Does Acl Prevent Anterior Dislocation - Injury prevention neuromuscular training (nmt) programs reduce the risk for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) injury. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing. This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee.
This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. Injury prevention neuromuscular training (nmt) programs reduce the risk for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) injury. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing.
Injury prevention neuromuscular training (nmt) programs reduce the risk for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) injury. This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing.
Five Ways to Prevent Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries NYU Langone News
The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing. This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. Injury prevention.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. Injury prevention neuromuscular training (nmt) programs reduce the risk for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) injury. The acl’s ability to counteract this.
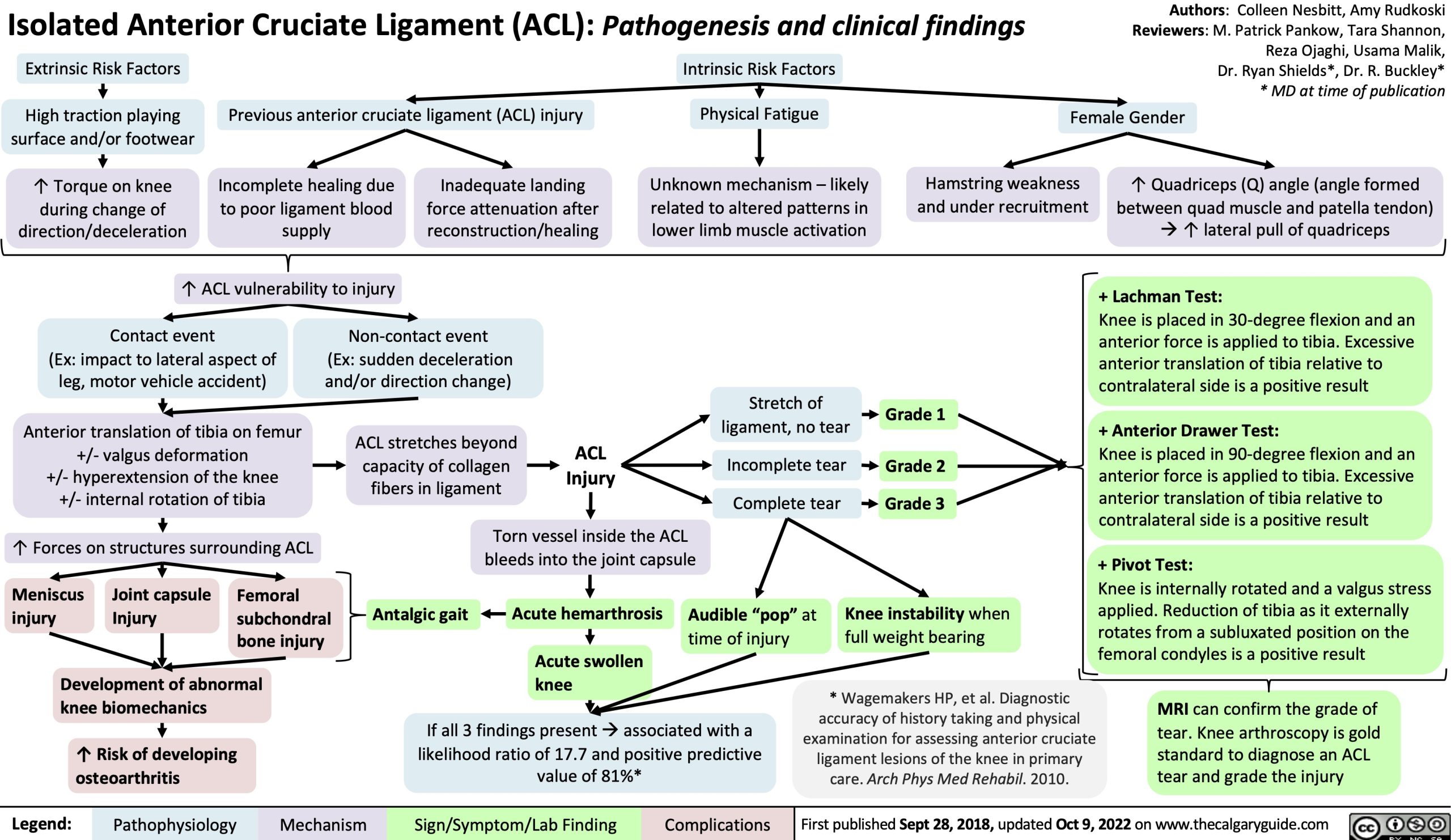
isolatedanteriorcruciateligamentaclinjurypathogenesisand
The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing. Injury prevention.
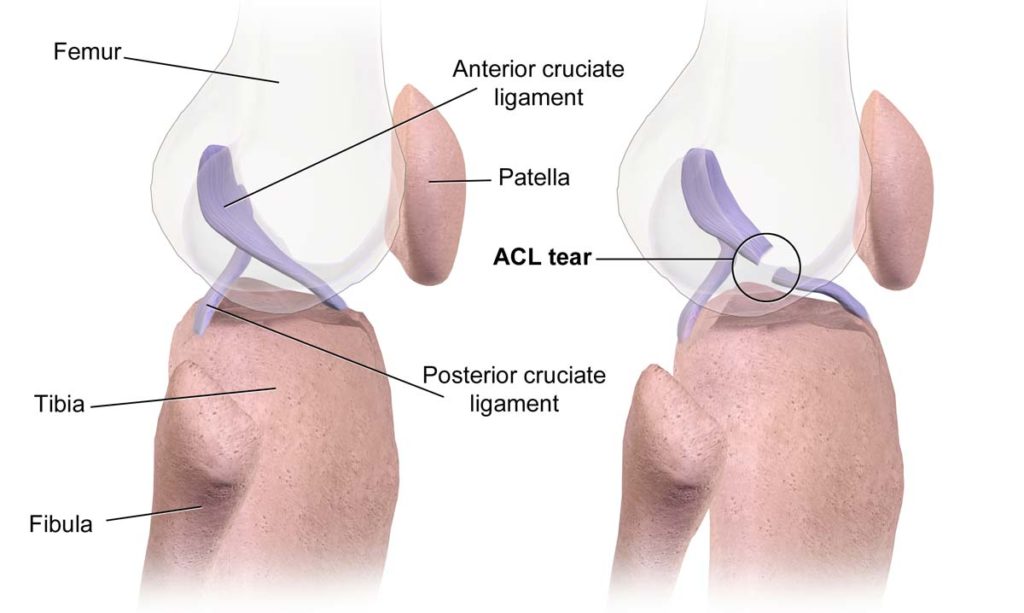
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear (ACL Tear) The Institute for Athletic
Injury prevention neuromuscular training (nmt) programs reduce the risk for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) injury. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing. This feedback helps prevent injuries by.
Acl amelatracking
Injury prevention neuromuscular training (nmt) programs reduce the risk for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) injury. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing. This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury Sports Medicine Information
The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing. This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. Injury prevention.
ACL Tear & Injury Symptoms & Recovery Acl tear, Acl, Acl knee
The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing. Injury prevention.
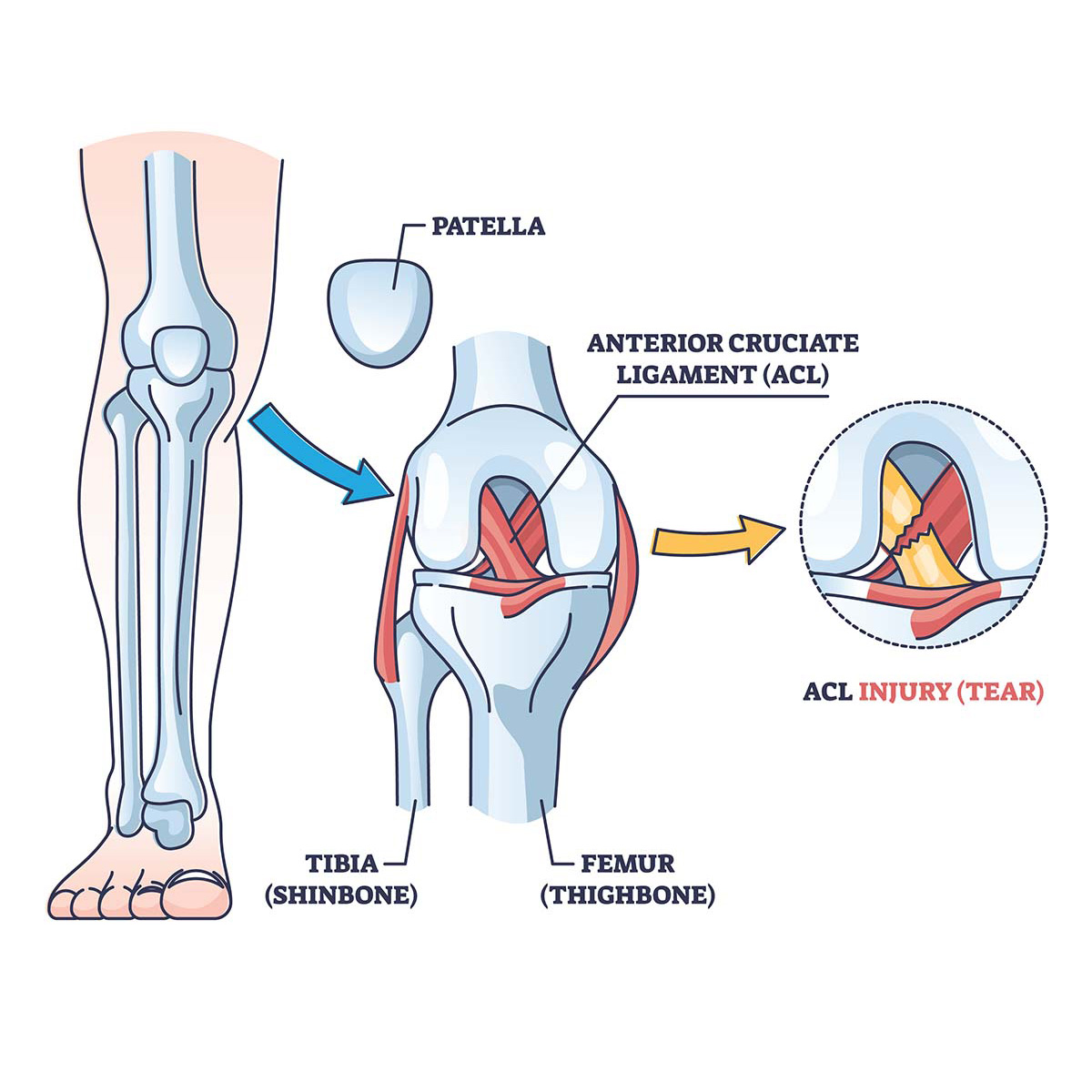
ACL Injury
The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing. This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. Injury prevention.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries What Are They,, 53 OFF
This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing. Injury prevention neuromuscular training (nmt) programs reduce the risk for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) injury. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation.
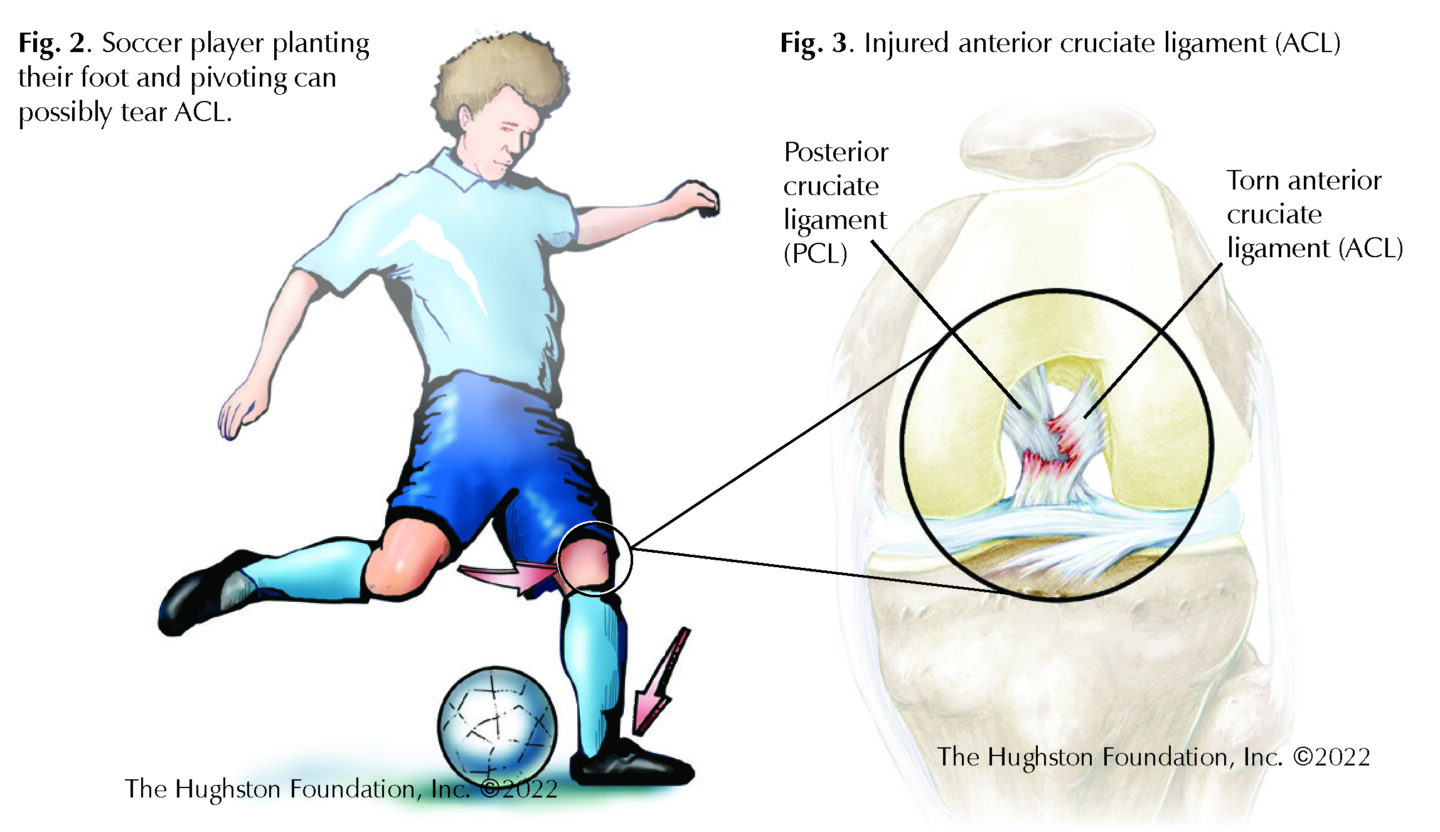
ACL Injuries Hughston Clinic
This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. Injury prevention neuromuscular training (nmt) programs reduce the risk for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) injury. The acl functions to prevent posterior translation of the femur on the tibia (or anterior displacement of the tibia) during. The acl’s ability to counteract this.
The Acl Functions To Prevent Posterior Translation Of The Femur On The Tibia (Or Anterior Displacement Of The Tibia) During.
Injury prevention neuromuscular training (nmt) programs reduce the risk for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) injury. This feedback helps prevent injuries by enabling quick reflexive actions when an unexpected force is applied to the knee. The acl’s ability to counteract this forward motion allows for smooth and controlled movement of the knee joint, preventing.