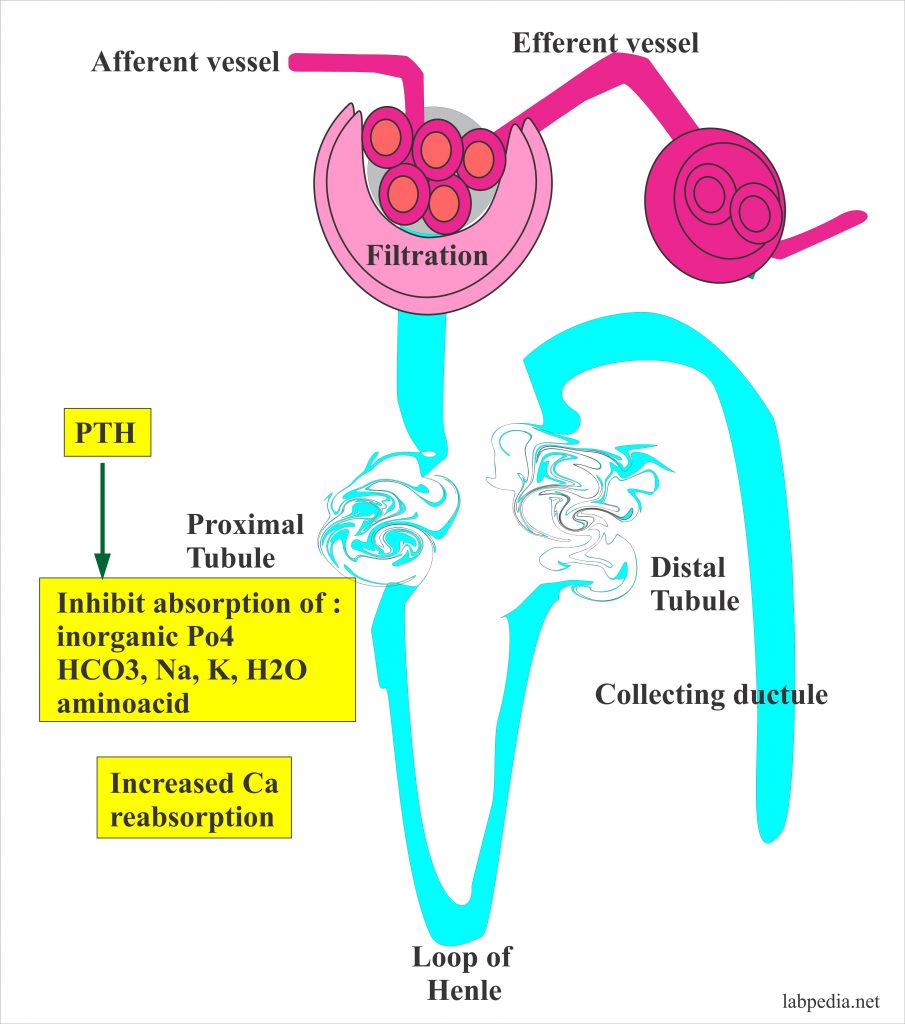
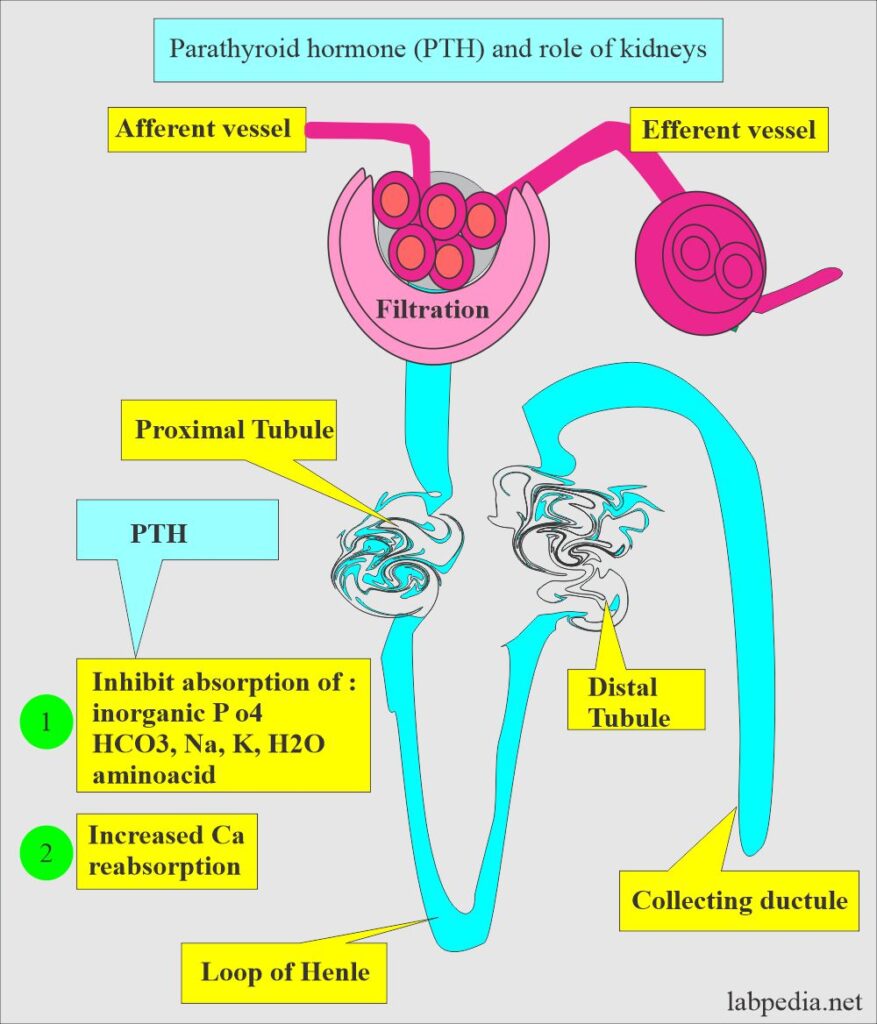
Which Organ Prevents Calcium Loss In Response To Pth Stimulation - Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation. Secreted in response to small. Bone is deposited by superficial osteoblasts. What is responsible for appositional growth? Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium. Here’s the best way to solve it. Pth hormones lowers the phosphate reabsorption at the. Pth plays a critical regulatory role in calcium metabolism. Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation?
What is responsible for appositional growth? Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium. Secreted in response to small. Bone is deposited by superficial osteoblasts. The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (pth) in response to lower calcium in. Pth plays a critical regulatory role in calcium metabolism. Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation. Pth hormones lowers the phosphate reabsorption at the. Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation?
Pth plays a critical regulatory role in calcium metabolism. Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Bone is deposited by superficial osteoblasts. Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium. What is responsible for appositional growth? Pth hormones lowers the phosphate reabsorption at the. The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (pth) in response to lower calcium in. Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation. Secreted in response to small. Here’s the best way to solve it.
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (pth) in response to lower calcium in. Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Bone is deposited by superficial osteoblasts. What is responsible for appositional growth? Here’s the best way to solve it.
Calcium and vitamin D homeostasis. PTH and 1,25(OH) 2 D tightly
Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Pth hormones lowers the phosphate reabsorption at the. Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation. Here’s the best way to solve it. The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (pth) in response to lower calcium in.
Calcium Homeostasis Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other
Secreted in response to small. Here’s the best way to solve it. Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation. Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (pth) in response to lower calcium in.
Hormones produced by the parathyroid gland. Parathyroid hormone (PTH
Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium. Here’s the best way to solve it. Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation. The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (pth) in response to lower calcium in. Pth hormones lowers the phosphate reabsorption at the.
PTH secretion and regulation PTH = Parathyroid Hormone; Ca2+ = Calcium
Secreted in response to small. Pth plays a critical regulatory role in calcium metabolism. Here’s the best way to solve it. What is responsible for appositional growth? Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium.
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Bone is deposited by superficial osteoblasts. Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium. Secreted in response to small. Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation.
Schematic representation of alteration of the relative calciumPTH
Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium. Here’s the best way to solve it. Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation. Pth hormones lowers the phosphate reabsorption at the. Secreted in response to small.
Calcitonin Is The Agonist To PTH Stock Vector Image 59085590
Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Bone is deposited by superficial osteoblasts. What is responsible for appositional growth? Secreted in response to small. Here’s the best way to solve it.
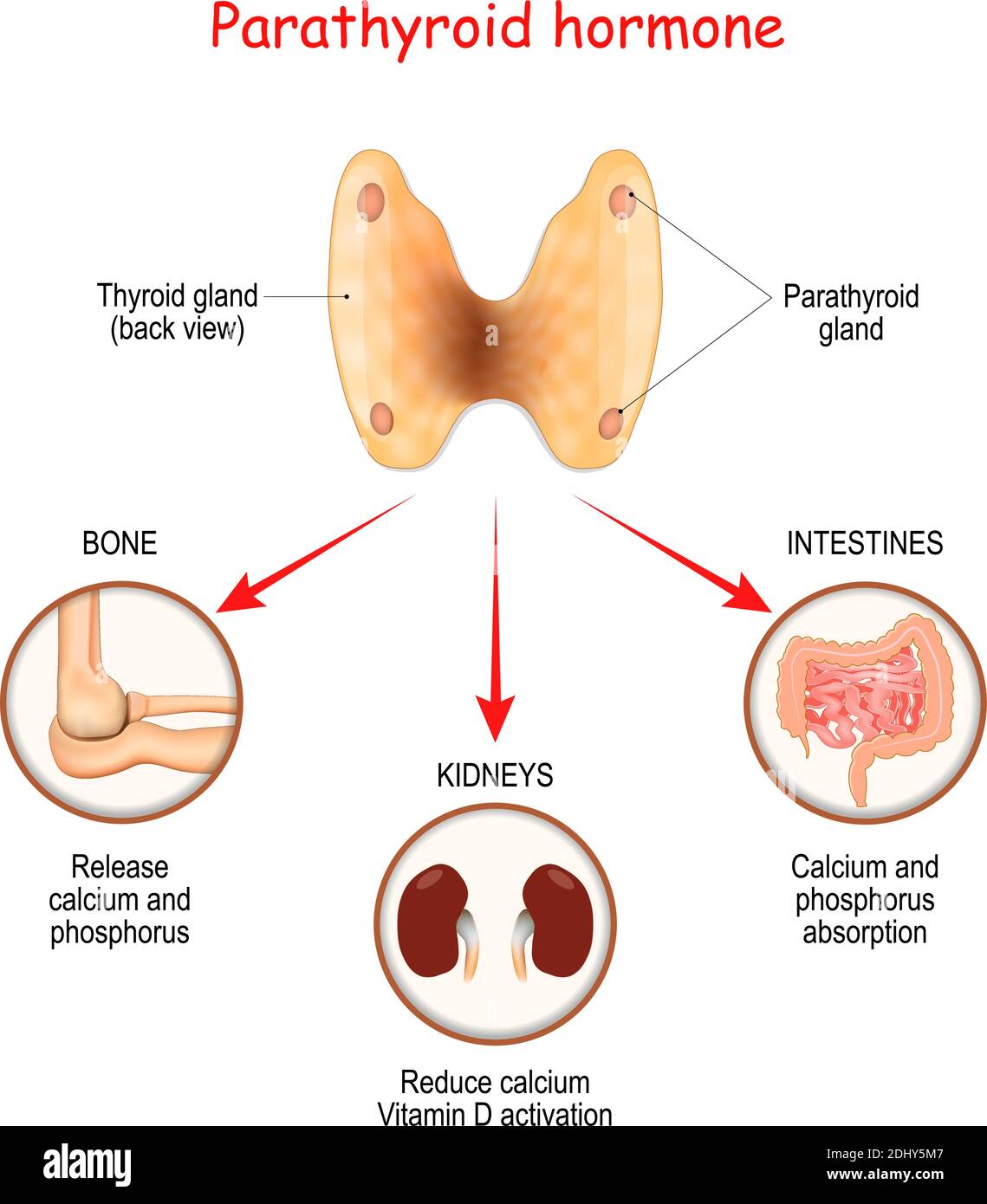
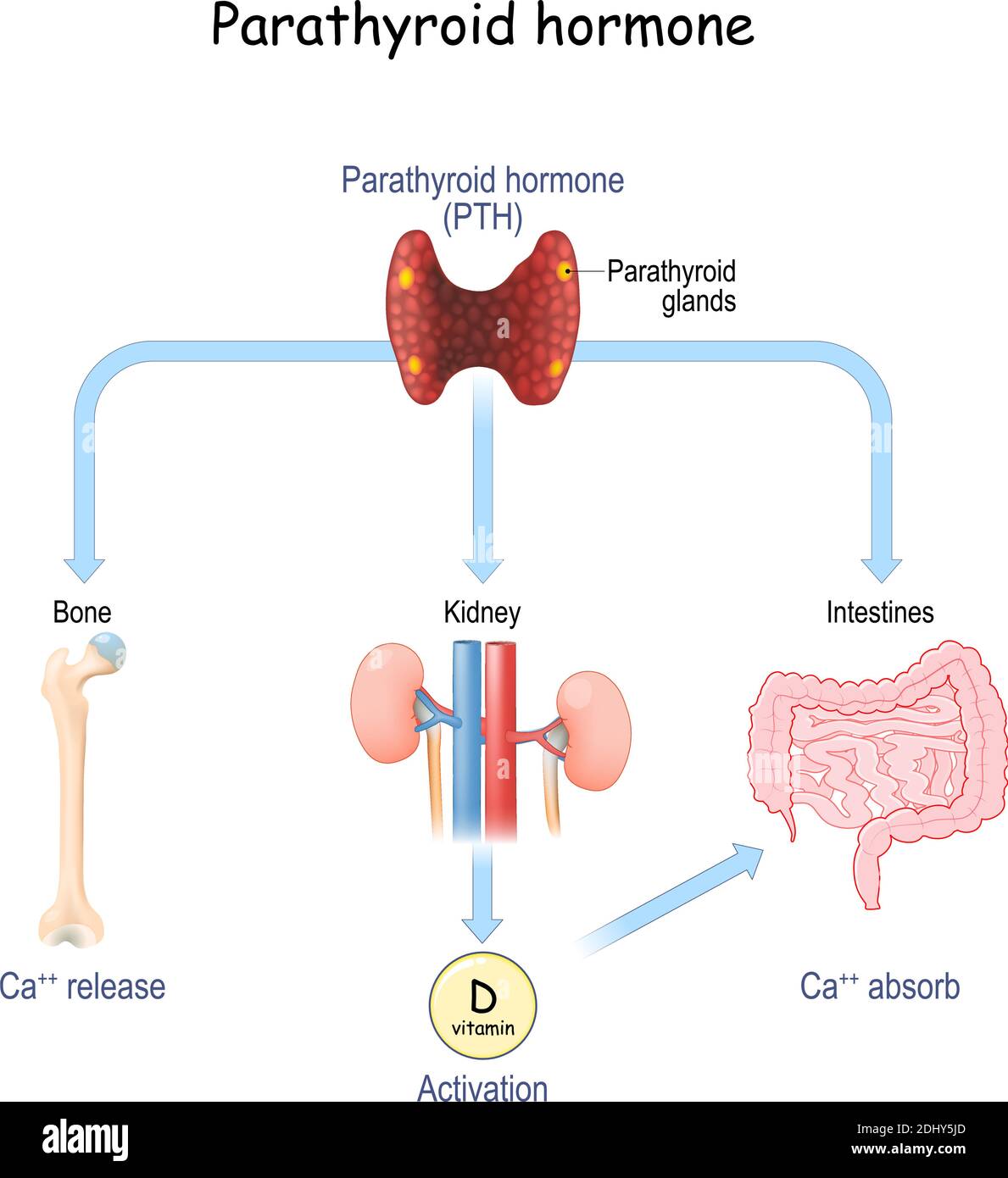
Parathyroid hormone and Calcium metabolism. parathormone or parathyrin
Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium. Pth hormones lowers the phosphate reabsorption at the. What is responsible for appositional growth? The parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone (pth) in response to lower calcium in.
Parathyroid Hormone. it is Working Control Calcium Levels in the Blood
Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation. Secreted in response to small. Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium.
Which Organ Prevents Calcium Loss In Response To Pth Stimulation?
Pth enhances the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules of the kidneys, preventing calcium. Here’s the best way to solve it. Which organ prevents calcium loss in response to pth stimulation? Secreted in response to small.
What Is Responsible For Appositional Growth?
Pth plays a critical regulatory role in calcium metabolism. Pth hormones lowers the phosphate reabsorption at the. Calcium loss is stopped by the bones organ in response to pth stimulation. Bone is deposited by superficial osteoblasts.