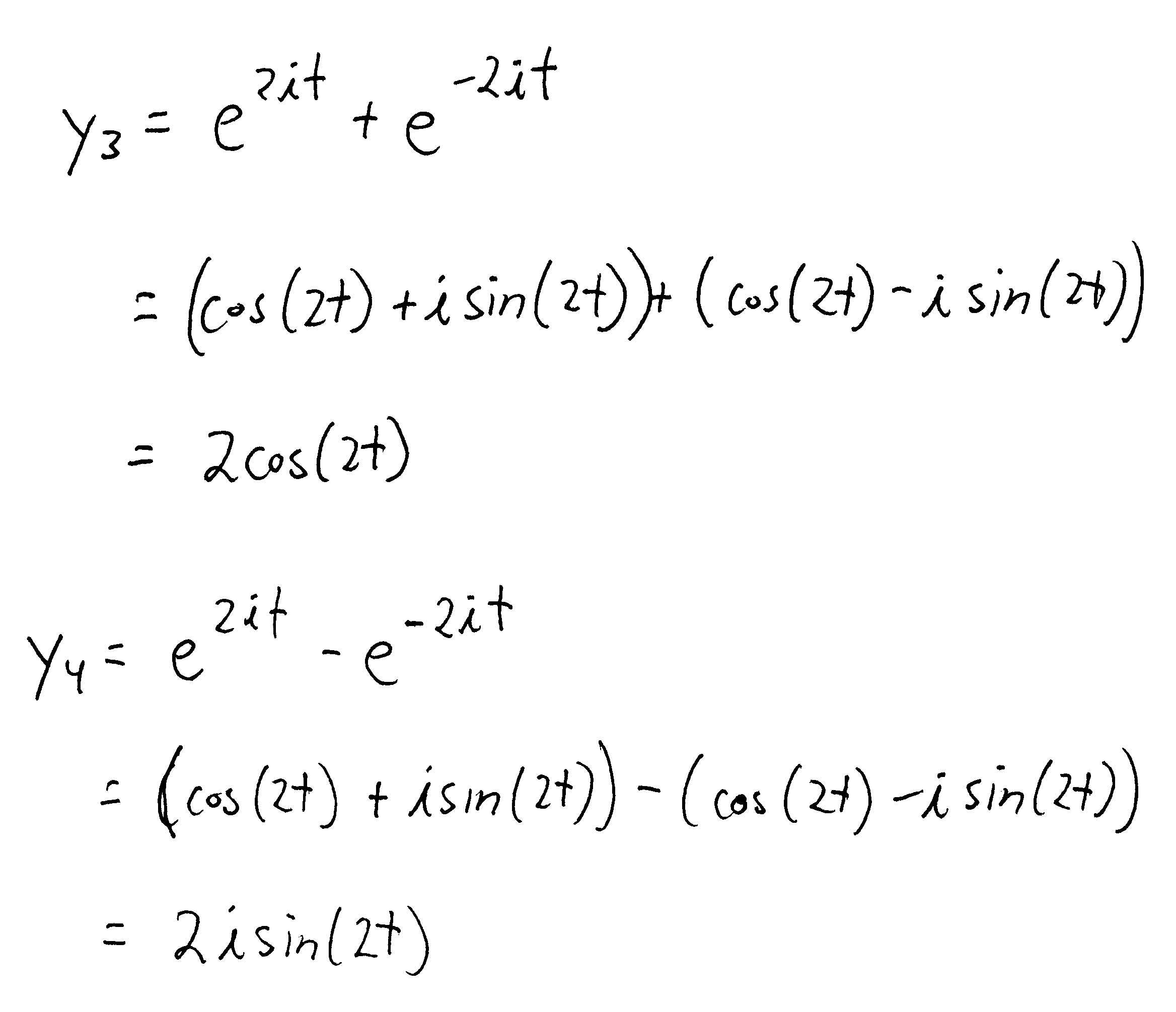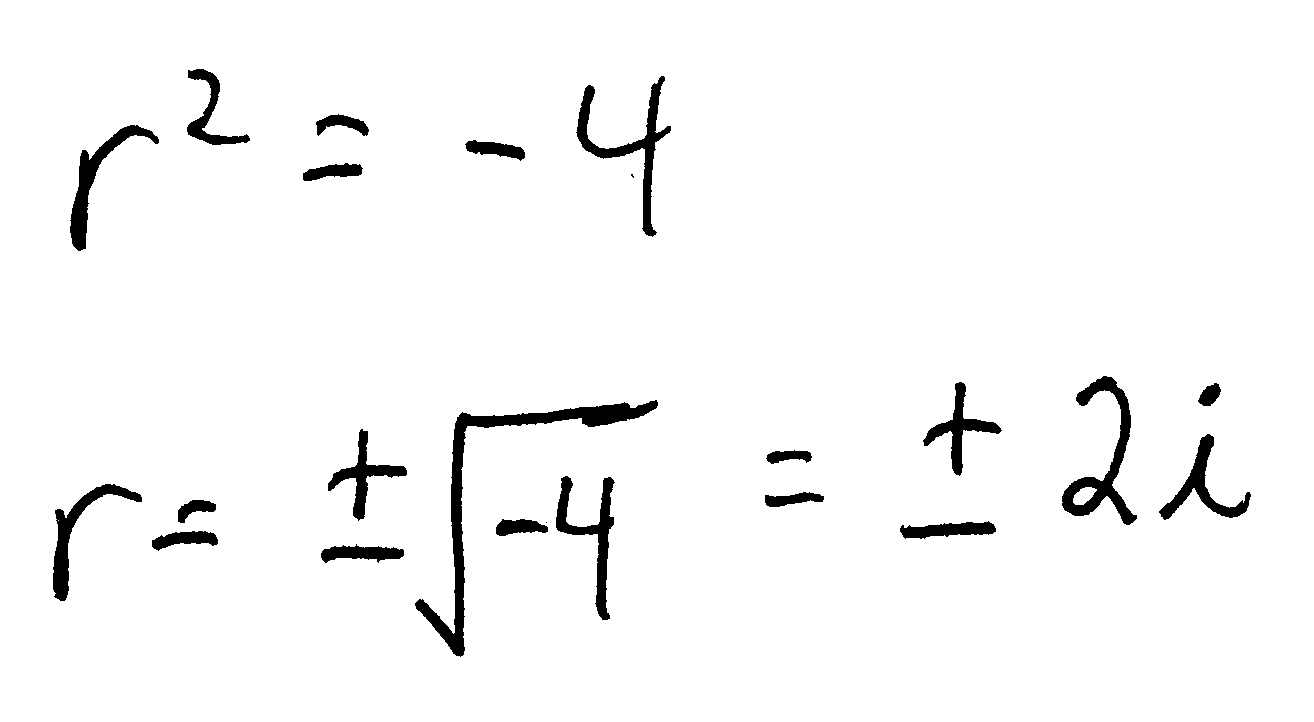Homogeneous Ordinary Differential Equation - A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. An example will show how it is all done: Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher.
Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. An example will show how it is all done: In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is.
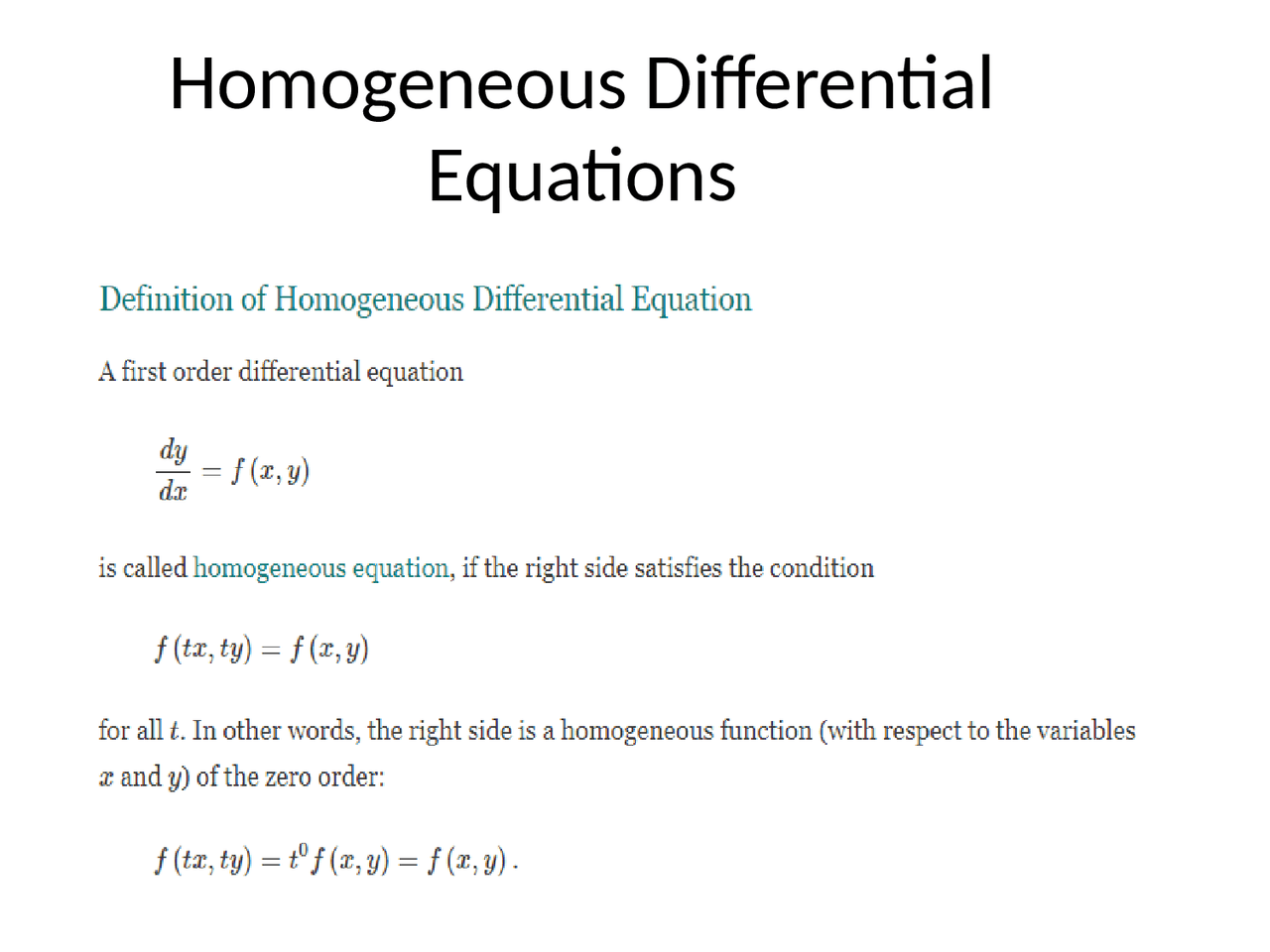
A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. An example will show how it is all done: In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher.
(PDF) Solution of First Order Linear Non Homogeneous Ordinary
Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x,.
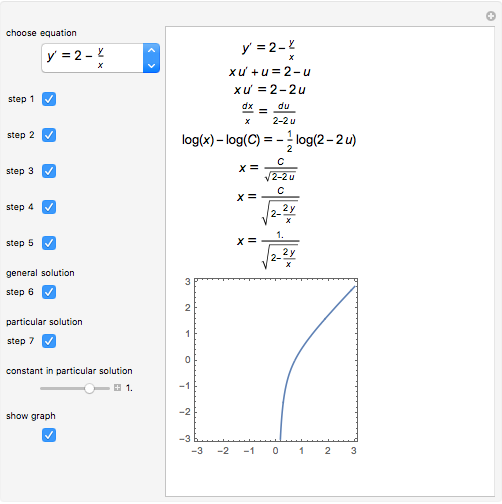
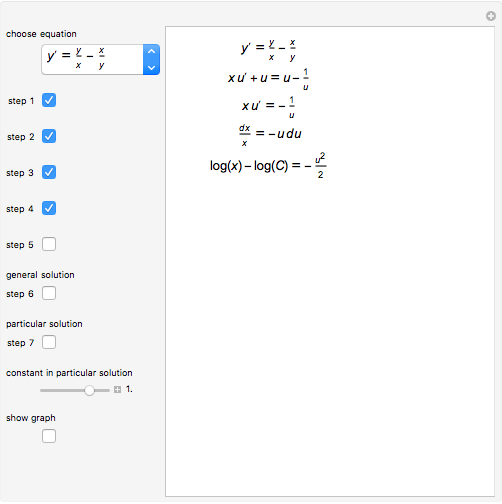
Some Homogeneous Ordinary Differential Equations Wolfram
A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. An example will show how it is all done: In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous.
Some Homogeneous Ordinary Differential Equations Wolfram
An example will show how it is all done: A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. Using y = vx and dy dx.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
An example will show how it is all done: A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear,.
Solved The homogeneous secondorder ordinary differential
A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve.
Homogeneous Differential Equations Docsity
An example will show how it is all done: In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we.
Differential Equations Ordinary differential equation ODE Partial
An example will show how it is all done: A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. Using y = vx and dy dx.
Differential Equation Calculator
A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. An example will show how it is all done: A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous.
College Park Tutors Blog Differential Equations Solving a second
Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is. A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is.
Homogeneous Differential Equation Know types, Steps to solve
An example will show how it is all done: Using y = vx and dy dx = v + x dv dx we can solve the differential equation. In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous.
Using Y = Vx And Dy Dx = V + X Dv Dx We Can Solve The Differential Equation.
A first order differential equation of the form m (x;y)dx + n dy = 0 is said to be. An example will show how it is all done: In this section we will extend the ideas behind solving 2nd order, linear, homogeneous differential equations to higher. A differential equation of the form f(x,y)dy = g(x,y)dx is said to be homogeneous differential equation if the degree of f(x,y) and g(x, y) is.