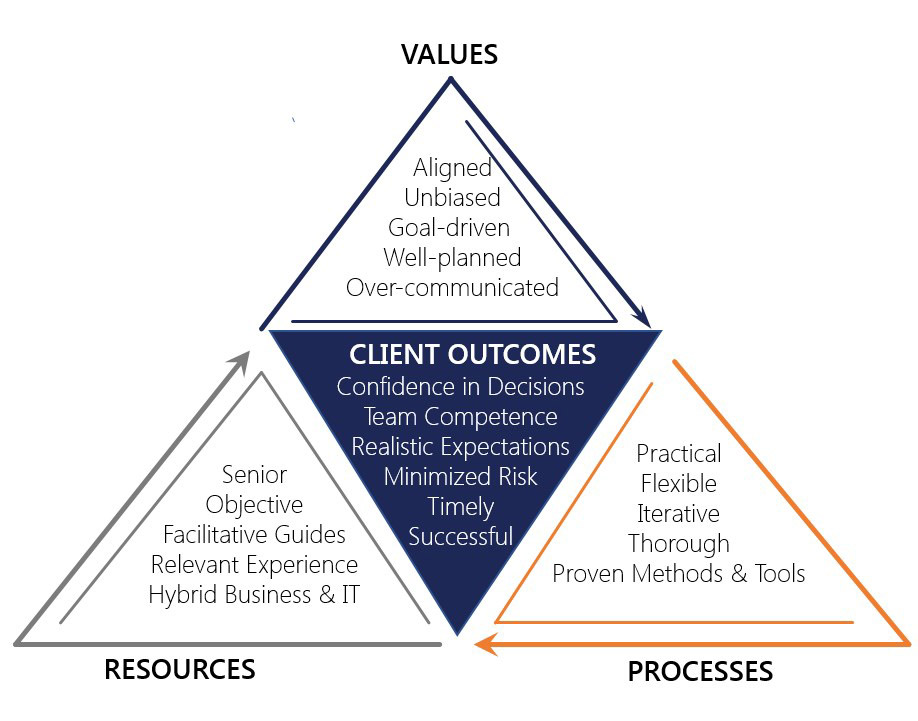
Differentiators - As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an rc network across the operational amplifier and the reactance ( xc ) of the capacitor plays a major role in the. Differentiators perform the complementary function to the integrator. In electronics, a differentiator is a circuit that outputs a signal approximately proportional to the rate of change (i.e. The derivative with respect to time) of its input signal. In this article, we explain how differentiation works, and we provide examples of strong professional services differentiators that you can use to sharpen your own firm’s brand. The base form of the differentiator is shown in figure 10.3.1 10.3. The output voltage is the. Differentiator, a device or set of components for performing the mathematical operation of differentiation —i.e., supplying an output proportional to the derivative of the input with.
The derivative with respect to time) of its input signal. Differentiator, a device or set of components for performing the mathematical operation of differentiation —i.e., supplying an output proportional to the derivative of the input with. Differentiators perform the complementary function to the integrator. In electronics, a differentiator is a circuit that outputs a signal approximately proportional to the rate of change (i.e. The base form of the differentiator is shown in figure 10.3.1 10.3. The output voltage is the. In this article, we explain how differentiation works, and we provide examples of strong professional services differentiators that you can use to sharpen your own firm’s brand. As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an rc network across the operational amplifier and the reactance ( xc ) of the capacitor plays a major role in the.
The output voltage is the. In this article, we explain how differentiation works, and we provide examples of strong professional services differentiators that you can use to sharpen your own firm’s brand. In electronics, a differentiator is a circuit that outputs a signal approximately proportional to the rate of change (i.e. Differentiators perform the complementary function to the integrator. The base form of the differentiator is shown in figure 10.3.1 10.3. The derivative with respect to time) of its input signal. As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an rc network across the operational amplifier and the reactance ( xc ) of the capacitor plays a major role in the. Differentiator, a device or set of components for performing the mathematical operation of differentiation —i.e., supplying an output proportional to the derivative of the input with.
bannerdifferentiators Ascent Geomatics Solutions
Differentiators perform the complementary function to the integrator. In electronics, a differentiator is a circuit that outputs a signal approximately proportional to the rate of change (i.e. As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an rc network across the operational amplifier and the reactance ( xc ) of the capacitor plays a major role in.
Key Differentiators of APS Software Optessa
The base form of the differentiator is shown in figure 10.3.1 10.3. In electronics, a differentiator is a circuit that outputs a signal approximately proportional to the rate of change (i.e. Differentiator, a device or set of components for performing the mathematical operation of differentiation —i.e., supplying an output proportional to the derivative of the input with. As with the.
Key Differentiators PowerPoint and Google Slides Template PPT Slides
Differentiator, a device or set of components for performing the mathematical operation of differentiation —i.e., supplying an output proportional to the derivative of the input with. As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an rc network across the operational amplifier and the reactance ( xc ) of the capacitor plays a major role in the..
Our Differentiators ITDirections
Differentiators perform the complementary function to the integrator. The derivative with respect to time) of its input signal. In this article, we explain how differentiation works, and we provide examples of strong professional services differentiators that you can use to sharpen your own firm’s brand. The output voltage is the. The base form of the differentiator is shown in figure.
Key Differentiators PowerPoint and Google Slides Template PPT Slides
Differentiator, a device or set of components for performing the mathematical operation of differentiation —i.e., supplying an output proportional to the derivative of the input with. In electronics, a differentiator is a circuit that outputs a signal approximately proportional to the rate of change (i.e. The derivative with respect to time) of its input signal. The base form of the.
Key Differentiators PowerPoint and Google Slides Template PPT Slides
In this article, we explain how differentiation works, and we provide examples of strong professional services differentiators that you can use to sharpen your own firm’s brand. As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an rc network across the operational amplifier and the reactance ( xc ) of the capacitor plays a major role in.
Key Differentiators PowerPoint and Google Slides Template PPT Slides
In this article, we explain how differentiation works, and we provide examples of strong professional services differentiators that you can use to sharpen your own firm’s brand. Differentiators perform the complementary function to the integrator. The base form of the differentiator is shown in figure 10.3.1 10.3. As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an.
Key Differentiators PowerPoint and Google Slides Template PPT Slides
The output voltage is the. The derivative with respect to time) of its input signal. As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an rc network across the operational amplifier and the reactance ( xc ) of the capacitor plays a major role in the. Differentiators perform the complementary function to the integrator. In electronics, a.
Key Differentiators of APS Software Optessa
The derivative with respect to time) of its input signal. In this article, we explain how differentiation works, and we provide examples of strong professional services differentiators that you can use to sharpen your own firm’s brand. The base form of the differentiator is shown in figure 10.3.1 10.3. Differentiators perform the complementary function to the integrator. In electronics, a.
Differentiators Proposal & Technical Writing GDI Consulting
Differentiators perform the complementary function to the integrator. As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an rc network across the operational amplifier and the reactance ( xc ) of the capacitor plays a major role in the. The derivative with respect to time) of its input signal. The base form of the differentiator is shown.
Differentiators Perform The Complementary Function To The Integrator.
In this article, we explain how differentiation works, and we provide examples of strong professional services differentiators that you can use to sharpen your own firm’s brand. As with the integrator circuit, we have a resistor and capacitor forming an rc network across the operational amplifier and the reactance ( xc ) of the capacitor plays a major role in the. Differentiator, a device or set of components for performing the mathematical operation of differentiation —i.e., supplying an output proportional to the derivative of the input with. In electronics, a differentiator is a circuit that outputs a signal approximately proportional to the rate of change (i.e.
The Derivative With Respect To Time) Of Its Input Signal.
The base form of the differentiator is shown in figure 10.3.1 10.3. The output voltage is the.