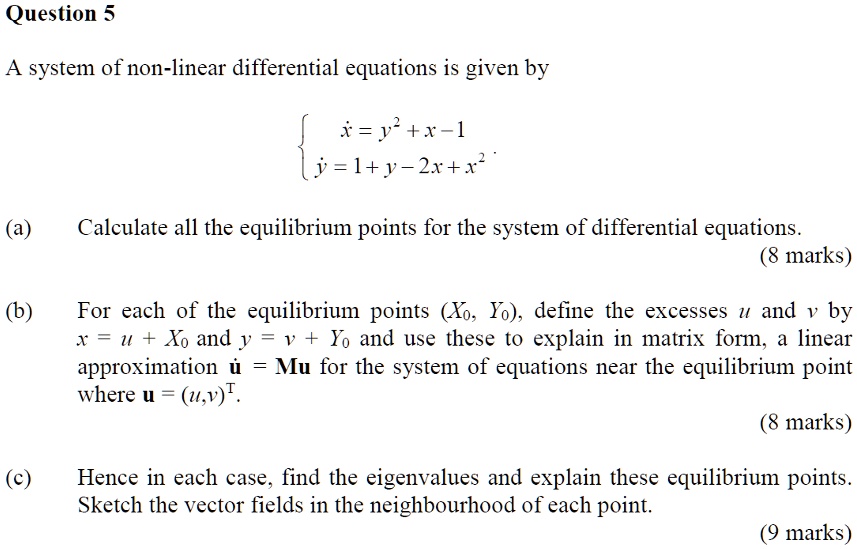
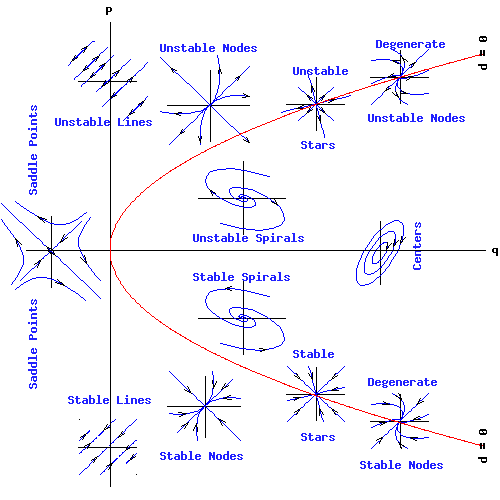
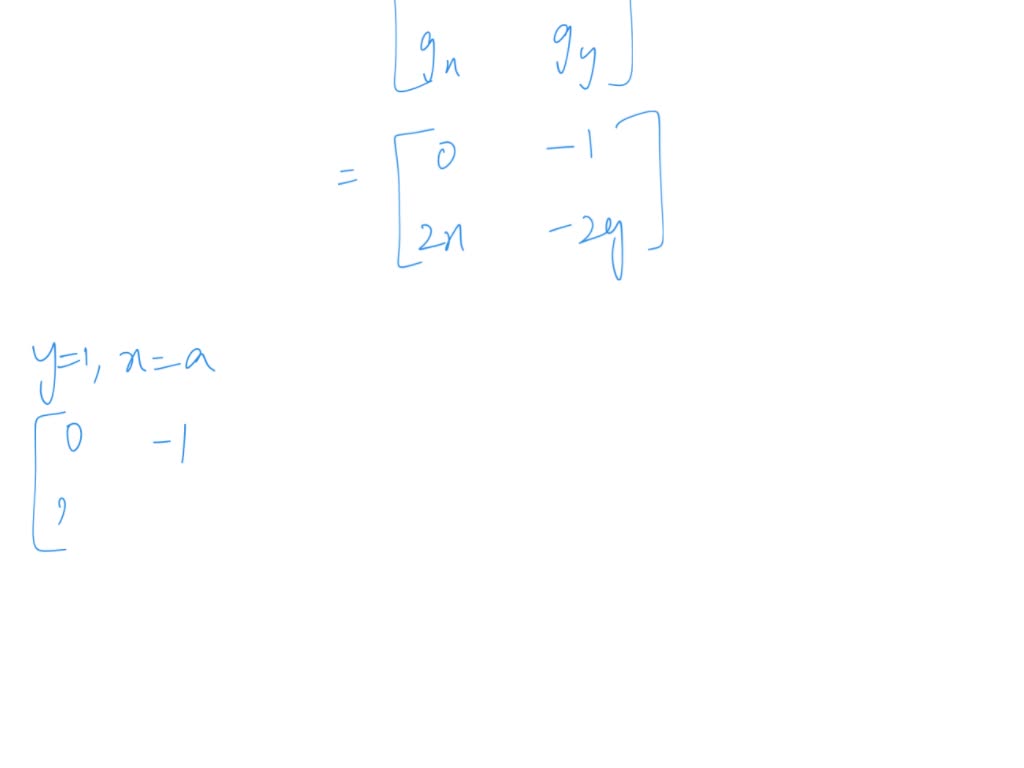Equilibrium Points Differential Equations - In terms of the solution operator, they are the fixed points of. These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero. (b) for y > 3: We define the equilibrium solution/point for a homogeneous system of differential equations and how phase portraits. Find and classify the equilibrium points of dy dt = (1 y)(3 y). In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). For orbits near an equilibrium solution, do the solutions tend towards, or away from, the equilibrium point? Let us define the critical points as the. Equilibrium points represent the simplest solutions to differential equations. (a) y(t) = 1 and y(t) = 3 are the equilibrium solutions.
In terms of the solution operator, they are the fixed points of. For orbits near an equilibrium solution, do the solutions tend towards, or away from, the equilibrium point? These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero. Equilibrium points represent the simplest solutions to differential equations. (a) y(t) = 1 and y(t) = 3 are the equilibrium solutions. Find and classify the equilibrium points of dy dt = (1 y)(3 y). Let us define the critical points as the. We define the equilibrium solution/point for a homogeneous system of differential equations and how phase portraits. (b) for y > 3: In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y).
In terms of the solution operator, they are the fixed points of. In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). For orbits near an equilibrium solution, do the solutions tend towards, or away from, the equilibrium point? We define the equilibrium solution/point for a homogeneous system of differential equations and how phase portraits. Equilibrium points represent the simplest solutions to differential equations. (b) for y > 3: Let us define the critical points as the. Find and classify the equilibrium points of dy dt = (1 y)(3 y). These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero. (a) y(t) = 1 and y(t) = 3 are the equilibrium solutions.
SOLUTION Differential equilibrium equations Studypool
Find and classify the equilibrium points of dy dt = (1 y)(3 y). Let us define the critical points as the. Equilibrium points represent the simplest solutions to differential equations. These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero. (a) y(t) = 1 and y(t) = 3 are the equilibrium solutions.
SOLVED A system of differential equations is given by x
For orbits near an equilibrium solution, do the solutions tend towards, or away from, the equilibrium point? Let us define the critical points as the. In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). In terms of the solution operator, they are the fixed points of. Find and classify the equilibrium.
[Solved] (a) (15 points) Find the equilibrium points for the
(a) y(t) = 1 and y(t) = 3 are the equilibrium solutions. Equilibrium points represent the simplest solutions to differential equations. (b) for y > 3: These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero. Let us define the critical points as the.
[Solved] (a) (15 points) Find the equilibrium points for the
For orbits near an equilibrium solution, do the solutions tend towards, or away from, the equilibrium point? (a) y(t) = 1 and y(t) = 3 are the equilibrium solutions. (b) for y > 3: These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero. Find and classify the equilibrium points of dy dt =.
Solved Equilibrium Points and Stability Complete this
These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero. Let us define the critical points as the. We define the equilibrium solution/point for a homogeneous system of differential equations and how phase portraits. (b) for y > 3: In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations,.
SOLUTION Differential equilibrium equations Studypool
We define the equilibrium solution/point for a homogeneous system of differential equations and how phase portraits. Find and classify the equilibrium points of dy dt = (1 y)(3 y). In terms of the solution operator, they are the fixed points of. (a) y(t) = 1 and y(t) = 3 are the equilibrium solutions. For orbits near an equilibrium solution, do.
Egwald Mathematics Linear Algebra Systems of Linear Differential
Let us define the critical points as the. We define the equilibrium solution/point for a homogeneous system of differential equations and how phase portraits. Find and classify the equilibrium points of dy dt = (1 y)(3 y). (b) for y > 3: In terms of the solution operator, they are the fixed points of.
Equilibrium equations
In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). We define the equilibrium solution/point for a homogeneous system of differential equations and how phase portraits. For orbits near an equilibrium solution, do the solutions tend towards, or away from, the equilibrium point? In terms of the solution operator, they are the.
SOLVED Question 3 (Unit 13) 16 marks Consider the pair of differential
In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero. Let us define the critical points as the. (b) for y > 3: For orbits near an equilibrium solution, do the solutions tend towards, or away.
dynamical systems Differential equation equilibrium points
Find and classify the equilibrium points of dy dt = (1 y)(3 y). These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero. (a) y(t) = 1 and y(t) = 3 are the equilibrium solutions. Let us define the critical points as the. We define the equilibrium solution/point for a homogeneous system of differential.
In This Section We Will Define Equilibrium Solutions (Or Equilibrium Points) For Autonomous Differential Equations, Y’ = F(Y).
Find and classify the equilibrium points of dy dt = (1 y)(3 y). For orbits near an equilibrium solution, do the solutions tend towards, or away from, the equilibrium point? We define the equilibrium solution/point for a homogeneous system of differential equations and how phase portraits. These points are precisely those points where the derivatives of both \(x\) and \(y\) are zero.
(B) For Y > 3:
In terms of the solution operator, they are the fixed points of. Equilibrium points represent the simplest solutions to differential equations. Let us define the critical points as the. (a) y(t) = 1 and y(t) = 3 are the equilibrium solutions.