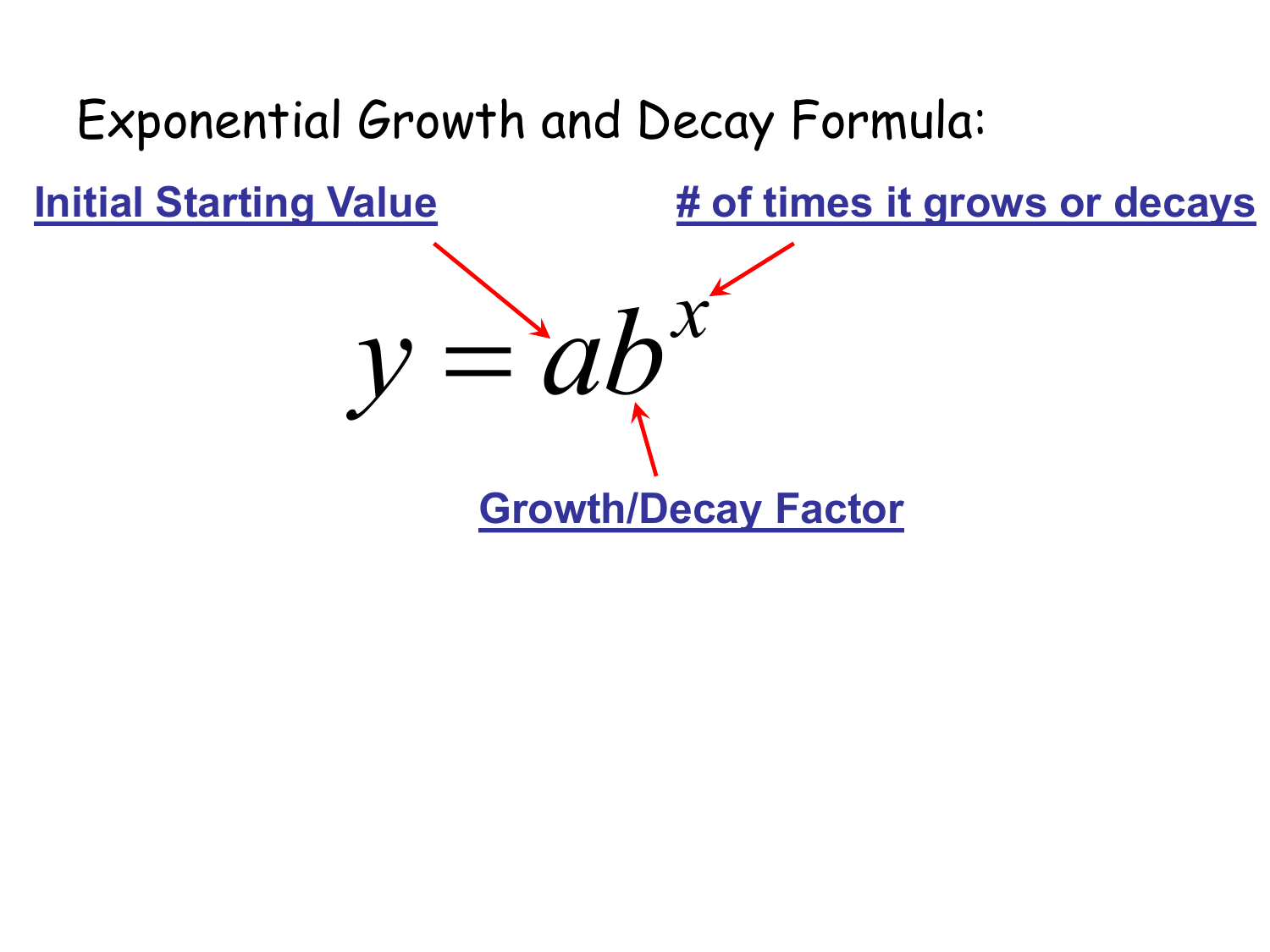
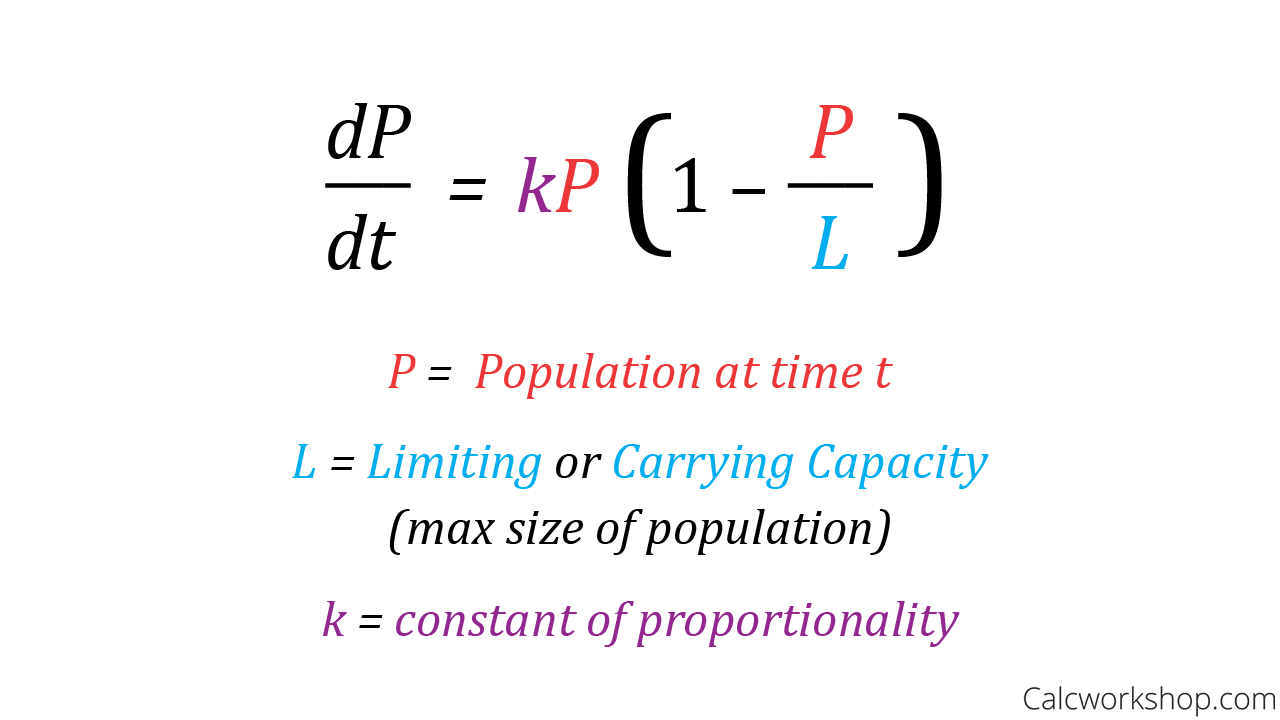
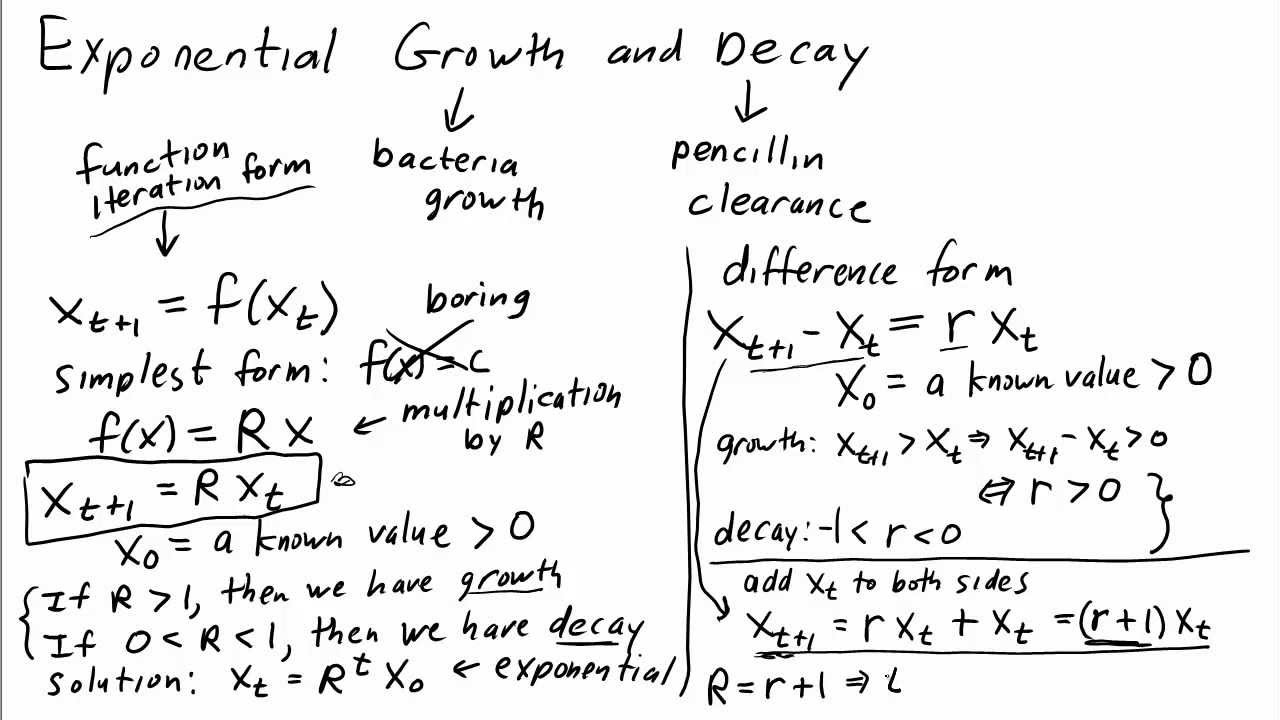
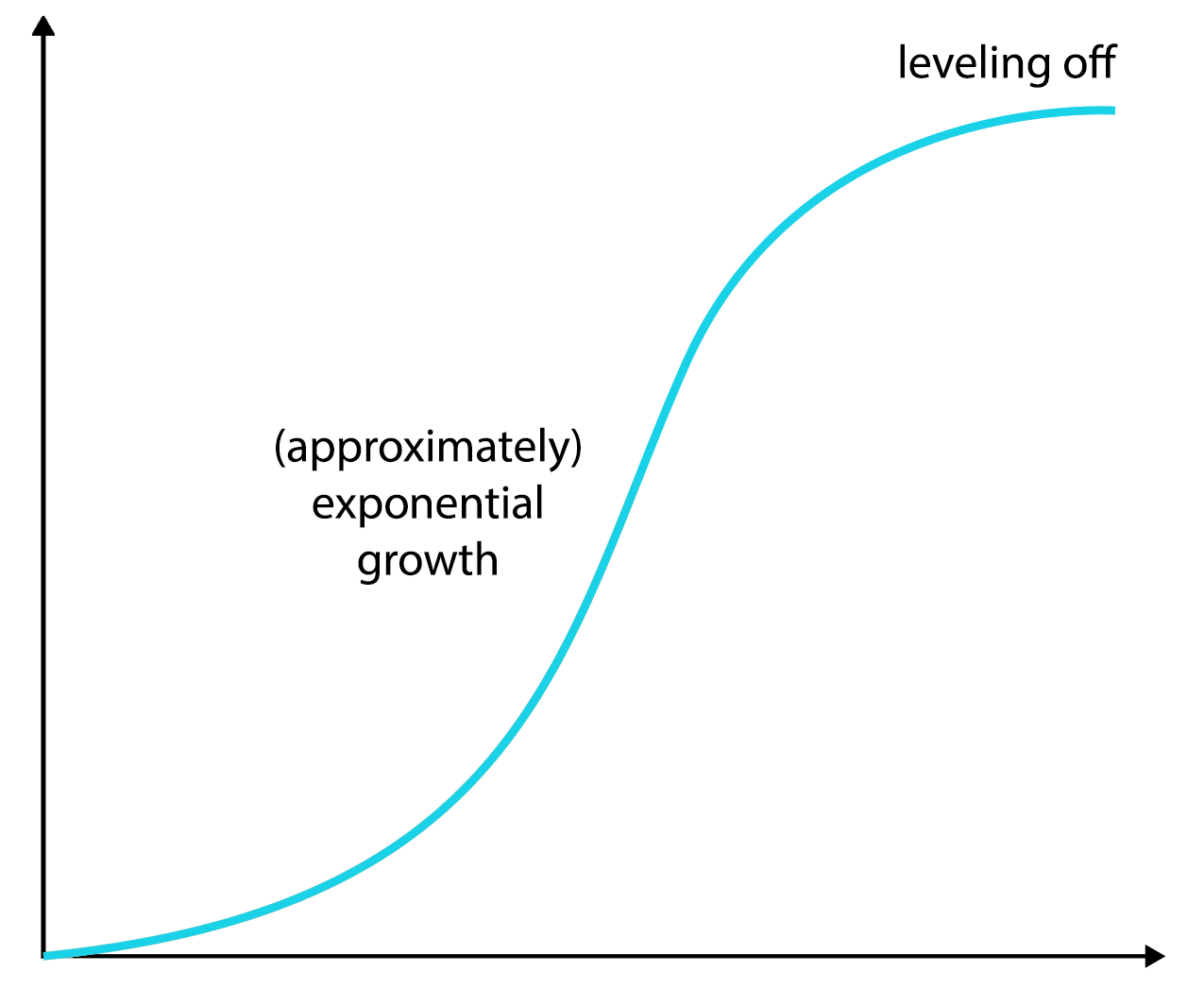
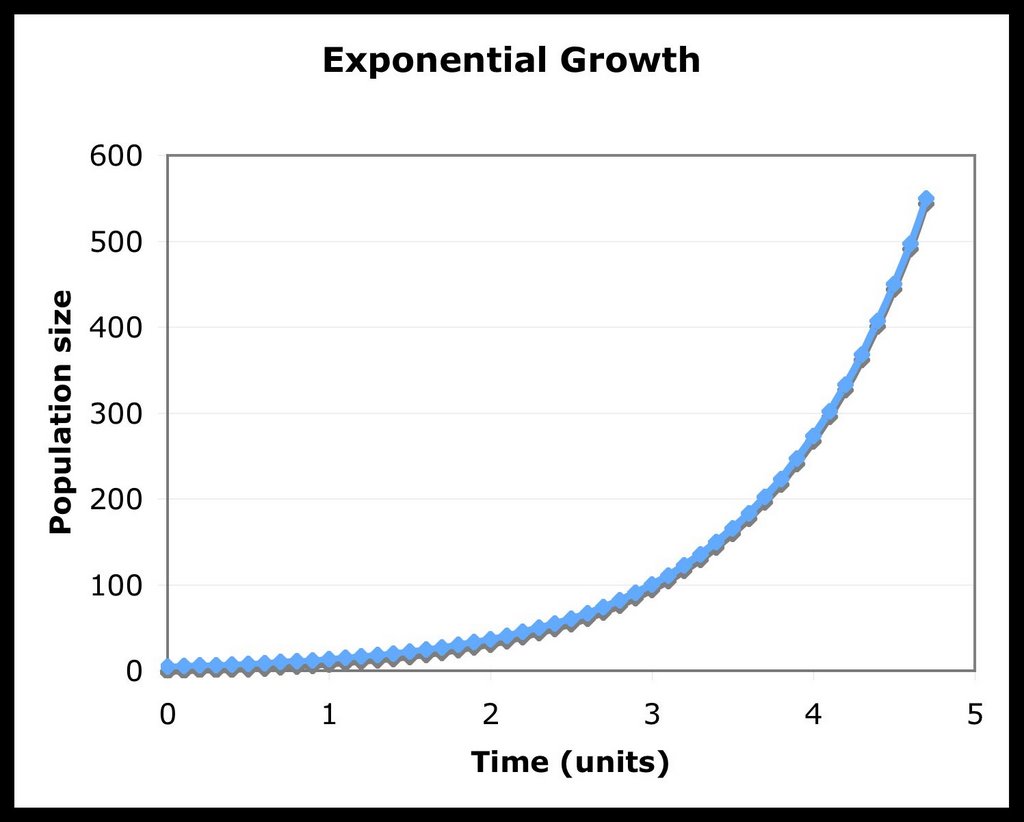
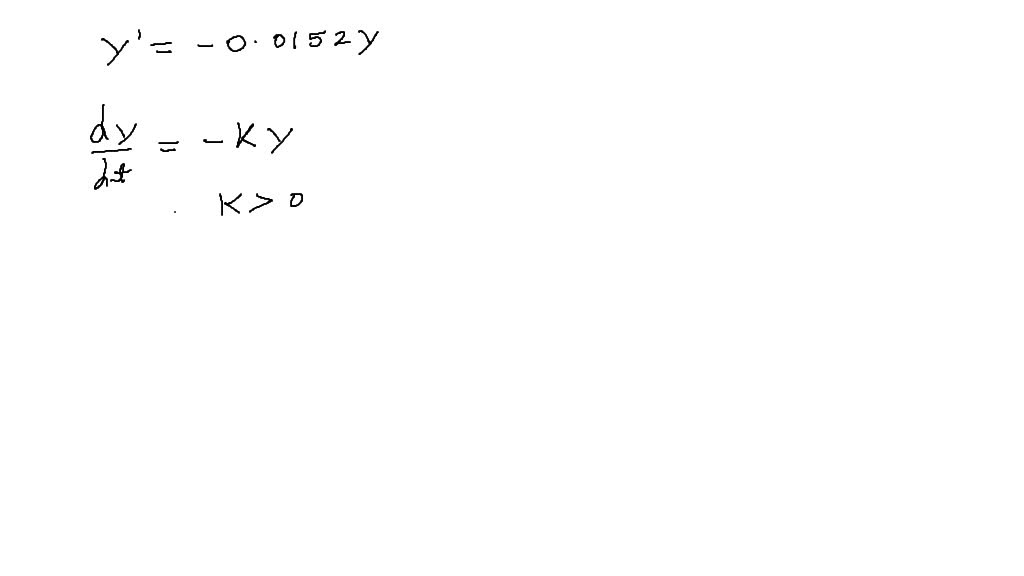Exponential Growth Differential Equation - Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. How differential equations arise in scientific problems, how we study their predictions, and what their solutions can tell us. In this chapter we will. I for example a colony of bacteria may double every hour. A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself.
I for example a colony of bacteria may double every hour. Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. How differential equations arise in scientific problems, how we study their predictions, and what their solutions can tell us. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself. In this chapter we will.
How differential equations arise in scientific problems, how we study their predictions, and what their solutions can tell us. Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. I for example a colony of bacteria may double every hour. In this chapter we will. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself.
Exponential Growth Equation Tessshebaylo
Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. In this chapter we will. How differential equations arise in scientific problems, how we study their predictions, and what their solutions can tell us. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself. A differential.
Exponential Growth Equation Population Tessshebaylo
Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. In this chapter we will. A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. I for example a colony of bacteria may double every hour. How differential equations arise in scientific problems, how we study their predictions,.
Solved 1. Differential Equation y ky (Exponential growth or
Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. In this chapter we will. How differential equations arise in scientific problems, how we study their predictions, and what their solutions can tell us. A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. We call this a.
Exponential Growth Equation Calculus Tessshebaylo
Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself. How differential equations arise in scientific problems, how we study their predictions, and what their solutions can tell us. A differential equation is an equation for.
Equation For Exponential Growth Tessshebaylo
We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself. Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. In this chapter we will. I for example a colony of bacteria may double every hour. A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function.
SOLVEDDoes the given differential equation model unlimited growth
A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. How differential equations arise in scientific problems, how we study their predictions, and what their solutions can tell us. Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. I for example a colony of bacteria may double.
Exponential Decay Equation Example Tessshebaylo
In this chapter we will. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself. A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. I for example a colony of bacteria may double every hour. Exponential growth many quantities grow or.
Exponential Growth Equation Tessshebaylo
I for example a colony of bacteria may double every hour. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself. In this chapter we will. How differential equations arise in scientific problems, how we study their predictions, and what their solutions can tell us. A differential equation is an.
Exponential Growth Equation Meaning Tessshebaylo
A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. Exponential growth many quantities grow or decay at a rate proportional to their size. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself. In this chapter we will. I for example.
Exponential Growth Equation Viewing Gallery
I for example a colony of bacteria may double every hour. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself. In this chapter we will. A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. How differential equations arise in scientific.
Exponential Growth Many Quantities Grow Or Decay At A Rate Proportional To Their Size.
In this chapter we will. A differential equation is an equation for an unknown function that involves the derivative of the unknown function. We call this a differential equation because it connects one (or more) derivatives of a function with the function itself. I for example a colony of bacteria may double every hour.