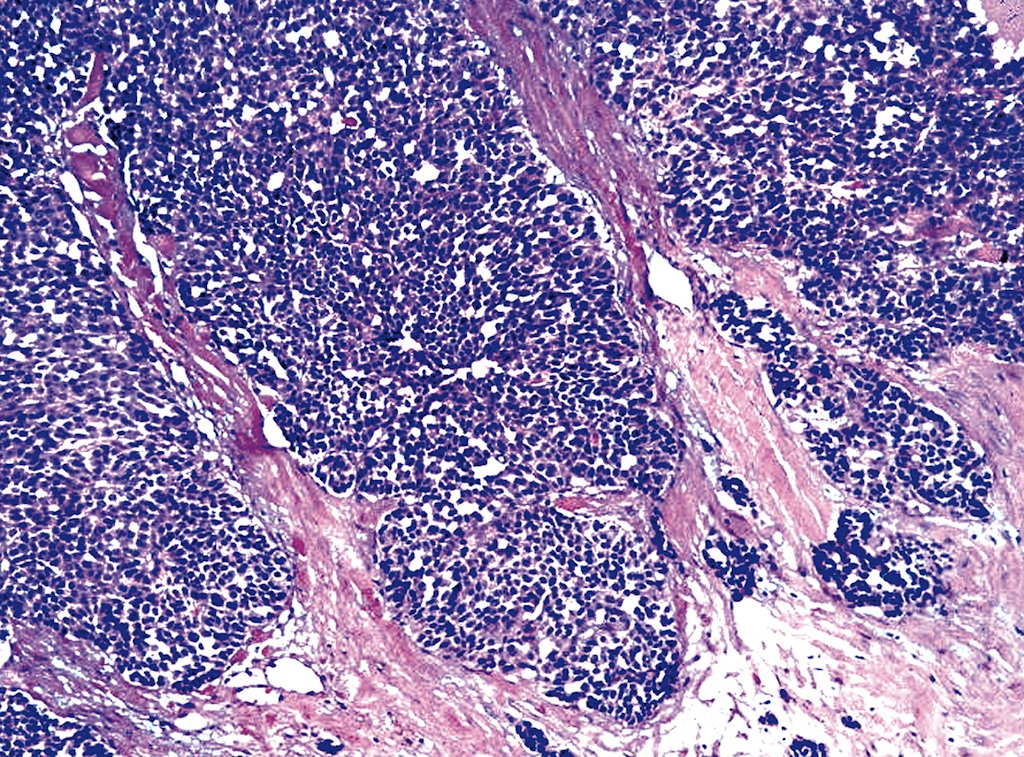
Poorly Differentiated Invasive Carcinoma - The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and.
The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer.
Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and.
Invasive Poorly Differentiated Keratinizing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of.
Histopathology of the axillary nodule. Poorly differentiated invasive
Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend.
Photomicrography of the poorly differentiated invasive squamous cell
Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive.
Gastric biopsy revealed a moderately to poorly differentiated invasive
Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive.
poorly differentiated carcinoma pathology
The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend.
Poorly differentiated invasive ductal carcinoma with
The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend.
Invasive ductal carcinoma, stage of anaplasia grade III poorly
Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a.
Invasive ductal breast carcinoma, poorly differentiated (G3). H&E
Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a.
Breast Cancer Awareness Microscopic image (photomicrograph) of
Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a.
Invasive poorly differentiated cervical squamous carcinoma (original
The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour. Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. Poorly differentiated colon cancers tend to be. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive.
Poorly Differentiated Colon Cancers Tend To Be.
Grade is one of the many factors that helps determine the aggressiveness of a given cancer. It is now clear that some patients with poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site have extremely responsive neoplasms, and. The diagnosis of poorly differentiated carcinoma is typically made through imaging studies, biopsy, and microscopic examination of the tumour.