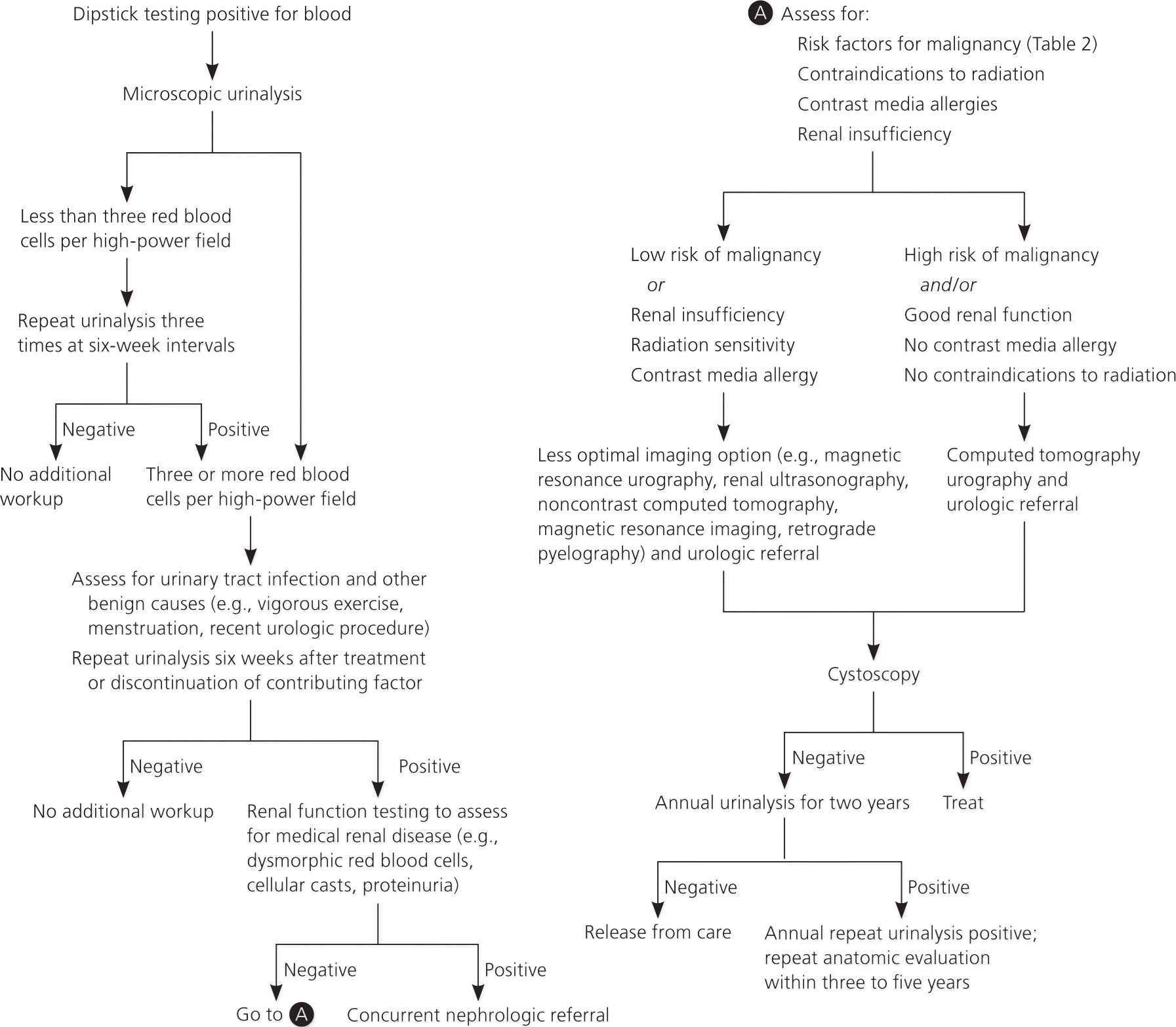
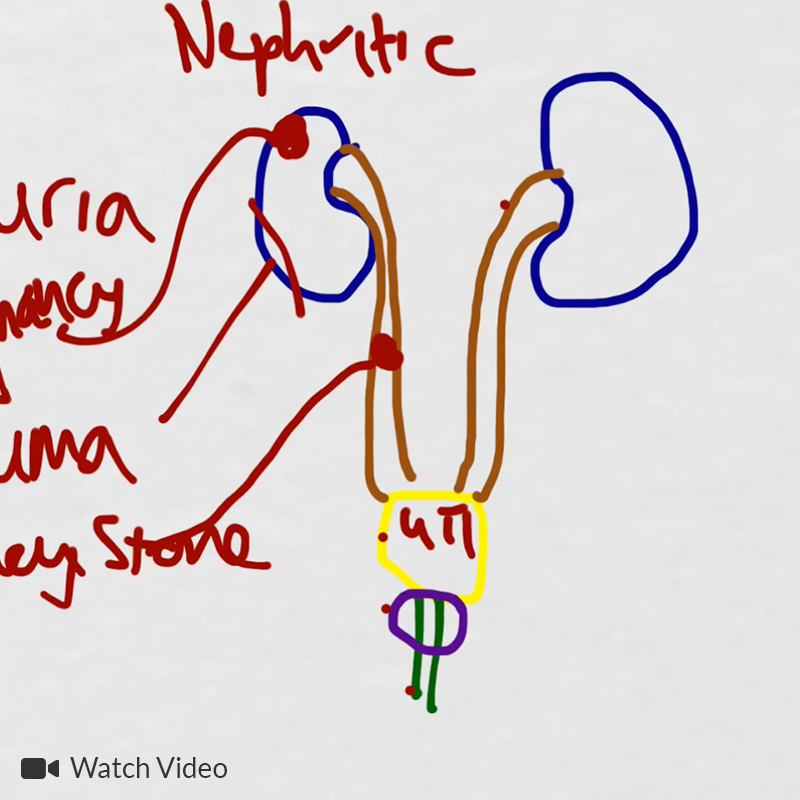
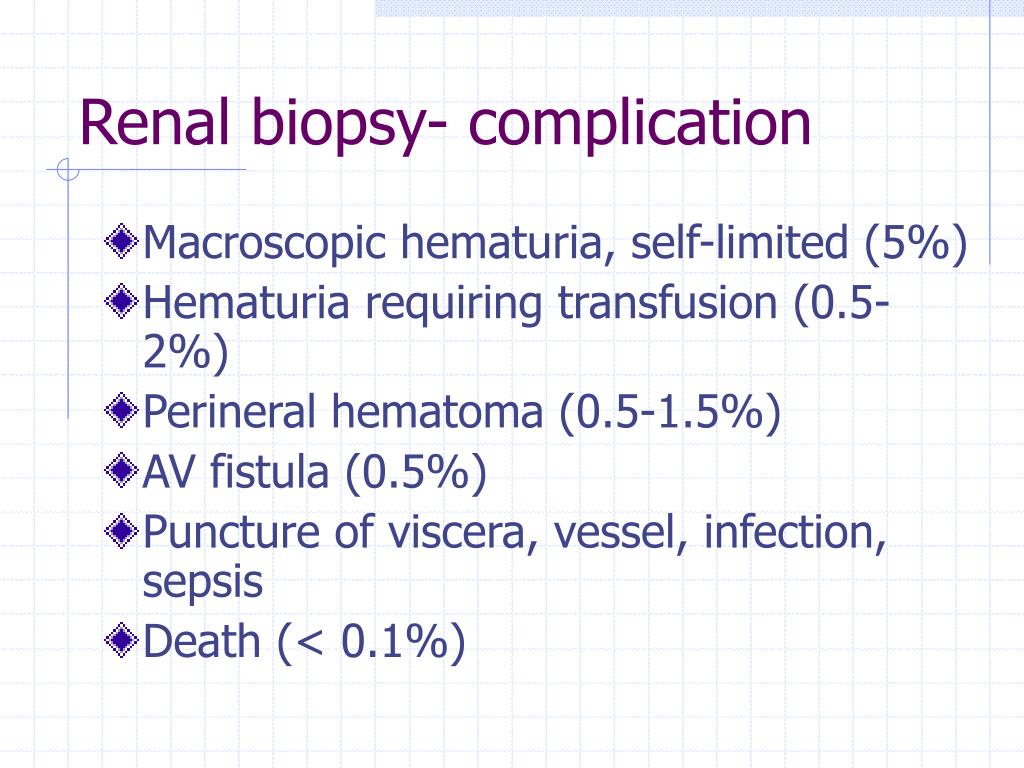
Hematuria Differential Diagnosis - The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate infection as a. It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine. The differential diagnosis of hematuria includes etiologies that cause the appearance of discolored red, pink, brown, or yellow urine, including: Urinalysis (urine dipstick testing) is usually the primary investigation in all settings*. Intervoid hematuria blood between voiding only (voided urine is. Among the most common causes of hematuria are infections of the lower urinary tract, especially the bladder. Hematuria is defined as the presence of blood in the urine. Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; Other causes to consider are stones.
Intervoid hematuria blood between voiding only (voided urine is. Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine. Urinalysis (urine dipstick testing) is usually the primary investigation in all settings*. The differential diagnosis of hematuria includes etiologies that cause the appearance of discolored red, pink, brown, or yellow urine, including: Other causes to consider are stones. The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate infection as a. Among the most common causes of hematuria are infections of the lower urinary tract, especially the bladder. Hematuria is defined as the presence of blood in the urine.
It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine. Among the most common causes of hematuria are infections of the lower urinary tract, especially the bladder. Intervoid hematuria blood between voiding only (voided urine is. Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; Hematuria is defined as the presence of blood in the urine. Urinalysis (urine dipstick testing) is usually the primary investigation in all settings*. The differential diagnosis of hematuria includes etiologies that cause the appearance of discolored red, pink, brown, or yellow urine, including: The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate infection as a. Other causes to consider are stones.
(PPT) Differential Diagnosis of Hematuria DOKUMEN.TIPS
It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine. The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate infection as a. The differential diagnosis of hematuria includes etiologies that cause the appearance of discolored red, pink, brown, or yellow urine, including: Intervoid hematuria blood between voiding only (voided.
Hematuria Differential Diagnosis USMLE Step 2 CS Mnemonics
Among the most common causes of hematuria are infections of the lower urinary tract, especially the bladder. Other causes to consider are stones. Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate infection as a. Intervoid hematuria blood between voiding only (voided urine is.
Hematuria Workup Hot Sex Picture
Urinalysis (urine dipstick testing) is usually the primary investigation in all settings*. The differential diagnosis of hematuria includes etiologies that cause the appearance of discolored red, pink, brown, or yellow urine, including: Among the most common causes of hematuria are infections of the lower urinary tract, especially the bladder. The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate.
PPT Differential Diagnosis of Hematuria PowerPoint Presentation ID
Other causes to consider are stones. Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; Urinalysis (urine dipstick testing) is usually the primary investigation in all settings*. The differential diagnosis of hematuria includes etiologies that cause the appearance of discolored red, pink, brown, or yellow urine, including: Hematuria is defined as the presence of blood in the urine.
Differential Diagnosis of Macroscopic Hematuria
Intervoid hematuria blood between voiding only (voided urine is. Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; Urinalysis (urine dipstick testing) is usually the primary investigation in all settings*. It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine. Other causes to consider are stones.
Hematuria, basics By RAEU Urology Cheatsheets
Intervoid hematuria blood between voiding only (voided urine is. The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate infection as a. Hematuria is defined as the presence of blood in the urine. Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; Urinalysis (urine dipstick testing) is usually the primary investigation in all settings*.
PPT Differential Diagnosis of Hematuria PowerPoint Presentation, free
The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate infection as a. Hematuria is defined as the presence of blood in the urine. Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; Other causes to consider are stones. It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine.
Hematuria Basicmedical Key
It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine. Urinalysis (urine dipstick testing) is usually the primary investigation in all settings*. Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; The differential diagnosis of hematuria includes etiologies that cause the appearance of discolored red, pink, brown, or yellow urine,.
PPT HEMATURIA BASIC COURSE OF DIAGNOSIS PowerPoint Presentation, free
Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing; It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine. Other causes to consider are stones. The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate infection as a. Intervoid hematuria blood between voiding only (voided urine is.
PPT Differential Diagnosis of Hematuria PowerPoint Presentation, free
Other causes to consider are stones. It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine. The differential diagnosis of hematuria includes etiologies that cause the appearance of discolored red, pink, brown, or yellow urine, including: Hematuria is defined as the presence of blood in the urine. Among the most common.
Other Causes To Consider Are Stones.
Among the most common causes of hematuria are infections of the lower urinary tract, especially the bladder. Intervoid hematuria blood between voiding only (voided urine is. The differential diagnosis of hematuria includes etiologies that cause the appearance of discolored red, pink, brown, or yellow urine, including: Initial hematuria blood at beginning of micturition with subsequent clearing;
Urinalysis (Urine Dipstick Testing) Is Usually The Primary Investigation In All Settings*.
Hematuria is defined as the presence of blood in the urine. It can be visible to the naked eye (gross [visible] hematuria) or detectable only on examination of the urine. The presence of nitrites and/or leukocytes on urinalysis may also indicate infection as a.