Generalized Weakness Differential Diagnosis - 3 to assess if the. Here we offer an algorithm that summarizes the diagnostic approach, along with 5 illustrative cases. The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. New onset of generalized muscle weakness: The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,. Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. Lumbar puncture (elevated csf protein with normal wbc), nerve conduction studies.
New onset of generalized muscle weakness: Lumbar puncture (elevated csf protein with normal wbc), nerve conduction studies. Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for. Here we offer an algorithm that summarizes the diagnostic approach, along with 5 illustrative cases. The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,. 3 to assess if the.
3 to assess if the. Lumbar puncture (elevated csf protein with normal wbc), nerve conduction studies. The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. Here we offer an algorithm that summarizes the diagnostic approach, along with 5 illustrative cases. The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,. New onset of generalized muscle weakness: Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for.
SOLUTION Limb weakness differential diagnosis Studypool
The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for. New onset of generalized muscle weakness: 3 to assess if the. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood.
SOLUTION Limb weakness differential diagnosis Studypool
Here we offer an algorithm that summarizes the diagnostic approach, along with 5 illustrative cases. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. New onset of generalized muscle weakness: 3 to assess if the. The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic.
Weakness Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan
The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,. Lumbar puncture (elevated csf protein with normal wbc), nerve conduction studies. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. Here we offer an algorithm that summarizes the diagnostic approach, along with 5 illustrative cases. New onset of.
SOLUTION Limb weakness differential diagnosis Studypool
The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,. Lumbar puncture (elevated csf protein with normal wbc), nerve conduction studies. 3 to assess if the. New onset of generalized muscle weakness: The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and.
HD An approach to Generalized Weakness EMRAP
Lumbar puncture (elevated csf protein with normal wbc), nerve conduction studies. The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,. The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. 3 to assess if the. Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for.
Differential Diagnosis of Congenital Facial Weakness Disorders
3 to assess if the. New onset of generalized muscle weakness: The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for. The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,.
Differential Diagnosis of Unilateral Upper Extremity Weakness A Case
The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,. Here we offer an algorithm that summarizes the diagnostic approach, along with 5 illustrative cases. The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for. Lumbar puncture (elevated csf.
Differential diagnosis of acute weakness in a pediatric patient
The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,. Here we offer an algorithm that summarizes the diagnostic approach, along with 5 illustrative cases. Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for. 3 to assess if the. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood.
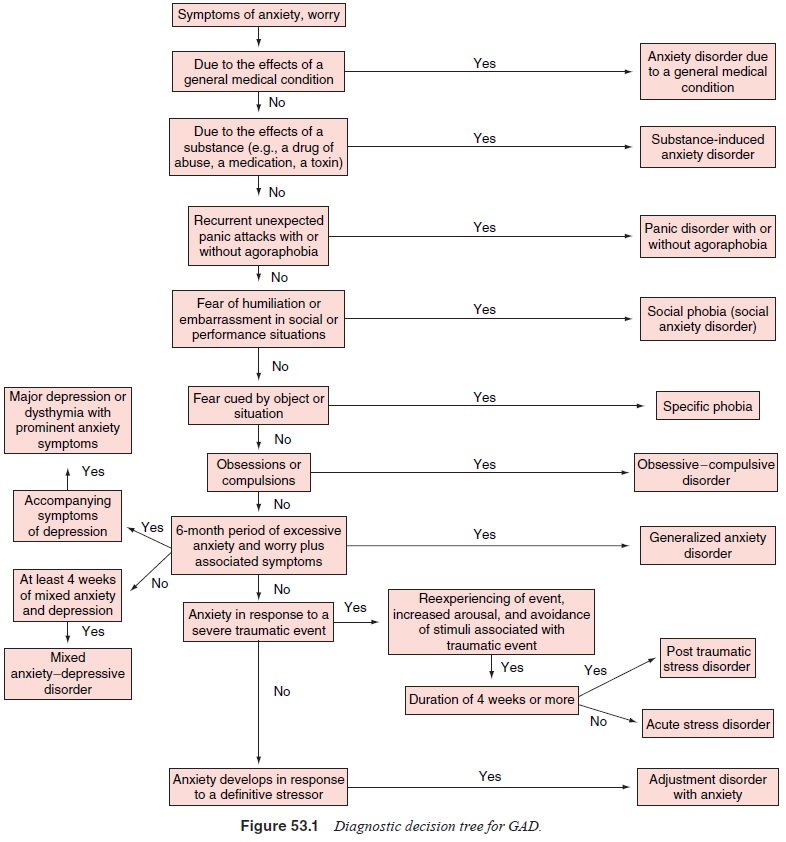
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Differential Diagnosis
New onset of generalized muscle weakness: Here we offer an algorithm that summarizes the diagnostic approach, along with 5 illustrative cases. The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. Lumbar puncture (elevated csf protein with normal wbc), nerve conduction studies. The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive,.
Broaden Your Differential Diagnosis of Weakness in the Elderly JEMS
Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for. New onset of generalized muscle weakness: Lumbar puncture (elevated csf protein with normal wbc), nerve conduction studies. The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial.
Lumbar Puncture (Elevated Csf Protein With Normal Wbc), Nerve Conduction Studies.
Here we offer an algorithm that summarizes the diagnostic approach, along with 5 illustrative cases. Muscle weakness in adults may also be caused by reduced extraction of oxygen from the arterial blood. The differential diagnosis of true muscle weakness is extensive, including neurologic, rheumatologic, endocrine, genetic,. 3 to assess if the.
New Onset Of Generalized Muscle Weakness:
The approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients presenting to the ed with acute, nontraumatic neurologic and. Brief case examples and a stepwise approach for.