What Is An Implicit Solution To A Differential Equation - The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. In the integral equation you need the. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Below we show how this method. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit.
A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. Below we show how this method. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. In the integral equation you need the. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit.
Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. Below we show how this method. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. In the integral equation you need the.
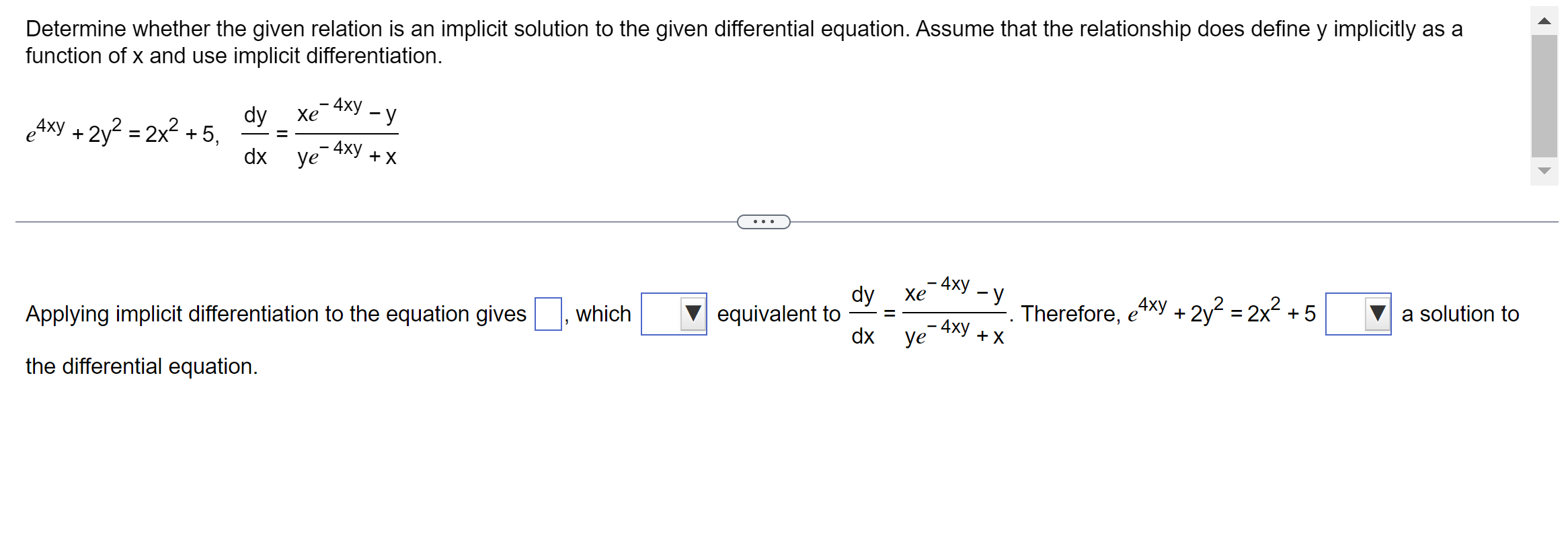
Solved Determine whether the given relation is an implicit
A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; $\begingroup$ an.
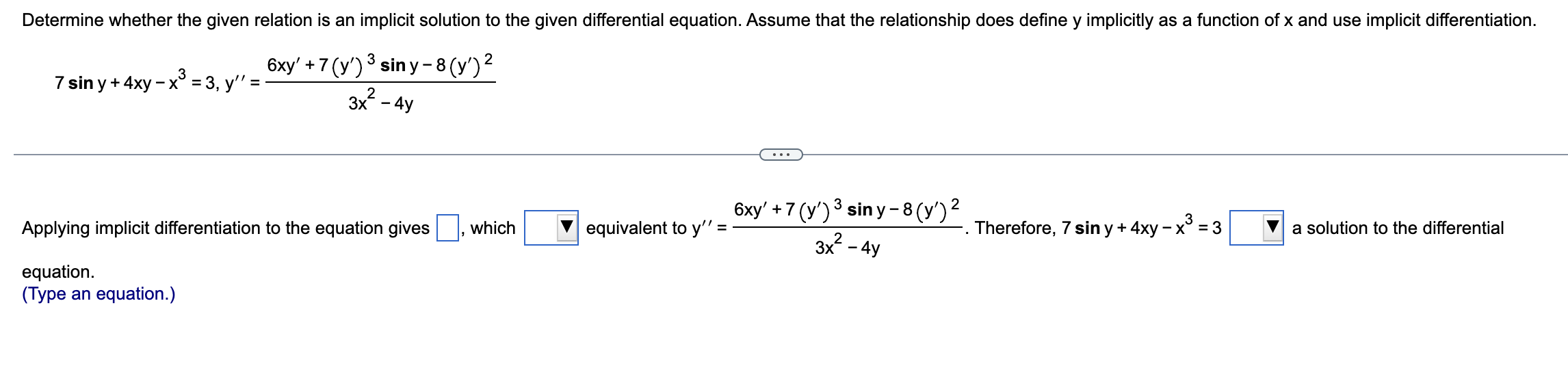
Solved Determine whether the given relation is an implicit
The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left(.
Solved Find the general solution for the differential
Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. A solution to a differential.
Solved 6. Find the implicit solution to the differential
Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. Here $y(x)$.
SOLVED Solve for the implicit general solution for the below
$\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. In the integral equation you need the. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta.
How to solve implicit differential equation? Mathematics Stack Exchange
$\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. In the integral equation you need the. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined.
calculus Verify that an implicit equation is the solution to the
Below we show how this method. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; In the integral equation you need the.
Solved Determine whether the given relation is an implicit
The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. $\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an.
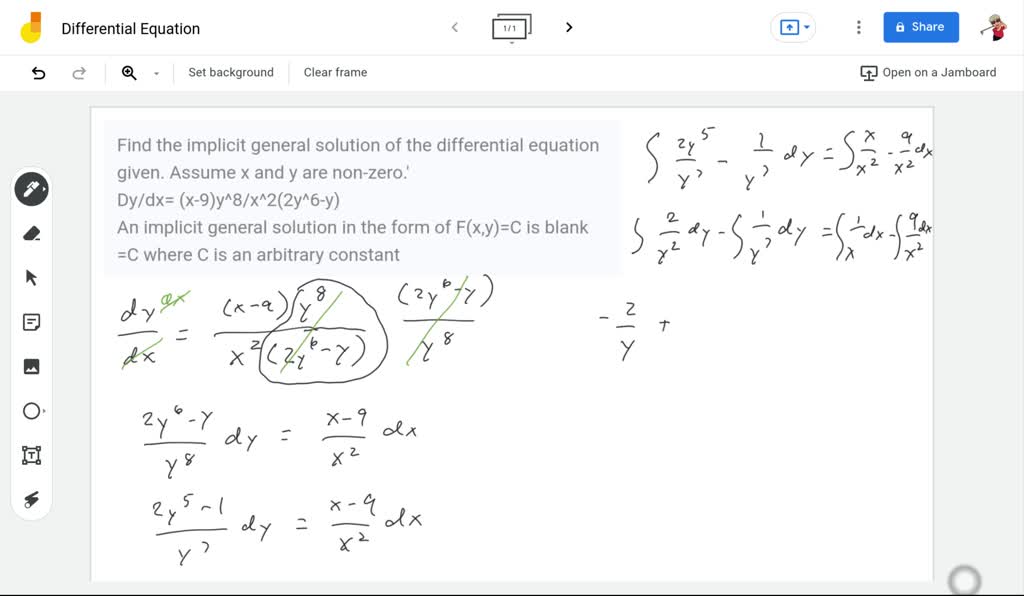
SOLVED Find the implicit general solution of the differential equation
Below we show how this method. A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y.
Show that the given relation defines an implicit solution to Quizlet
$\begingroup$ an implicit solution is an implicit equation that allows to compute the solution. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. The implicit solution of this differential equation is $x^2+y(x)^2=r^2$; A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. In the integral equation you need the.
$\Begingroup$ An Implicit Solution Is An Implicit Equation That Allows To Compute The Solution.
The main techniques for solving an implicit differential equation is the method of introducing a parameter. A relation f(x,y)=0 is said to be an implicit solution of a differential equation involving x, y, and derivatives of y with respect to x if f(x,y)=0. Also in nagle, implicit solutions are defined as a solution on the interval i if it defines one or more explicit solutions, and an explicit. In the integral equation you need the.
The Implicit Solution Of This Differential Equation Is $X^2+Y(X)^2=R^2$;
A solution to a differential equation on an interval \(\alpha < t < \beta \) is any function \(y\left( t \right)\) which satisfies the. Here $y(x)$ is implicitly defined. Below we show how this method.