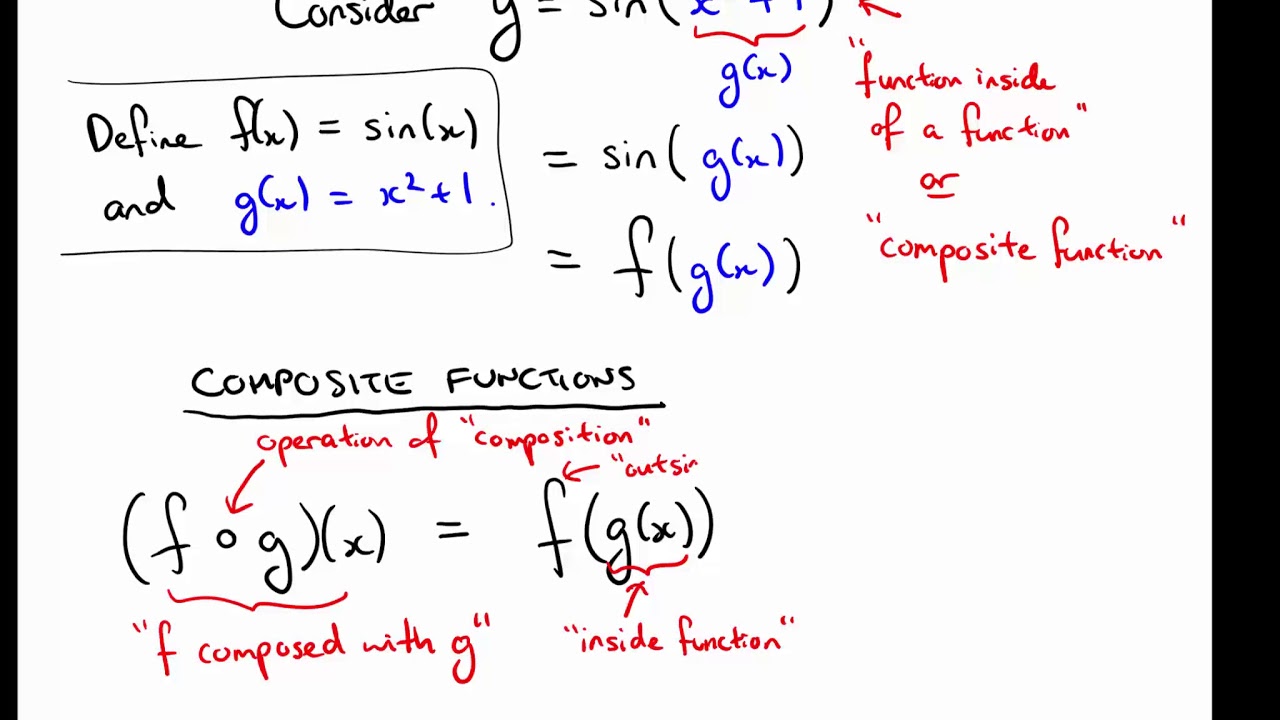
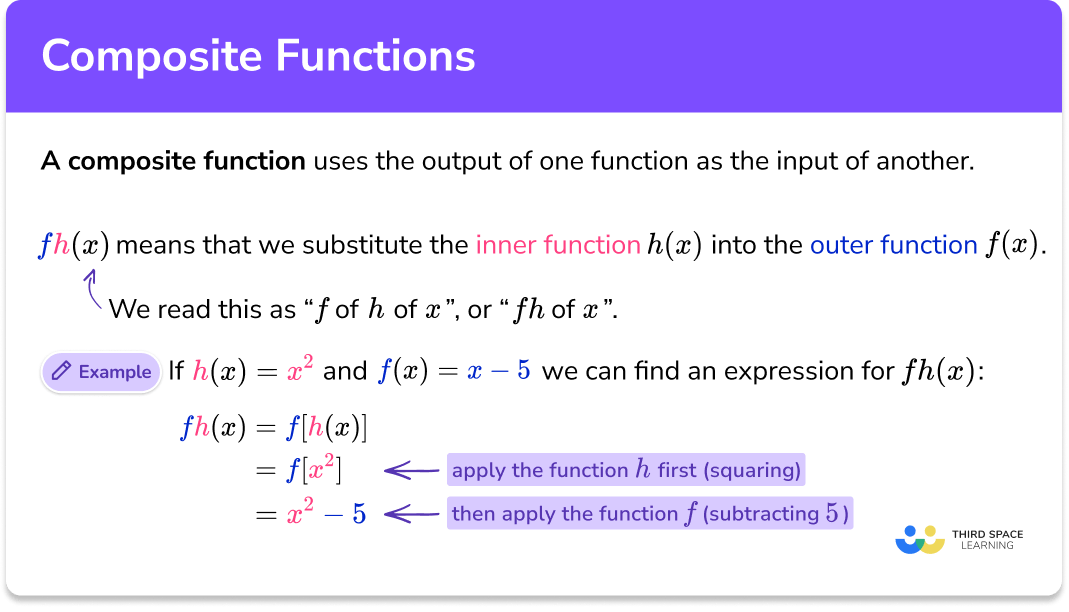
Differentiating Composite Functions - It is quite common in mathematics to. Learn how to differentiate composite functions using the chain rule, with examples and exercises. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then. Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation.
In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. Learn how to differentiate composite functions using the chain rule, with examples and exercises. Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation. It is quite common in mathematics to.
Learn how to differentiate composite functions using the chain rule, with examples and exercises. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation. It is quite common in mathematics to. The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then.
Differentiating Composite Functions Using the Chain Rule Calculus
The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then. Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation. In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. It is quite common in mathematics to. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function.
core pure 3 notes differentiating trig functions
The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. Learn how to differentiate composite functions using the.
Revision of composite functions and using the chain rule to
Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation. In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. It is quite.
Understanding Composite Functions PDF Function (Mathematics
In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. Learn how to.
Composite Functions GCSE Maths Steps & Examples
Learn how to differentiate composite functions using the chain rule, with examples and exercises. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. The chain rule says.
Composite Functions A Complete Guide
The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then. Learn how to differentiate composite functions using the chain rule, with examples and exercises. In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation. In words, the chain rule.
Composite functions Functions math, Math vocabulary, Math made easy
In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then. Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation. It is quite common in mathematics to. Learn how.
Composite Functions Starting Points Maths
It is quite common in mathematics to. Learn how to differentiate composite functions using the chain rule, with examples and exercises. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then. Learn how to.
Composite Functions.pptx
The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then. Learn how to differentiate composite functions using the chain rule, with examples and exercises. Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation. In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. It is quite common in.
Composite_Functions
The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then. In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. It is quite common in mathematics to. Learn how to calculate the derivatives of composite functions using the chain rule of differentiation. Learn how.
Learn How To Calculate The Derivatives Of Composite Functions Using The Chain Rule Of Differentiation.
In words, the chain rule says, the derivative of a composite function is the product of the derivative of the outer function evaluated at the inner. Learn how to differentiate composite functions using the chain rule, with examples and exercises. In this article, we will look at using the chain rule to differentiate a composite function. The chain rule says that if f(x) = h(g(x)) then.