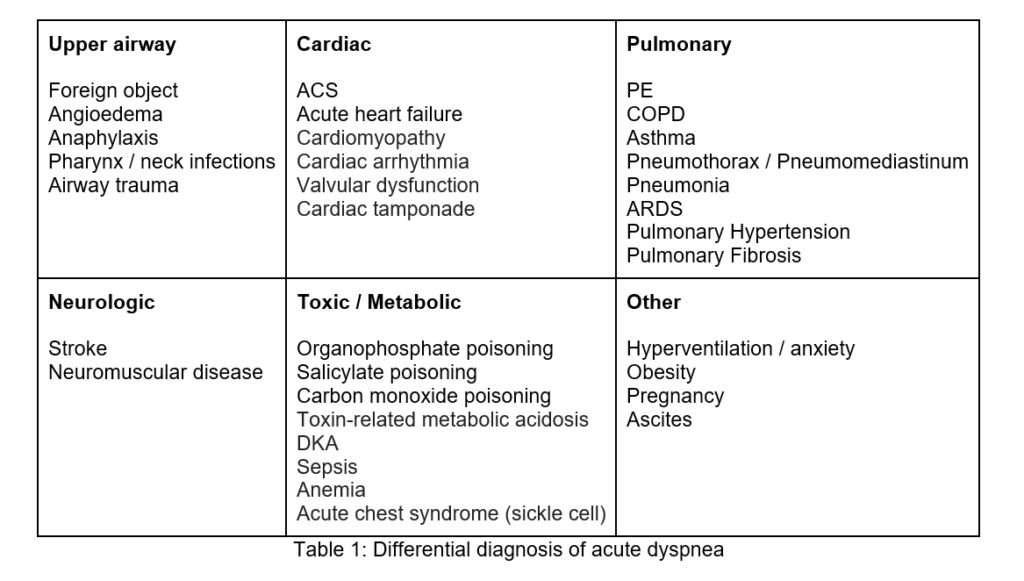
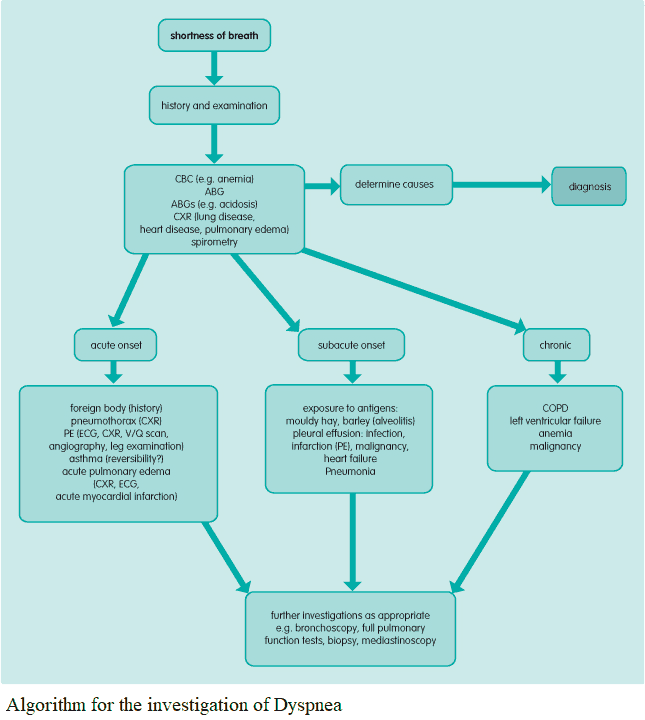
Dyspnea Chest Pain Differential Diagnosis - Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea.
The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea.
Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea. Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds:
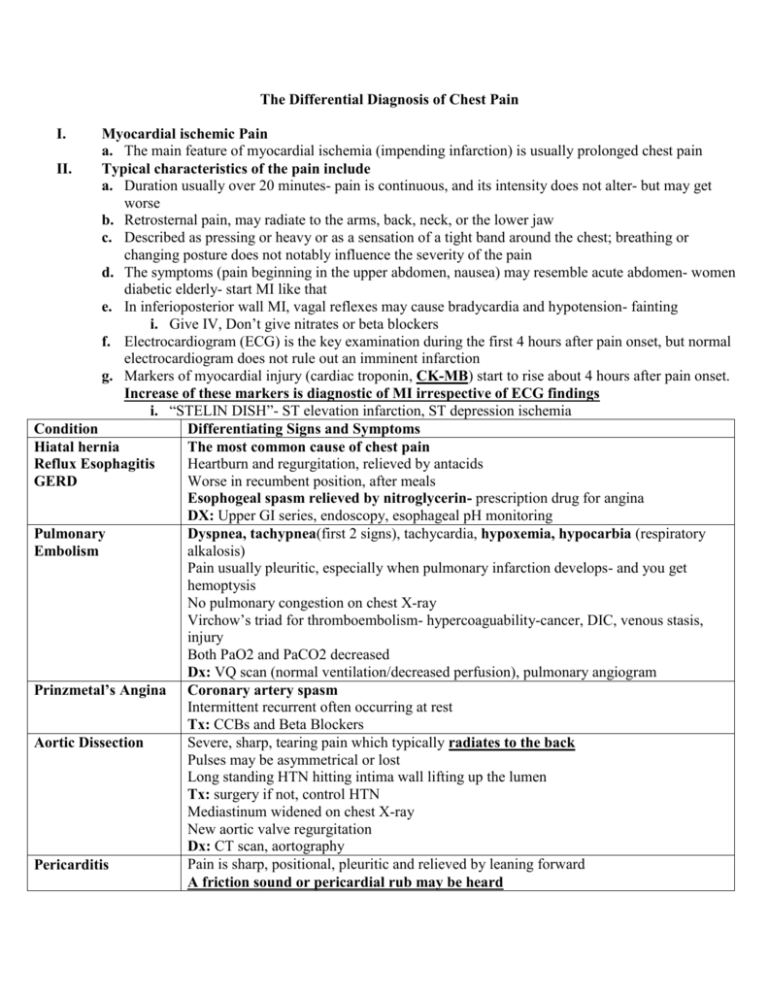
The Differential Diagnosis of Chest Pain
The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea. Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and.
Dyspnea Thoracic Key
The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea. The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and.
Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea) Differential Diagnosis, Examination and
Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea.
Figure 2 from The Differential Diagnosis of Dyspnea. Semantic Scholar
The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea.
[PDF] The Differential Diagnosis of Dyspnea. Semantic Scholar
The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea. The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and.
Pediatric Chest Pain Keys to the Diagnosis Consultant360
The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea. The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds:
Table 1 from The Differential Diagnosis of Dyspnea. Semantic Scholar
Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea.
Acute Dyspnea Diagnosis Summary BC Emergency Medicine Network
The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea. The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest.
Chest Pain Differential Diagnosis Chest Pain Differential Diagnosis
Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea. Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds:
Shortness of Breath (Dyspnea) Differential Diagnosis, Examination and
The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. The criteria that can be used in the differential diagnosis of dyspnea are of three kinds: Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea.
The Criteria That Can Be Used In The Differential Diagnosis Of Dyspnea Are Of Three Kinds:
Chest pain may be pleuritic or nonpleuritic and. The differential diagnosis of dyspnea includes a number of pulmonary and cardiac diseases, as well as neuromuscular diseases of the chest. Chest pain (covered extensively in chapter 9) is another pivotal clue in patients with dyspnea.
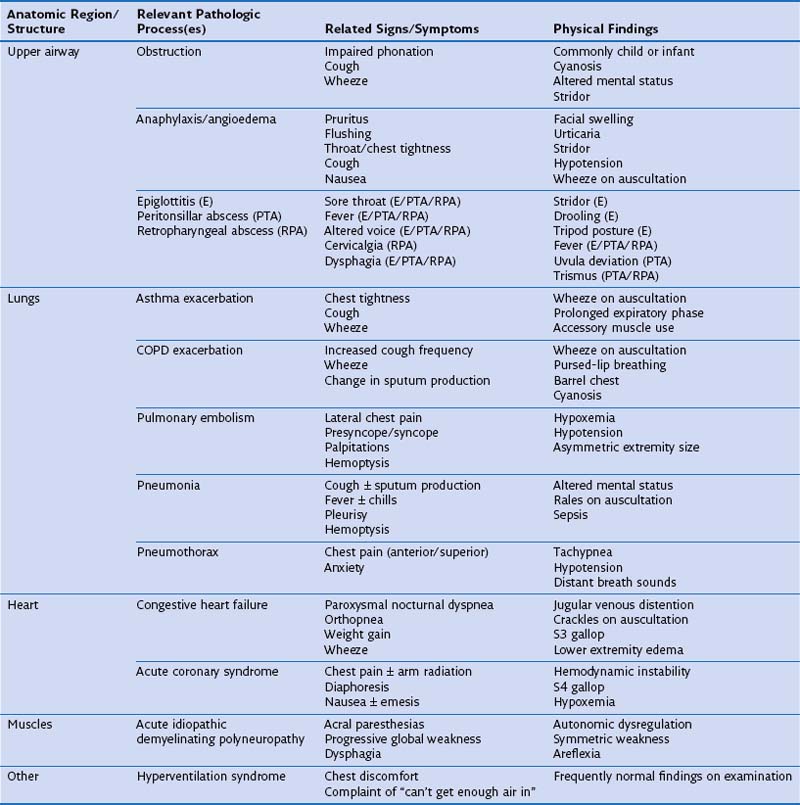
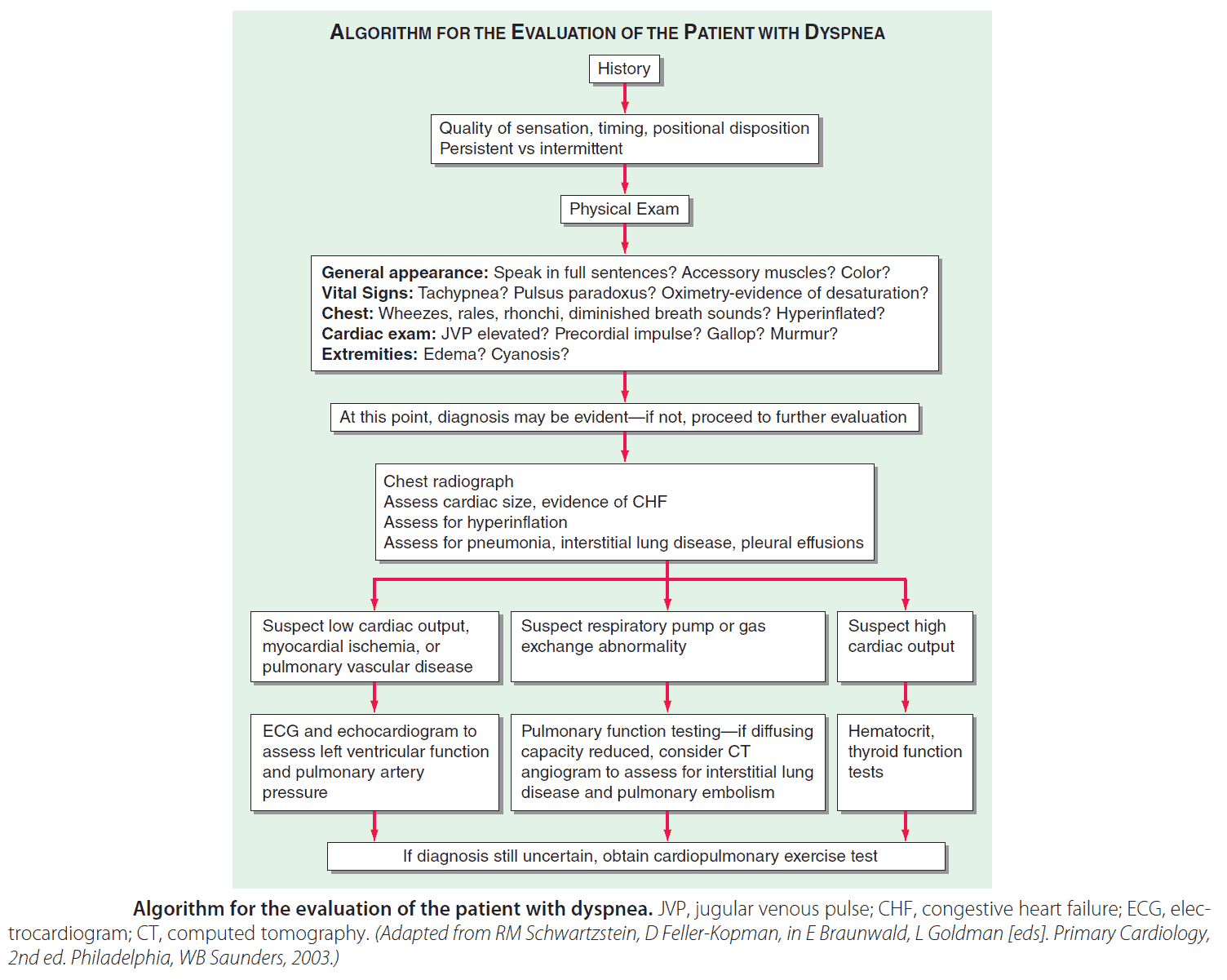

![[PDF] The Differential Diagnosis of Dyspnea. Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/2ba379fe7766ca6529ba2b88a864dfdd1ba9d913/5-Figure1-1.png)