R L Circuit Differential Equation - Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic = c dvc dt, and vl =. Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the variables and. Vl il r l step 1: Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant current source is trivial to analyze.
Vl il r l step 1: Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the variables and. Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant current source is trivial to analyze. Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic = c dvc dt, and vl =.
Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the variables and. Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic = c dvc dt, and vl =. Vl il r l step 1: Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant current source is trivial to analyze.
First order rc circuit differential equation
Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the variables and. Vl il r l step 1: Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic = c dvc dt, and vl =. Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r.
The LR series circuit differential equation acted on by an
Vl il r l step 1: Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant current source is trivial to analyze. Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the.
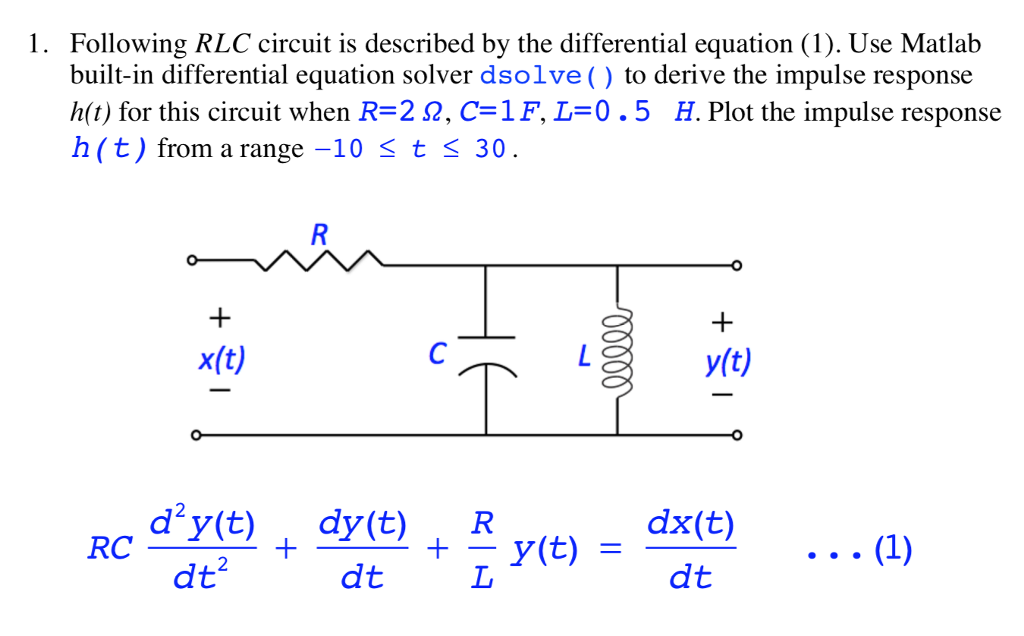
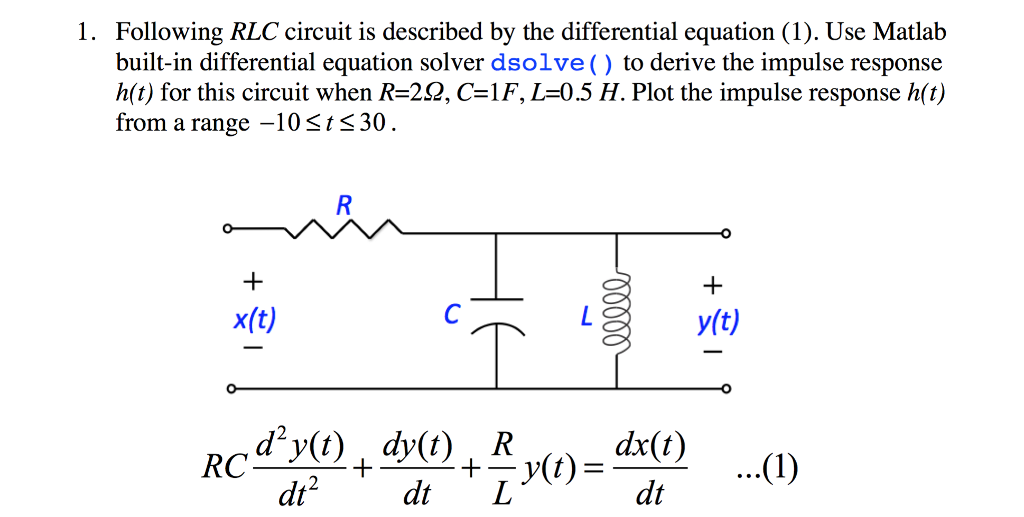
Solved 1. Following RLC circuit is described by the
Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the variables and. Vl il r l step 1: Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic = c dvc dt, and vl =. Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r.
Differential equation for RLC circuit
Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant current source is trivial to analyze. Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the variables and. Deriving the differential equation.
How to solve the differential equation for driven series RLC circuit?
Vl il r l step 1: Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic = c dvc dt, and vl =. Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant.
"RLC Circuit, Differential Equation Electrical Engineering Basics
Vl il r l step 1: Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant current source is trivial to analyze. Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the.
capacitor how does the differential equation for a series RC circuit
Vl il r l step 1: Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant current source is trivial to analyze. Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic =.
Solved 1. Following RLC circuit is described by the
Vl il r l step 1: Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the variables and. Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic = c dvc dt, and vl =. Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r.
RL Circuit differential equation electrical engineering basi Inspire
Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the variables and. Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic = c dvc dt, and vl =. Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r.
"RLC Circuit, Differential Equation Electrical Engineering Basics
Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant current source is trivial to analyze. Vl il r l step 1: Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the.
Vl Il R L Step 1:
Series/parallel rlc circuits r l c i r l c v ir il r vc v ic l i 0v * a series rlc circuit driven by a constant current source is trivial to analyze. Equation (0.2) is a first order homogeneous differential equation and its solution may be easily determined by separating the variables and. Deriving the differential equation from the constitutive relations for a capacitor and an inductor, we can write ic = c dvc dt, and vl =.