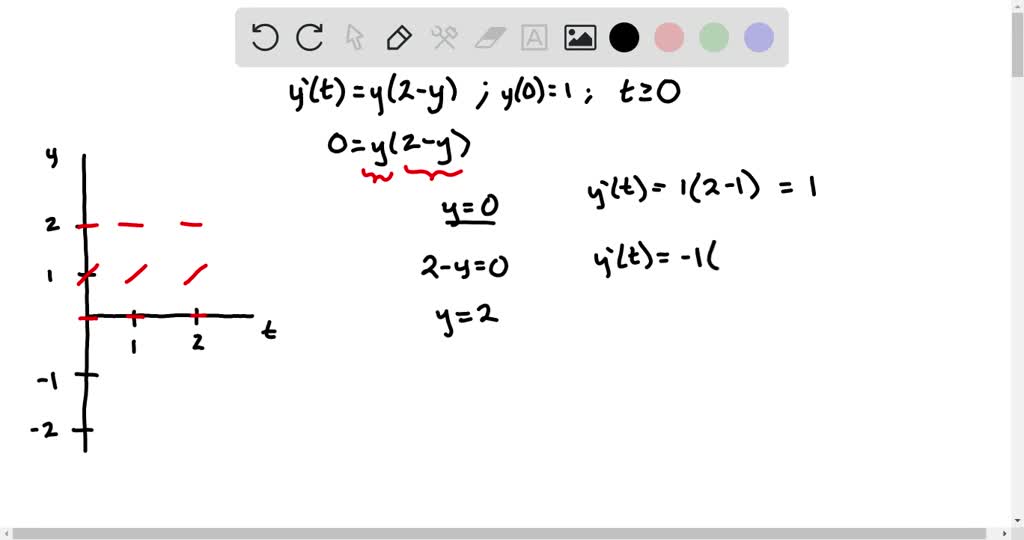
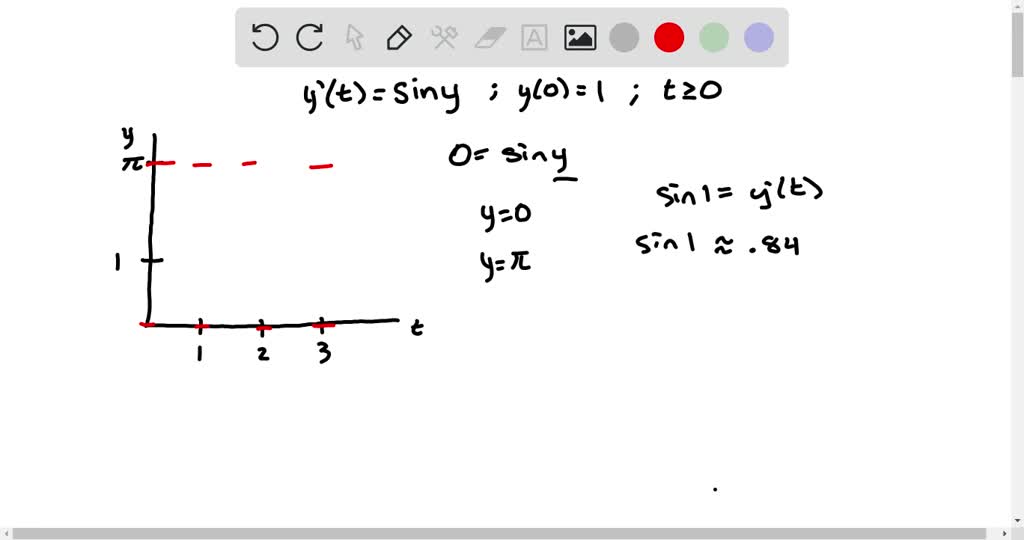
Equilibrium Solution Differential Equation - Sometimes it is easy to. Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di erential equation. In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). In studying systems of differential equations, it is often useful to study the behavior of solutions without obtaining an algebraic form. Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$.
In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di erential equation. Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$. Sometimes it is easy to. In studying systems of differential equations, it is often useful to study the behavior of solutions without obtaining an algebraic form.
In studying systems of differential equations, it is often useful to study the behavior of solutions without obtaining an algebraic form. In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Sometimes it is easy to. Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$. Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di erential equation.
Solved An equilibrium solution of an autonomous differential
Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di erential equation. In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$. Sometimes it is easy to. Values of \(y\) for.
(PDF) Quantitative analysis of equilibrium solution and stability for
In studying systems of differential equations, it is often useful to study the behavior of solutions without obtaining an algebraic form. Sometimes it is easy to. Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function.
SOLVEDExercise 2 Construct an autonomous differential equation that
Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$. Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di erential equation. In this section.
Solution of differential equation Practice to perfection
In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). Sometimes it is easy to. Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to.
SOLVED point) Given the differential equation z' (t) = r3 + lx2 + 202
Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. Sometimes it is easy to. Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$. In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium.
SOLVEDIf the given differential equation is autonomous, identify the
Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$. Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. In studying systems of differential equations, it is often useful to study the behavior of solutions without obtaining an algebraic form. Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di erential equation. Sometimes.
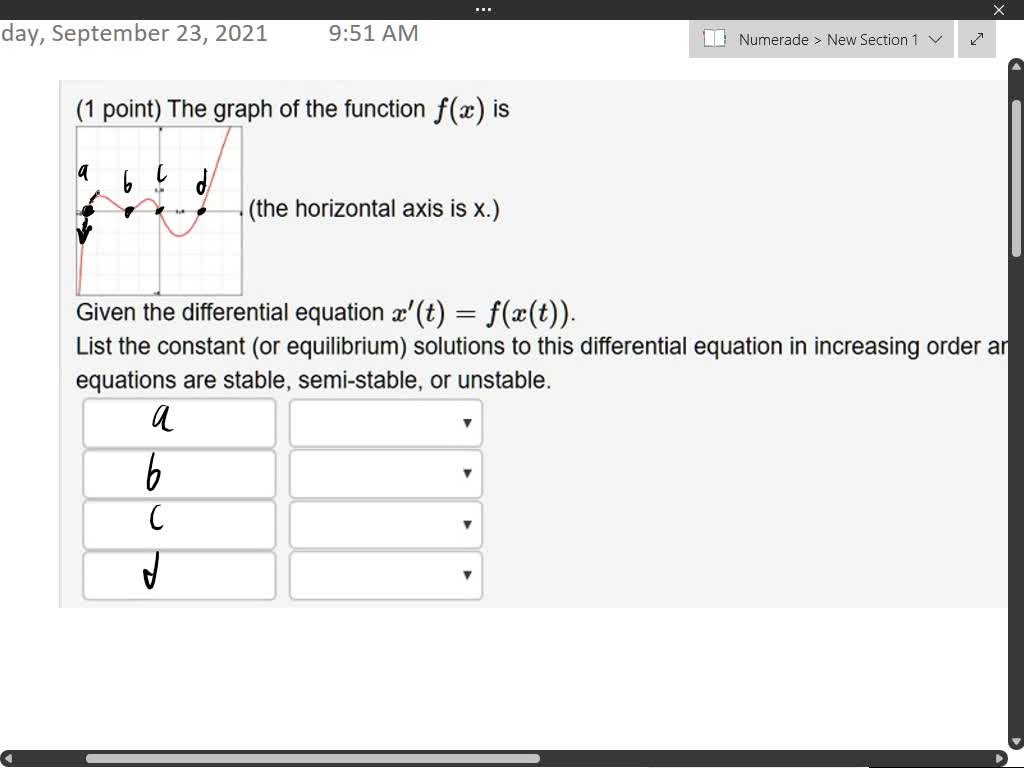
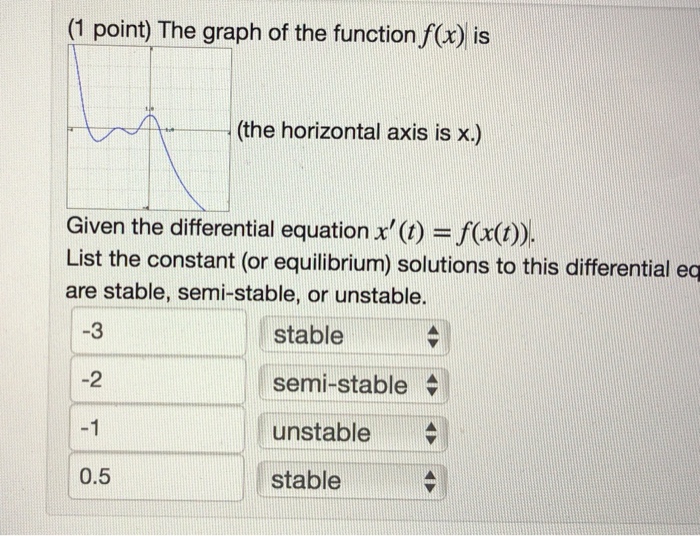
Solved Given the differential equation x’(t)=f(x(t)). List
Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. In studying systems of differential equations, it is often useful to study the behavior of solutions without obtaining an algebraic form. Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di.
Differential Equation ,Finding solution by sketching the graph
Sometimes it is easy to. In studying systems of differential equations, it is often useful to study the behavior of solutions without obtaining an algebraic form. Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$. Equilibrium solutions to differential.
[Solved] Find the general solution of the following differential
Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$. Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. Sometimes it is easy to. Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di.
Solved lyze the following differential equation Find
Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di erential equation. Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. Suppose that we have a differential equation $\frac{dy}{dt} = f(t, y)$. In this section.
Suppose That We Have A Differential Equation $\Frac{Dy}{Dt} = F(T, Y)$.
In this section we will define equilibrium solutions (or equilibrium points) for autonomous differential equations, y’ = f(y). Values of \(y\) for which \(f(y) = 0\) in an autonomous differential equation \(\frac{dy}{dt} = f(y)\) are called equilibrium. Equilibrium solutions to differential equations. Recall that an equilibrium solution is any constant (horizontal) function y(t) = c that is a solution to the di erential equation.
In Studying Systems Of Differential Equations, It Is Often Useful To Study The Behavior Of Solutions Without Obtaining An Algebraic Form.
Sometimes it is easy to.