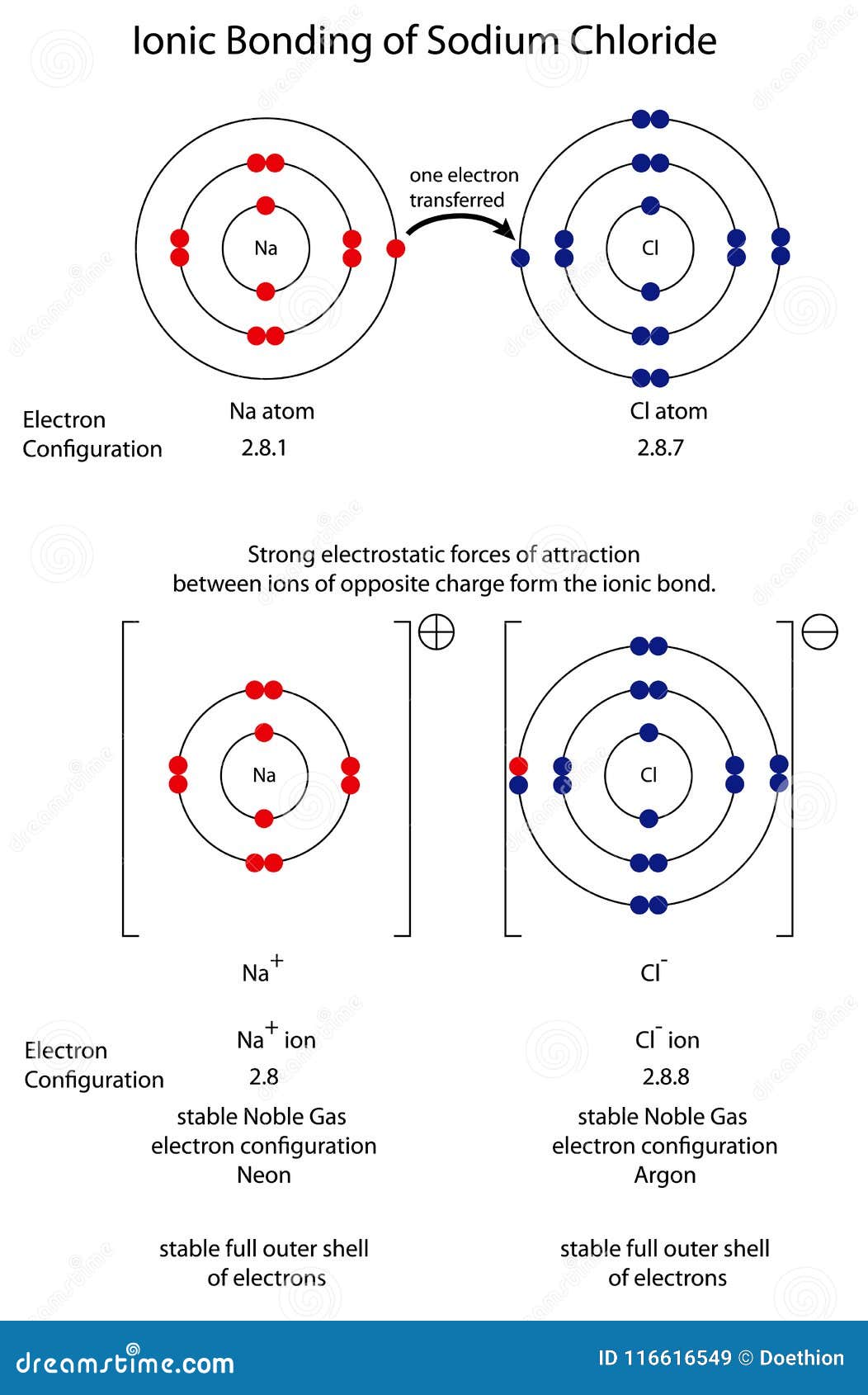
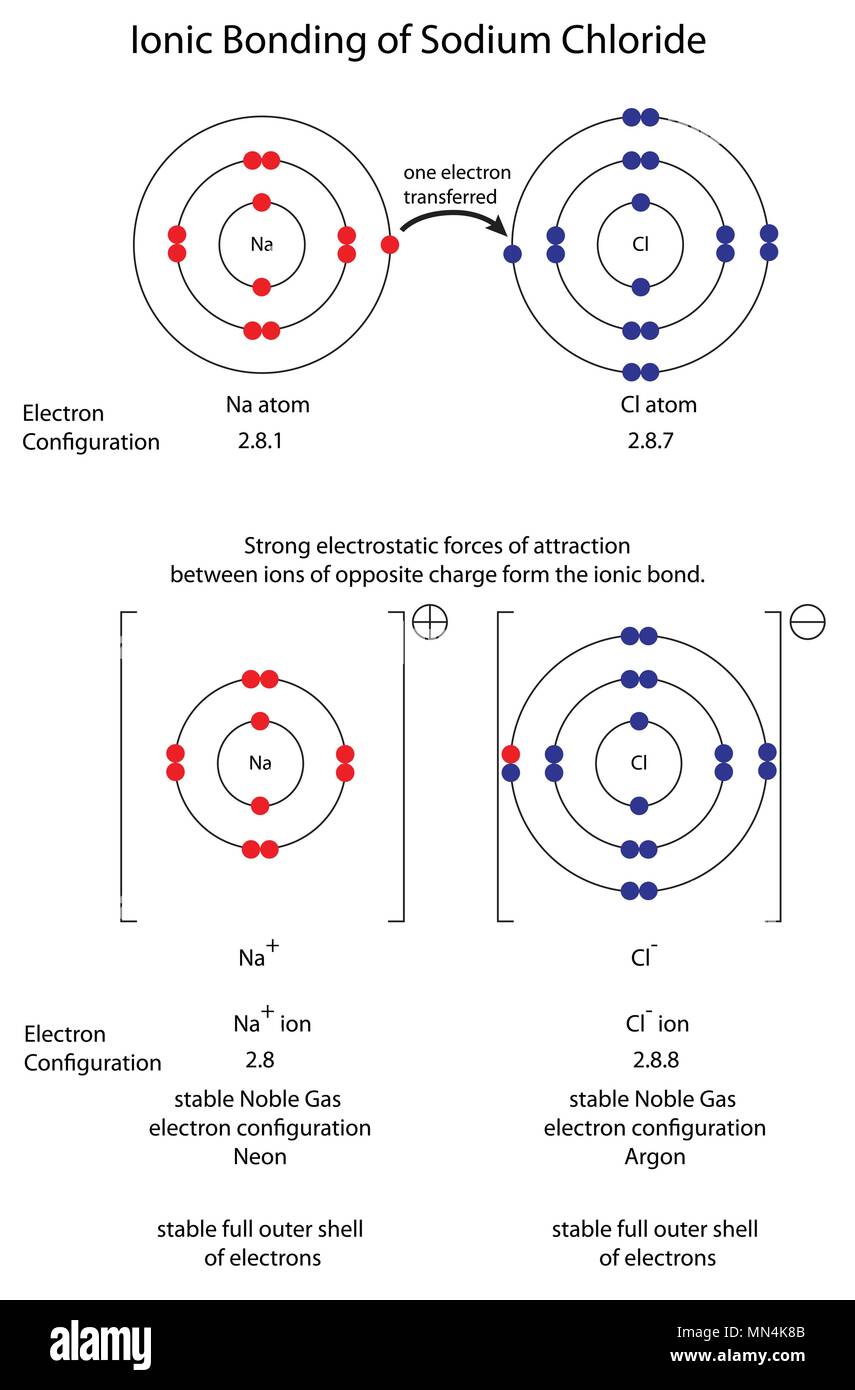
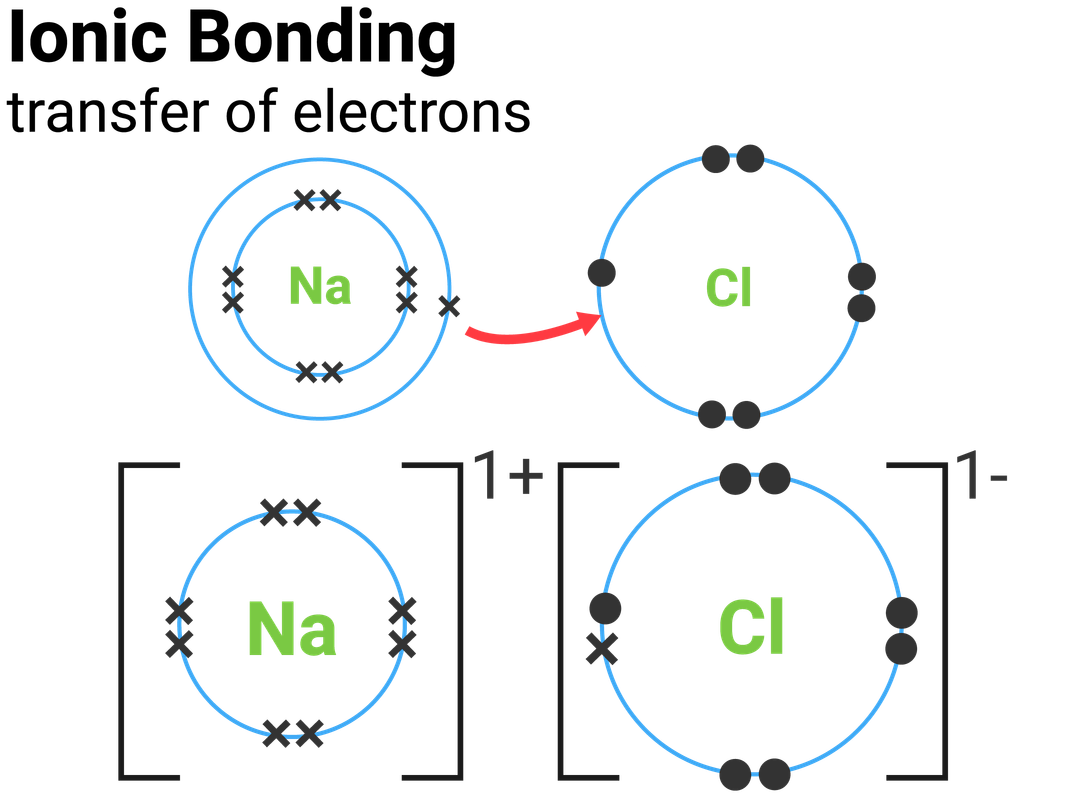
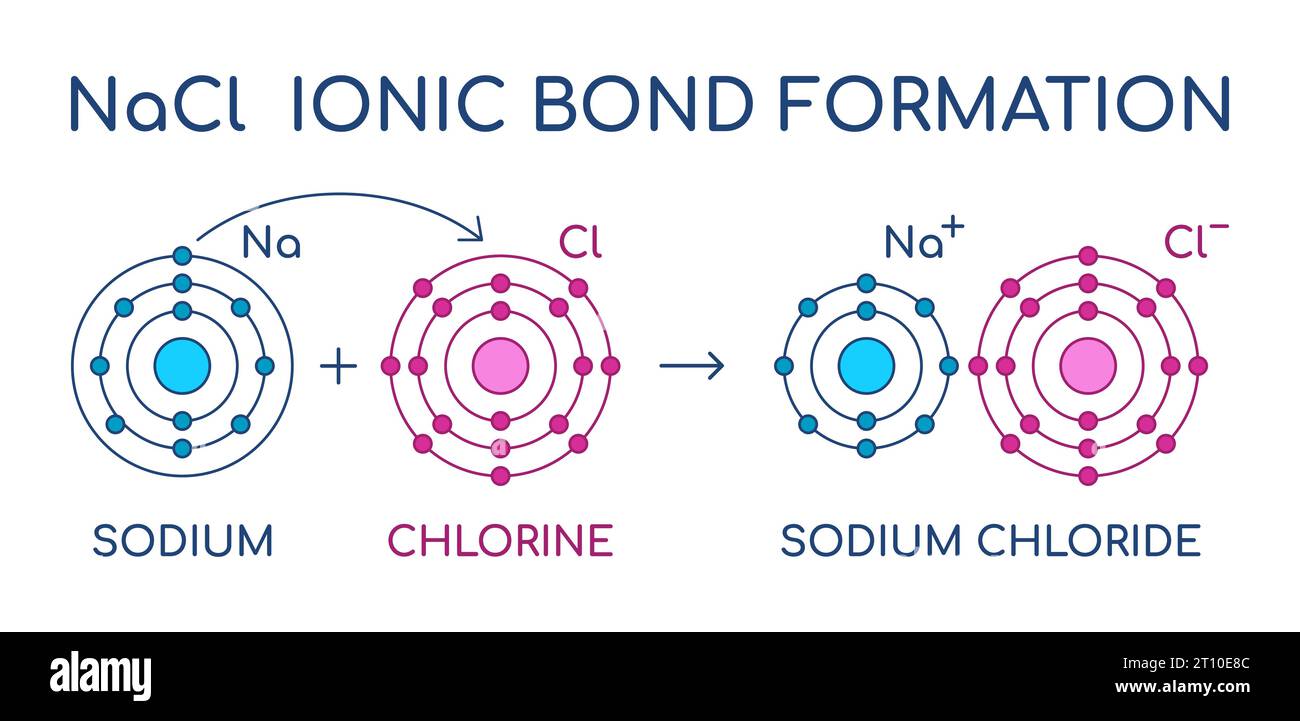
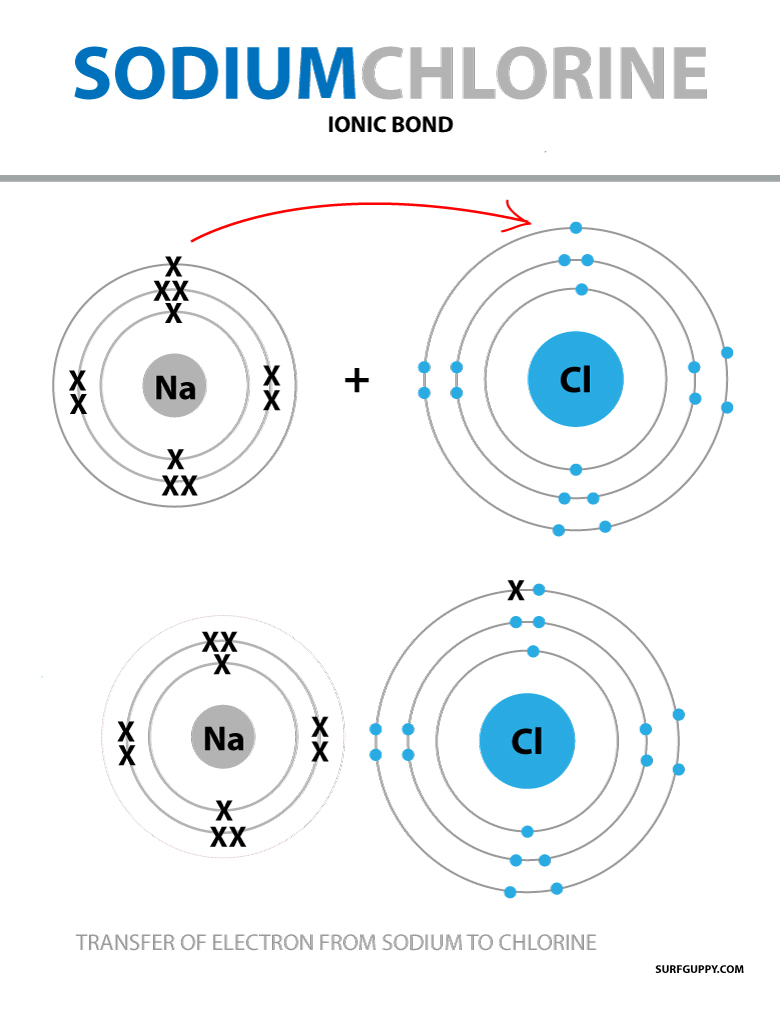
The Ionic Bond Of Sodium Chloride Is Formed When - The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus.
The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus. The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of.
So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus. The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged.
Diagram Of Ionic Bonding In Sodium Chloride
The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus.
Ionic bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica
The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus.
What is Ionic Bond Surfguppy Chemistry made easy visual learning
So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus. The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of.
What Is An Ionic Bond Sciencing Ionic Bonding Ionic Chemical Bond
So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus. The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged.
Diagram To Show Ionic Bonding in Sodium Chloride Stock Illustration
The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus.
Diagram to show ionic bonding in sodium chloride Stock Vector Image
The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus.
Sodium Chloride Ionic Bonding Diagram
So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus. The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged.
ionic bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica
The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus.
Sodium Chloride ionic bond formation. NaCl structure. Sodium and
The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus.
Ionic Bond in Sodium Chloride Stock Vector Illustration of sodium
The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of. The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. So, the excess one electron is transferred to a chlorine atom from n a(sodium) atom and thus.
So, The Excess One Electron Is Transferred To A Chlorine Atom From N A(Sodium) Atom And Thus.
The ions are held together in the lattice by strong ionic bonds between the oppositely charged. The classic case of ionic bonding, the sodium chloride molecule forms by the ionization of.


.PNG)