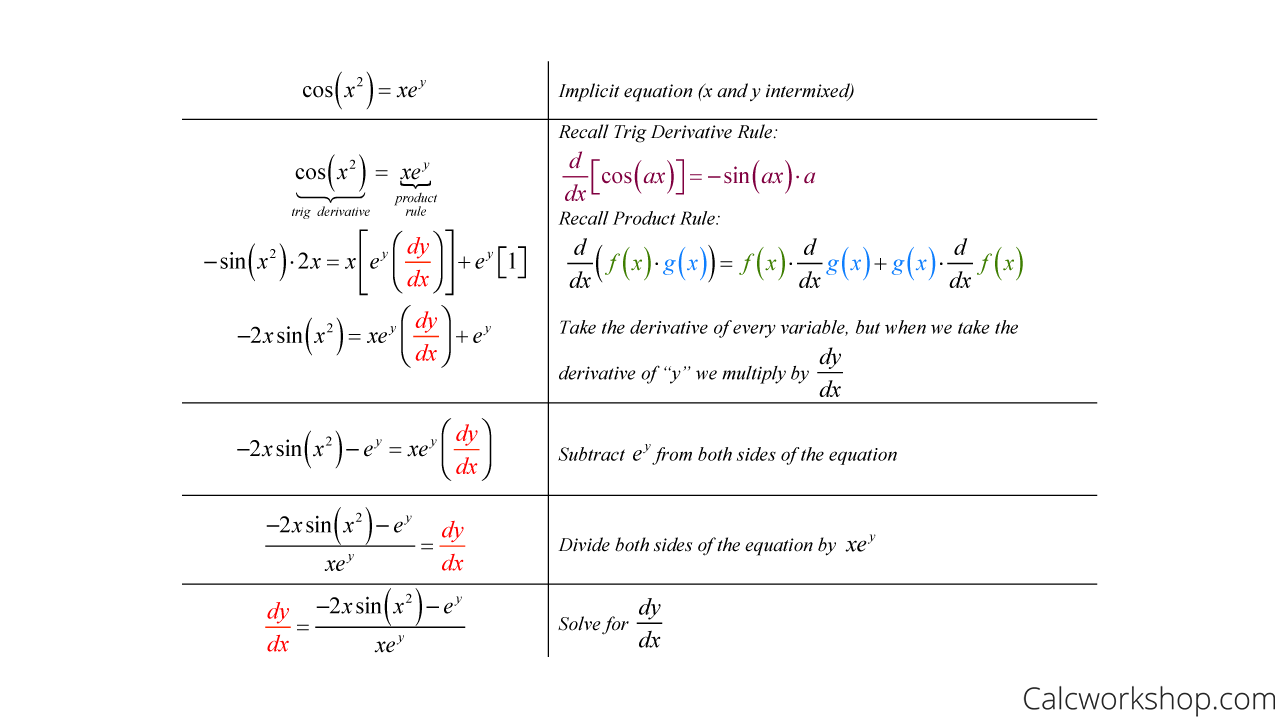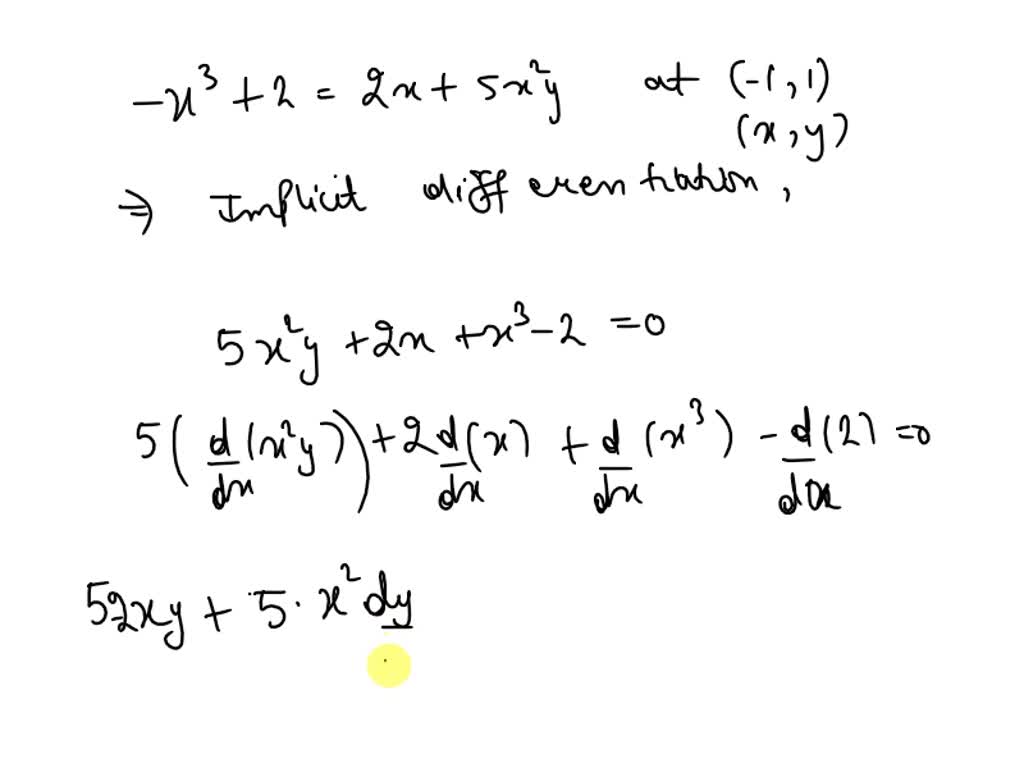Implicit Differentiation With Natural Log - Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. Apply the natural logarithm to both sides and rewrite: The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved. Usually it is easiest to. Given a function \(y=f(x)\text{,}\) the following steps outline the logarithmic differentiation.
Usually it is easiest to. Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved. Apply the natural logarithm to both sides and rewrite: Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. Given a function \(y=f(x)\text{,}\) the following steps outline the logarithmic differentiation. The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f.
Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. Given a function \(y=f(x)\text{,}\) the following steps outline the logarithmic differentiation. Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved. Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Apply the natural logarithm to both sides and rewrite: Usually it is easiest to.
intro to Implicit differentiation PDF Free Download
Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved. The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. Usually it is easiest to.
core pure 3 notes implicit differentiation
Given a function \(y=f(x)\text{,}\) the following steps outline the logarithmic differentiation. Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved. Usually it is easiest to.
Implicit Differentiation (w/ Examples And Worksheets!)
The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Usually it is easiest to. Given a function \(y=f(x)\text{,}\) the following steps outline the logarithmic differentiation. Apply the natural logarithm to both sides and rewrite: Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved.
How to Do Implicit Differentiation 7 Steps (with Pictures)
Apply the natural logarithm to both sides and rewrite: Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved. Usually it is easiest to. Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f.
How to Do Implicit Differentiation 7 Steps (with Pictures)
Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: Usually it is easiest to. The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Apply the natural logarithm to both sides and rewrite:
SOLVED Implicit differentiation examples
Apply the natural logarithm to both sides and rewrite: The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. Usually it is easiest to. Given a function \(y=f(x)\text{,}\) the following steps outline the logarithmic differentiation.
ML1983Mathematics Logarithmic Differentiation Examples and Answers
Usually it is easiest to. Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved. The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so:
Implicit Differentiation PDF Mathematical Analysis Differential
Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: Apply the natural logarithm to both sides and rewrite: Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved. The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use.
Implicit Differentiation (w/ Examples And Worksheets!), 47 OFF
Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Usually it is easiest to. Implicit differentiation is an alternate method for differentiating equations that can be solved. Given a function \(y=f(x)\text{,}\) the following steps outline the logarithmic differentiation.
Implicit Differentiation Questions Revisely
Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use. The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: Usually it is easiest to. Given a function \(y=f(x)\text{,}\) the following steps outline the logarithmic differentiation.
Implicit Differentiation Is An Alternate Method For Differentiating Equations That Can Be Solved.
The derivative of f is f times the derivative of the natural logarithm of f. Usually it is easiest to. Given a function \(y=f(x)\text{,}\) the following steps outline the logarithmic differentiation. Apply the natural logarithm to both sides and rewrite:
Now That We Have The Derivative Of The Natural Exponential Function, We Can Use.
Ln(f(x)) = ln(xx) = x ·ln(x) so: