Parabolic Differential Equation - (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde. This pde has to be. If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue.
Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. This pde has to be. (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat).
(6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde. This pde has to be. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue.
Parabolic Partial Differential Equation from Wolfram MathWorld
If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). This pde has to be. (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde.
(PDF) Normal Forms For Parabolic Partial Differential Equations
If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde. Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. This pde has to be.
SOLUTION Chapter 7 parabolic differential equations Studypool
Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde. This pde has to be. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave).
Localized orthogonal for a multiscale parabolic
If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). This pde has to be. Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde.
PPT Parabolic Partial Differential Equations PowerPoint Presentation
This pde has to be. (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde. Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat).
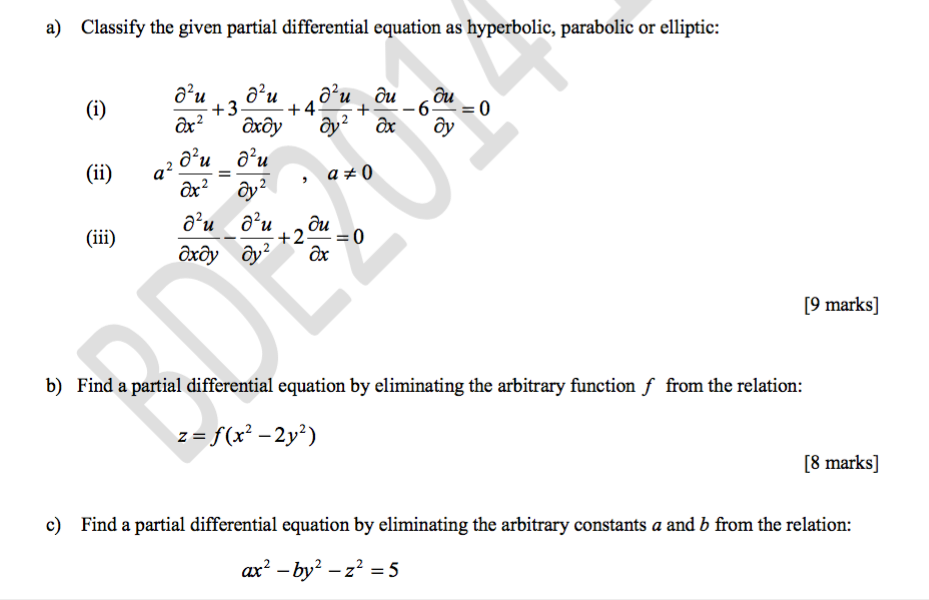
Solved a) Classify the given partial differential equation
(6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde. If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). This pde has to be. Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave).
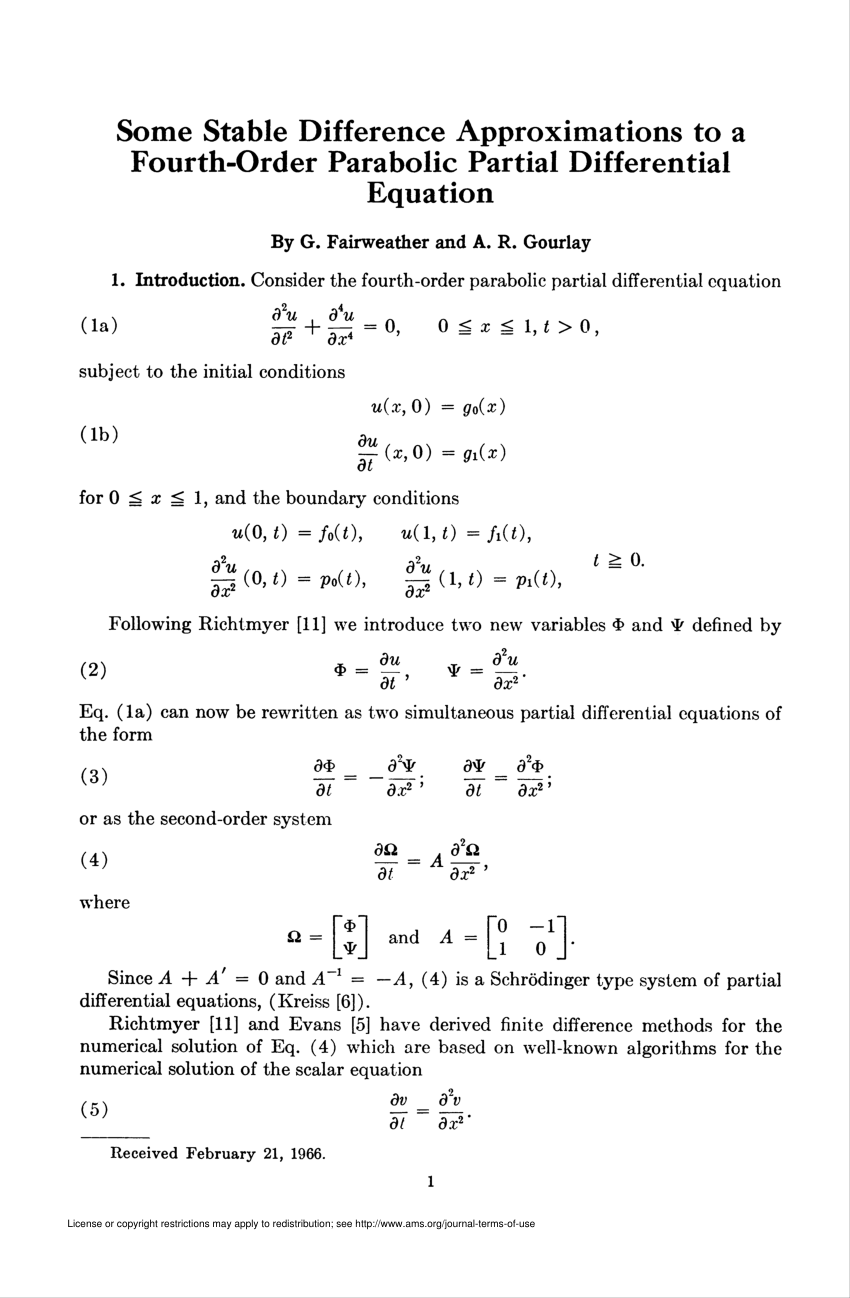
(PDF) Some Stable Difference Approximations to a FourthOrder Parabolic
If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. This pde has to be. (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde.
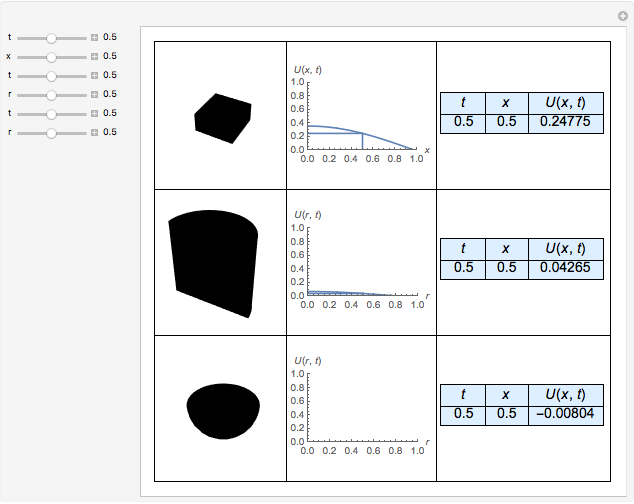
A Parabolic Partial Differential Equation in Three Different Geometries
If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). This pde has to be. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde. Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue.
(PDF) Parameteruniformly convergent numerical scheme for singularly
Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. This pde has to be. If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde.
(PDF) Structure of a Parabolic Partial Differential Equation on Graphs
This pde has to be. If b2 4ac = 0, then the pde is parabolic (heat). (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde. Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave).
If B2 4Ac = 0, Then The Pde Is Parabolic (Heat).
Tumor growth models describe the diffusion of cancer cells through the tissue. This pde has to be. If b2 4ac > 0, then the pde is hyperbolic (wave). (6.1) ut = ∆u + f is a prototypical example of a parabolic pde.