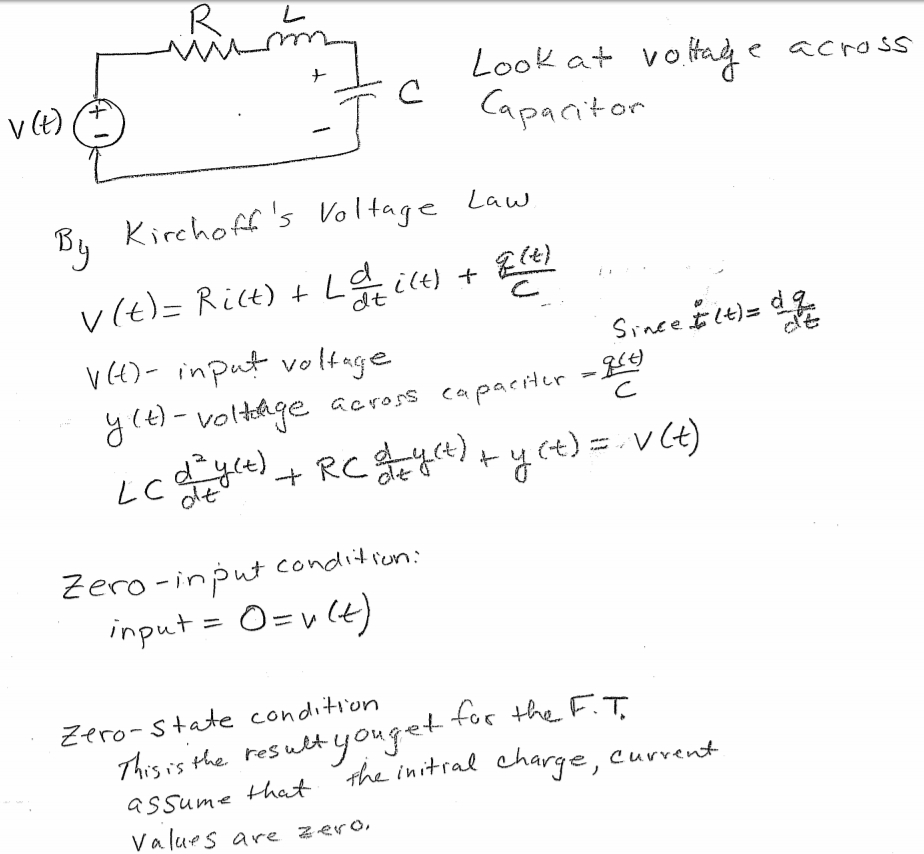
Rlc Differential Equation - Suppose that vout(0) = 0 and il(0) = 1a. However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =. Kvl implies the total voltage. Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r corresponding to the under. Rlc circuits have differential equations in the form: Assuming that r, l, c and v are known, this is still one differential equation in two unknowns, i and q. We can model vout(t) using differential equations. Rlc circuits ocw 18.03sc 3. From kvl, we have vc(t) = vl(t) (7) vout(t) = l dil(t) dt (8). A 2 d 2 x d t 2 + a 1 d x d t + a 0 x = f ( t ) {\displaystyle a_{2}{\frac.
Rlc circuits ocw 18.03sc 3. However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =. Kvl implies the total voltage. Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r corresponding to the under. From kvl, we have vc(t) = vl(t) (7) vout(t) = l dil(t) dt (8). We can model vout(t) using differential equations. A 2 d 2 x d t 2 + a 1 d x d t + a 0 x = f ( t ) {\displaystyle a_{2}{\frac. Assuming that r, l, c and v are known, this is still one differential equation in two unknowns, i and q. Rlc circuits have differential equations in the form: Suppose that vout(0) = 0 and il(0) = 1a.
Kvl implies the total voltage. From kvl, we have vc(t) = vl(t) (7) vout(t) = l dil(t) dt (8). Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r corresponding to the under. Rlc circuits ocw 18.03sc 3. We can model vout(t) using differential equations. Assuming that r, l, c and v are known, this is still one differential equation in two unknowns, i and q. Rlc circuits have differential equations in the form: However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =. A 2 d 2 x d t 2 + a 1 d x d t + a 0 x = f ( t ) {\displaystyle a_{2}{\frac. Suppose that vout(0) = 0 and il(0) = 1a.
Find the second order differential equation for this RLC circuit
We can model vout(t) using differential equations. Assuming that r, l, c and v are known, this is still one differential equation in two unknowns, i and q. Kvl implies the total voltage. Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r corresponding to the under. From kvl, we.
Solved 4. A series RLC circuit (or resonant circuit has the
Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r corresponding to the under. From kvl, we have vc(t) = vl(t) (7) vout(t) = l dil(t) dt (8). Suppose that vout(0) = 0 and il(0) = 1a. Rlc circuits have differential equations in the form: However the two unknowns are.
Differential equation for RLC circuit Mathematics Stack Exchange
However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =. A 2 d 2 x d t 2 + a 1 d x d t + a 0 x = f ( t ) {\displaystyle a_{2}{\frac. We can model vout(t) using differential equations. Rlc circuits ocw 18.03sc 3. Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf.
RLC Circuit, differential equation, electrical engineering basics
Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r corresponding to the under. Rlc circuits ocw 18.03sc 3. However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =. Kvl implies the total voltage. Suppose that vout(0) = 0 and il(0) = 1a.
(PDF) Differential equation of rlc circuit.pptx DOKUMEN.TIPS
A 2 d 2 x d t 2 + a 1 d x d t + a 0 x = f ( t ) {\displaystyle a_{2}{\frac. However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =. Rlc circuits have differential equations in the form: We can model vout(t) using differential equations. Suppose that vout(0) = 0 and il(0) = 1a.
Differential equation for RLC circuit
We can model vout(t) using differential equations. From kvl, we have vc(t) = vl(t) (7) vout(t) = l dil(t) dt (8). However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =. Assuming that r, l, c and v are known, this is still one differential equation in two unknowns, i and q. A 2 d 2 x d t 2 +.
"RLC Circuit, Differential Equation Electrical Engineering Basics
Kvl implies the total voltage. We can model vout(t) using differential equations. From kvl, we have vc(t) = vl(t) (7) vout(t) = l dil(t) dt (8). Assuming that r, l, c and v are known, this is still one differential equation in two unknowns, i and q. However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =.
power electronics Calculating Differential equation RLC Circuit
A 2 d 2 x d t 2 + a 1 d x d t + a 0 x = f ( t ) {\displaystyle a_{2}{\frac. Kvl implies the total voltage. However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =. Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r.
power electronics Calculating Differential equation RLC Circuit
We can model vout(t) using differential equations. Rlc circuits ocw 18.03sc 3. However the two unknowns are related by i(t) =. Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r corresponding to the under. From kvl, we have vc(t) = vl(t) (7) vout(t) = l dil(t) dt (8).
Differential equation for RLC circuit Mathematics Stack Exchange
Rlc circuits have differential equations in the form: Assuming that r, l, c and v are known, this is still one differential equation in two unknowns, i and q. Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r corresponding to the under. Kvl implies the total voltage. We can.
However The Two Unknowns Are Related By I(T) =.
Rlc circuits have differential equations in the form: We can model vout(t) using differential equations. A 2 d 2 x d t 2 + a 1 d x d t + a 0 x = f ( t ) {\displaystyle a_{2}{\frac. Kvl implies the total voltage.
Rlc Circuits Ocw 18.03Sc 3.
From kvl, we have vc(t) = vl(t) (7) vout(t) = l dil(t) dt (8). Suppose that vout(0) = 0 and il(0) = 1a. Figure 2 shows the response of the series rlc circuit with l=47mh, c=47nf and for three different values of r corresponding to the under. Assuming that r, l, c and v are known, this is still one differential equation in two unknowns, i and q.