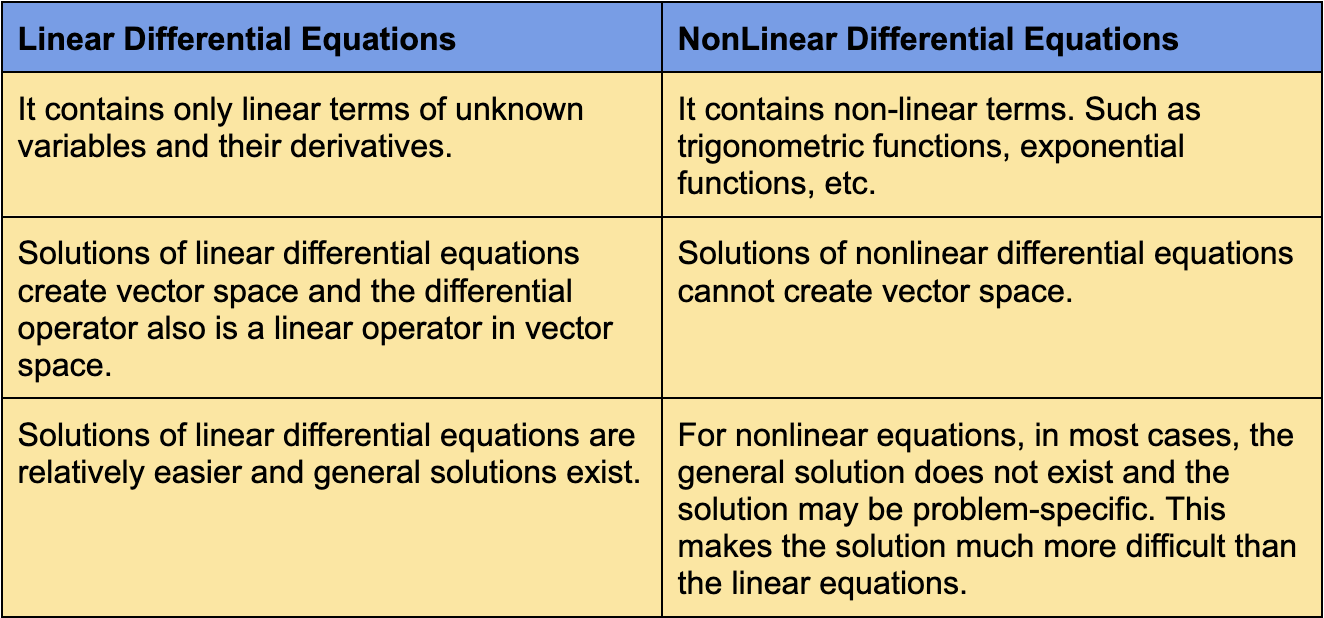
Linear Vs Non Linear Differential Equations - A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. We explain the distinction between linear and nonlinear differential equations and why it matters. The variables and their derivatives must always. In a differential equation, when the variables and their derivatives are only multiplied by constants, then the equation is linear. A differential equation is linear if there are no products of y y and its differentials. Materials include course notes and a problem set with solutions. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent to said form: A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. This section provides materials for a session on linear versus nonlinear ordinary differential equations.
A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent to said form: In a differential equation, when the variables and their derivatives are only multiplied by constants, then the equation is linear. We explain the distinction between linear and nonlinear differential equations and why it matters. The variables and their derivatives must always. A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. A differential equation is linear if there are no products of y y and its differentials. A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. Materials include course notes and a problem set with solutions. This section provides materials for a session on linear versus nonlinear ordinary differential equations.
A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. A differential equation is linear if there are no products of y y and its differentials. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent to said form: The variables and their derivatives must always. This section provides materials for a session on linear versus nonlinear ordinary differential equations. We explain the distinction between linear and nonlinear differential equations and why it matters. Materials include course notes and a problem set with solutions. In a differential equation, when the variables and their derivatives are only multiplied by constants, then the equation is linear. A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms.
Linear and equations worksheet Live Worksheets
A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. This section provides materials for a session on linear versus nonlinear ordinary differential equations. We explain the distinction between linear and nonlinear differential equations and why it matters. The variables and their derivatives must always. In a differential equation, when the variables and their derivatives are only multiplied by constants, then.
How to define linear and differential equation Mathematics
A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. In a differential equation, when the variables and their derivatives are only multiplied by constants, then the equation is linear. The variables and their derivatives must always. Materials include course notes and a.
Difference Between Linear And Differential Equations
In a differential equation, when the variables and their derivatives are only multiplied by constants, then the equation is linear. A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. This section provides materials for a session on linear versus nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Materials include course notes and a problem set with solutions. A first order differential equation is said.
Differential Equations Owlcation
A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent to said form: This section provides materials for a session on linear versus nonlinear ordinary differential equations. A (x)*y + b (x)*y' +.
How to solve these types of differentia... PTC Community
In a differential equation, when the variables and their derivatives are only multiplied by constants, then the equation is linear. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent to said form: Materials include course notes and a problem set with solutions. This section provides materials for a session on.
SOLUTION Examples of linear and Differential Equations with
A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. This section provides materials for a session on linear versus nonlinear ordinary differential equations. A differential equation is linear if there are no products of y y and its differentials. The variables and their derivatives must always. A differential equation is linear.
SOLUTION linear and non linear differential equation examples Studypool
In a differential equation, when the variables and their derivatives are only multiplied by constants, then the equation is linear. A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. The variables and their derivatives must always. A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. Materials include course notes and a.
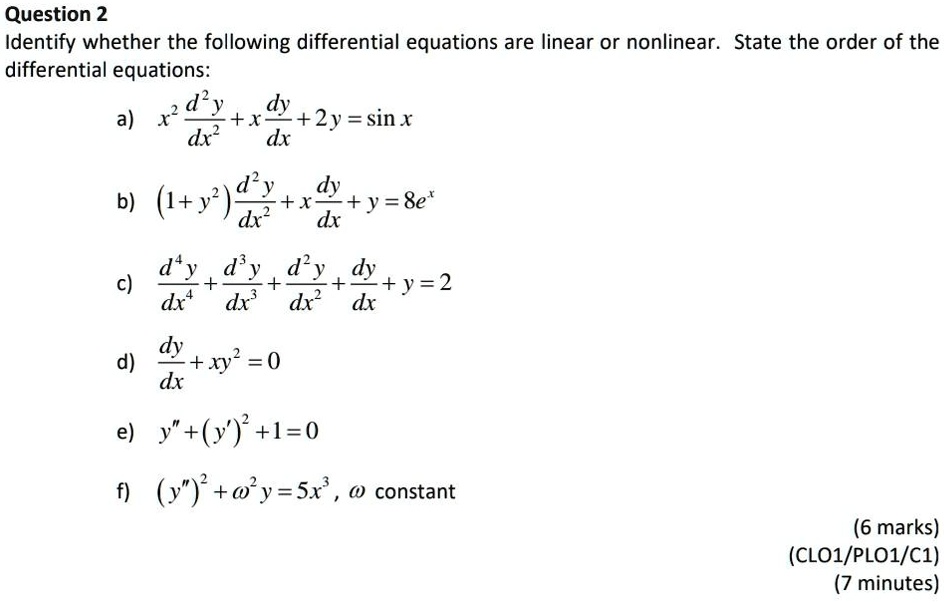
SOLVEDQuestion 2 Identify whether the following differential equations
The variables and their derivatives must always. A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. We explain the distinction between linear and nonlinear differential equations and why it matters. A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. A differential equation is linear if there are no products of y.
SOLUTION linear and non linear differential equation examples Studypool
The variables and their derivatives must always. A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent to said form: A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. Materials include course notes.
SOLUTION Examples of linear and Differential Equations with
Materials include course notes and a problem set with solutions. We explain the distinction between linear and nonlinear differential equations and why it matters. A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. In a differential equation, when the variables and their derivatives are only multiplied by constants, then the equation.
In A Differential Equation, When The Variables And Their Derivatives Are Only Multiplied By Constants, Then The Equation Is Linear.
A differential equation is linear if and only if it is in the following form or is mathematically equivalent to said form: This section provides materials for a session on linear versus nonlinear ordinary differential equations. A first order differential equation is said to be linear if it is a linear combination of terms. A differential equation is linear if there are no products of y y and its differentials.
Materials Include Course Notes And A Problem Set With Solutions.
A (x)*y + b (x)*y' + c (x)*y'' +. The variables and their derivatives must always. We explain the distinction between linear and nonlinear differential equations and why it matters.