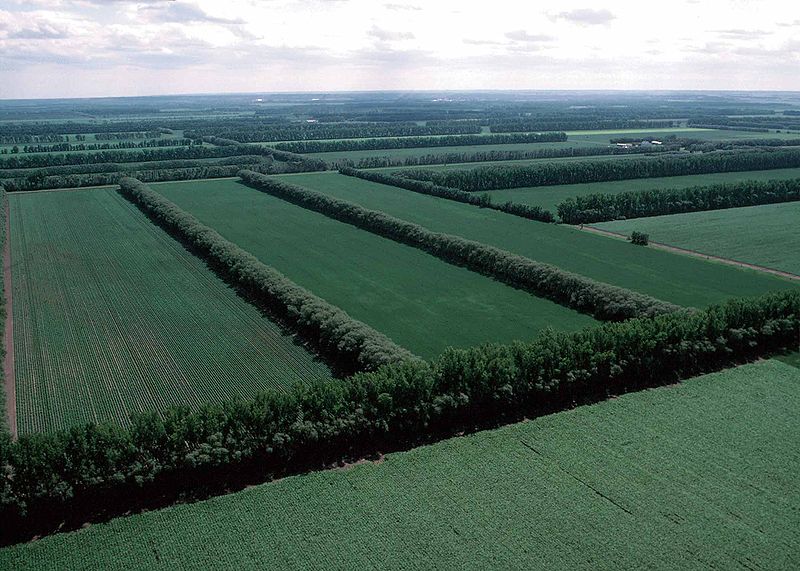
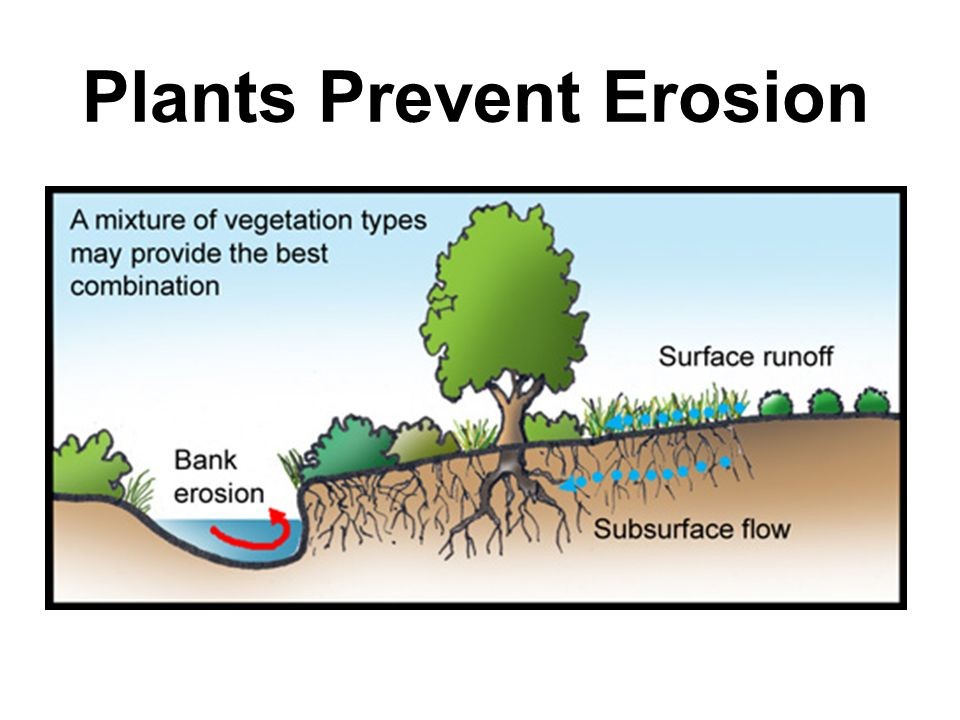
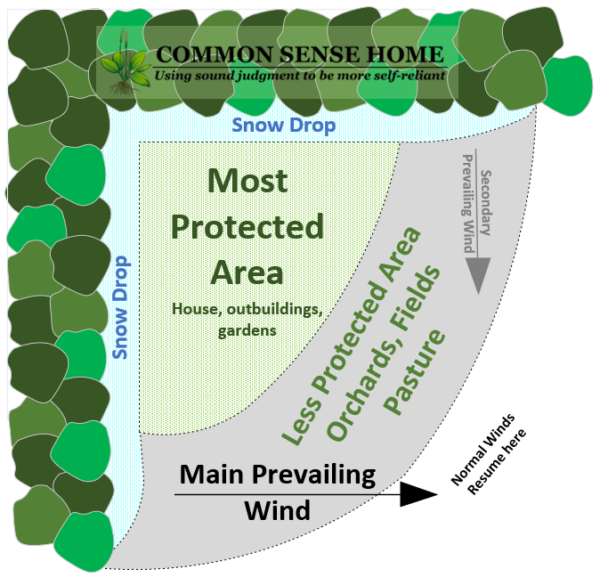
How Does A Windbreak Help Prevent Erosion - These vegetative barriers are made up of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to provide shelter from the wind and to protect against soil. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion, maintain soil moisture levels, and. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees.
A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. These vegetative barriers are made up of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to provide shelter from the wind and to protect against soil. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion, maintain soil moisture levels, and.
By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion, maintain soil moisture levels, and. These vegetative barriers are made up of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to provide shelter from the wind and to protect against soil. A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees.
P14 111 Windbreak Of Trees To Prevent Erosion In Large Fields Stock
By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion, maintain soil moisture levels, and. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times.
Plants vs Erosion The Power of Erosion Control Plants
A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion,.
Windbreak Design Maximize Your Land's Potential
A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion,.
Windbreak Design Maximize Your Land's Potential
A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. These vegetative barriers are made up of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to provide shelter from the wind and to protect against soil. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. By reducing wind.
How does the use of windbreaks help prevent soil erosion? Gardening
These vegetative barriers are made up of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to provide shelter from the wind and to protect against soil. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. A.
How does windbreak planting help protect plants from strong winds
A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion, maintain soil moisture levels, and. These vegetative barriers are made up of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to provide shelter from the wind and to protect against soil. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and.
Extruded Windbreak Netting as Garden Fence to Stop Wind, Sand and Hails
Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion,.
Windbreak Wikipedia
These vegetative barriers are made up of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to provide shelter from the wind and to protect against soil. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. A.
How does windbreak planting help create a wildlifefriendly garden
These vegetative barriers are made up of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to provide shelter from the wind and to protect against soil. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. A.
(PDF) Optimal windbreak design for winderosion control Wim Cornelis
By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion, maintain soil moisture levels, and. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. These vegetative barriers are made up of trees, shrubs and/or grasses planted to provide shelter from the wind and to protect against soil. A windbreak density of 40 to.
These Vegetative Barriers Are Made Up Of Trees, Shrubs And/Or Grasses Planted To Provide Shelter From The Wind And To Protect Against Soil.
By reducing wind speed and turbulence, windbreaks help to prevent soil erosion, maintain soil moisture levels, and. A windbreak density of 40 to 60 percent provides the greatest downwind. A windbreak protects an area 10 to 15 times the height of the trees. Windbreaks are the barriers, used to reduce and redirect the wind, with the objective to check the soil erosion due to wind.