General Solution Of 2Nd Order Differential Equation - The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other. Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second.
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other. Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y.
Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other. Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second.
[Solved] The general solution to the secondorder differential equation
The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x),.
A Complete Guide to Understanding Second Order Differential Equations
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y. The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as.
Solving Second Order Differential Equation Images and Photos finder
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y. The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as.
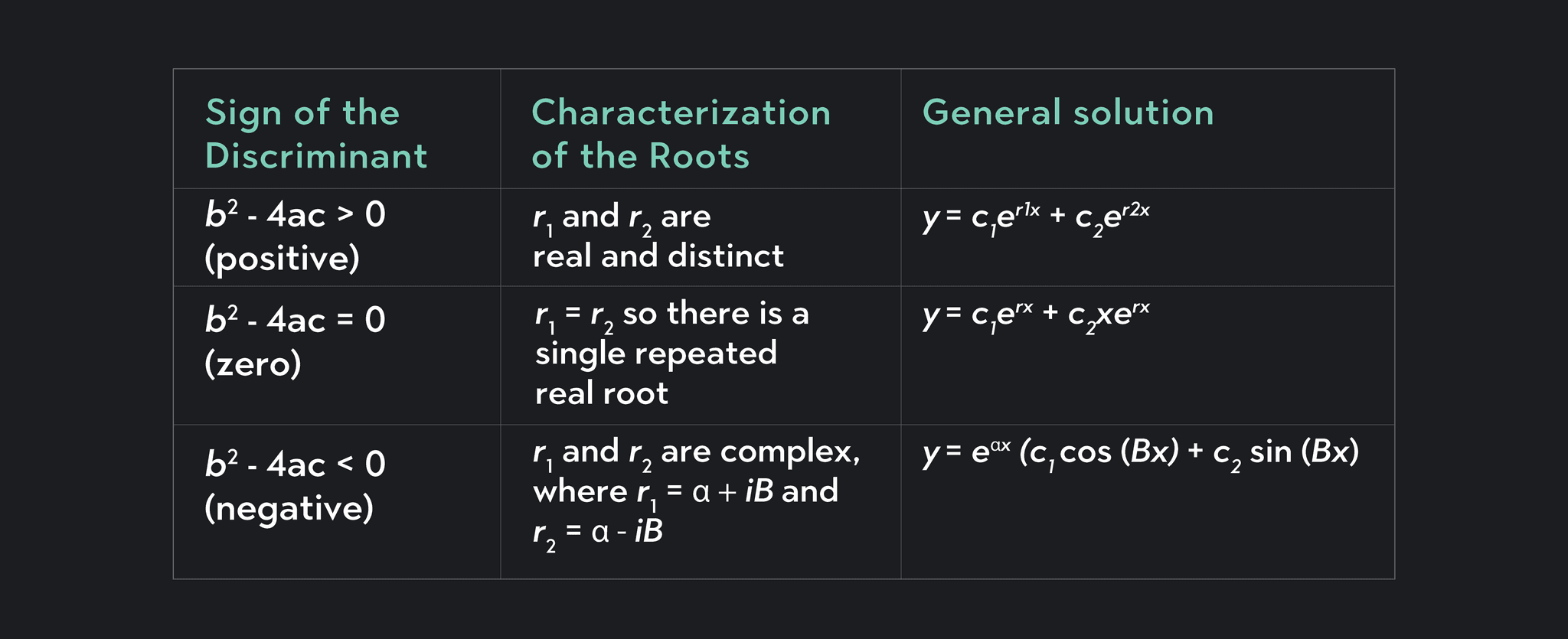
Solution Of Second Order Differential Equation Differential Equation
Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to.
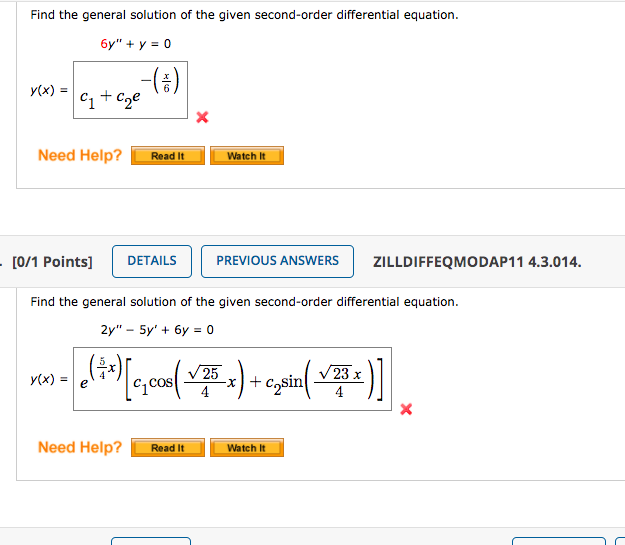
Solved Find the general solution of the given secondorder
The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other. Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as.
Solved Find the general solution of the given secondorder
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x),.
[Solved] . A secondorder differential equation and its general
Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other..
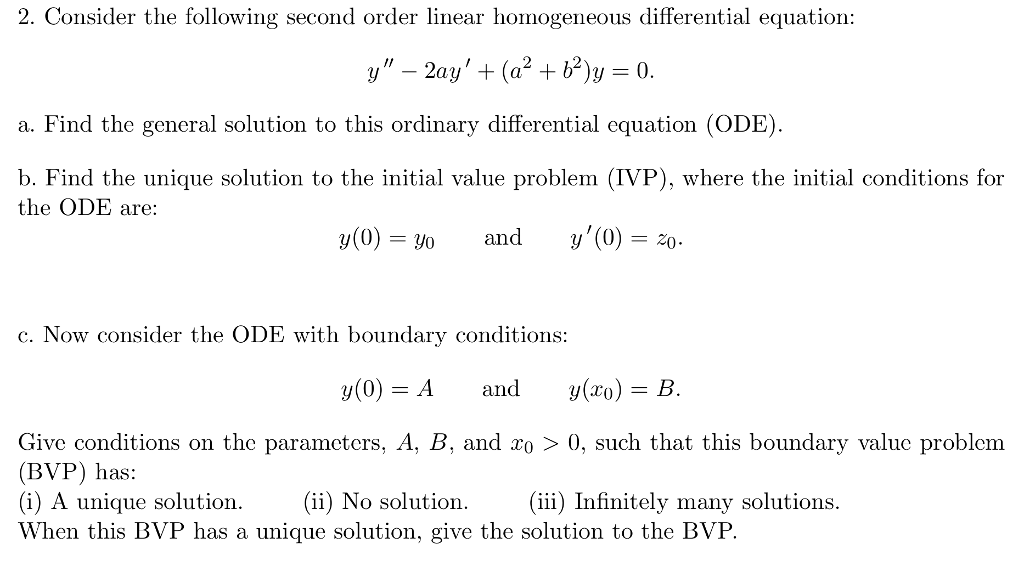
Solved 2. Consider the following second order linear
Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to.
Solved Consider the second order differential equation is a
We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. Example 5 verify that y 1 =.
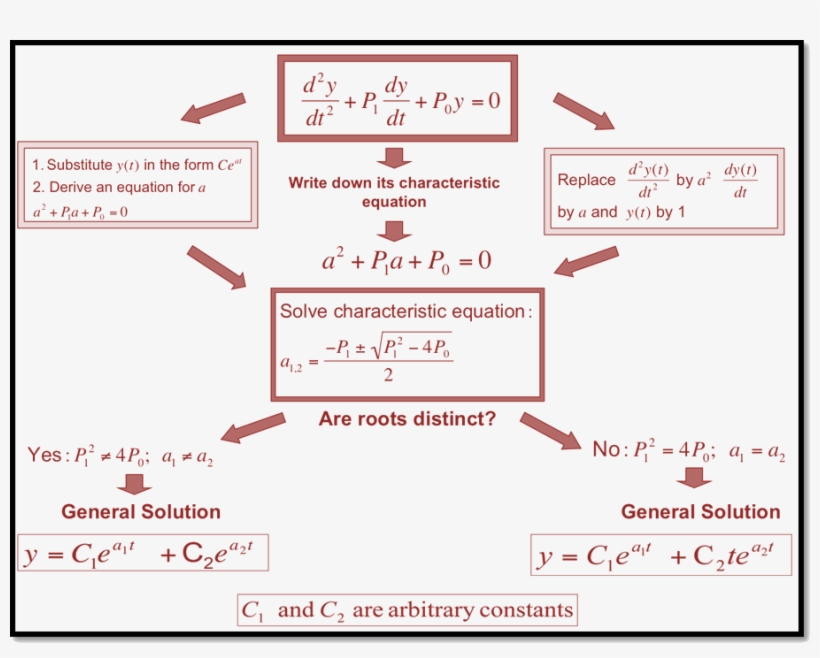
Finding a second solution to a 2nd order differential equation
Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y. We define fundamental sets of solutions and discuss how they can be used to get a general solution to a homogeneous second. Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are.
We Define Fundamental Sets Of Solutions And Discuss How They Can Be Used To Get A General Solution To A Homogeneous Second.
Generally, we write a second order differential equation as y'' + p (x)y' + q (x)y = f (x), where p (x), q (x), and f (x) are functions of x. The functions y 1(x) and y 2(x) are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other. Example 5 verify that y 1 = e4x and y.