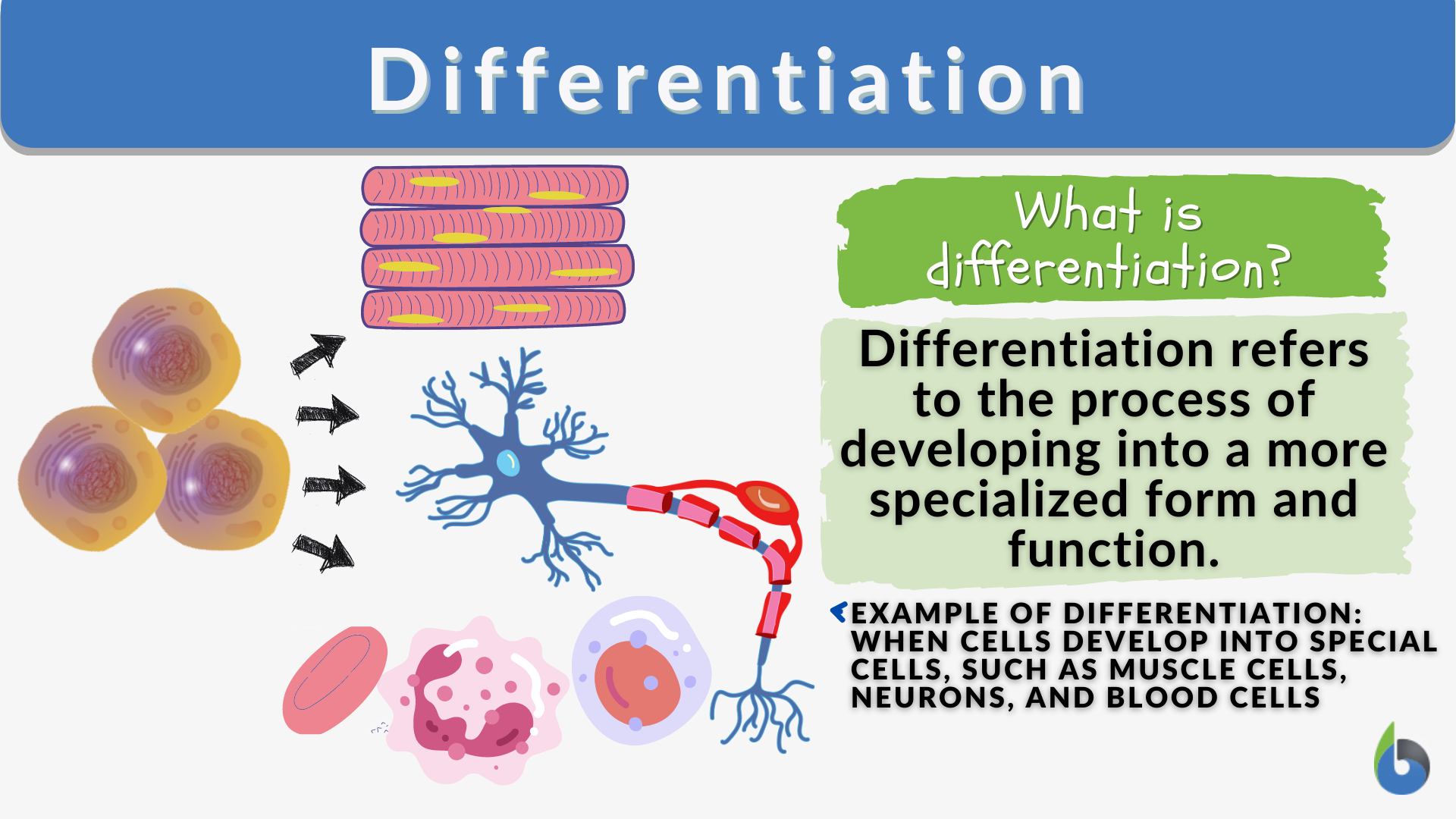
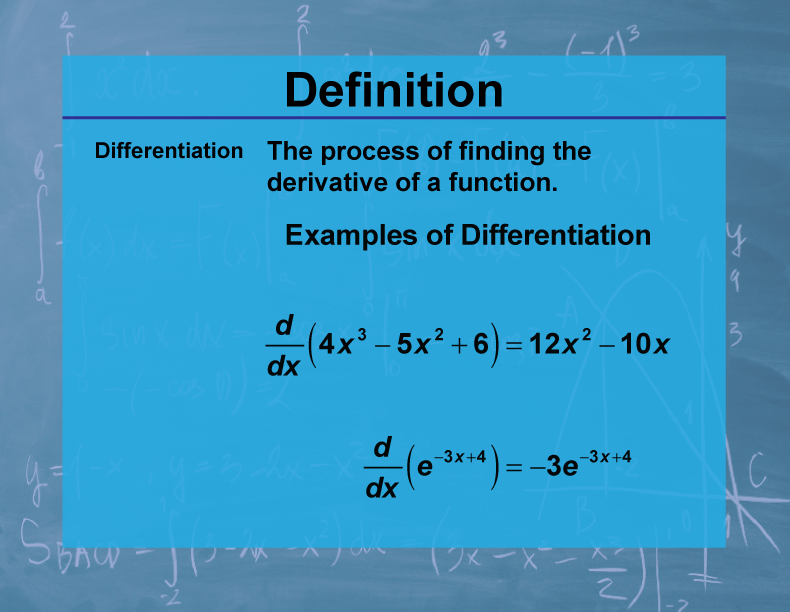
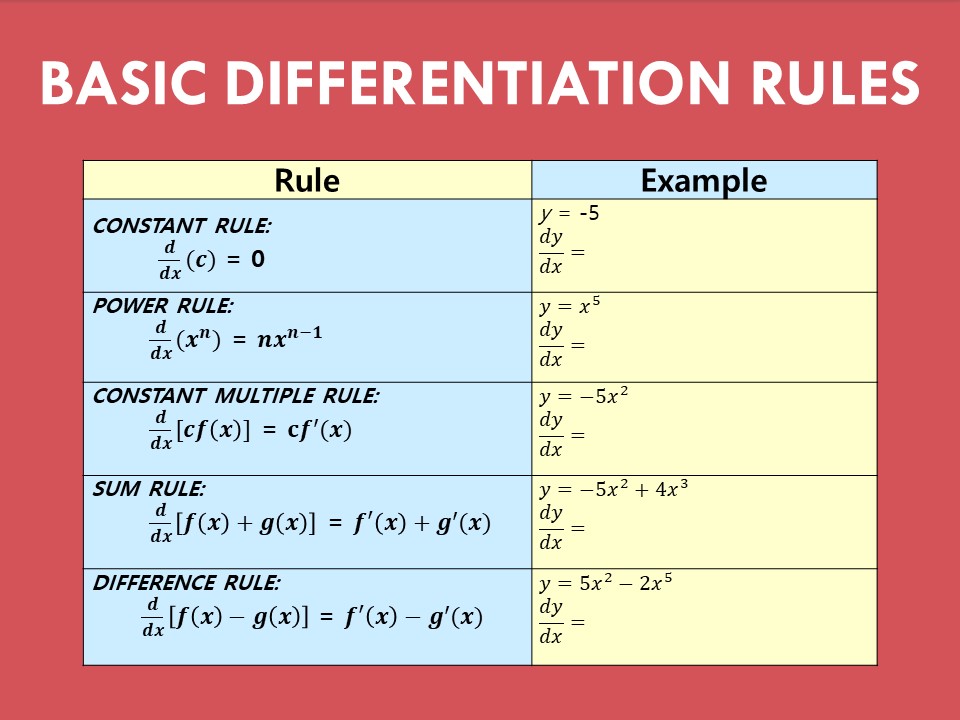
Zone Of Differentiation - A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. Up to now, three different zones along the longitudinal axis of the primary root of. The major functions of roots, thus, can be summarized simply as absorption, conduction,. Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. The root tip can be divided into three zones: The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit the mitotic. The root tip can be divided into three zones: A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a.
The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit the mitotic. Up to now, three different zones along the longitudinal axis of the primary root of. The root tip can be divided into three zones: The root tip can be divided into three zones: A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. The major functions of roots, thus, can be summarized simply as absorption, conduction,.
Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. The major functions of roots, thus, can be summarized simply as absorption, conduction,. Up to now, three different zones along the longitudinal axis of the primary root of. The root tip can be divided into three zones: The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit the mitotic. The root tip can be divided into three zones: A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a.
Differentiation icon Generic gradient outline
Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. Up to now, three different zones along the longitudinal axis of the primary root of. The root tip can be divided into three zones: The root tip can be divided into three zones: The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit.
Differentiation Set the Brand and Product apart
Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. Up to now, three different zones along the longitudinal axis of the primary root of. The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit the mitotic. A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. The major functions of roots,.
Differentiation Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. Up to now, three different zones along the longitudinal axis of the primary root of. Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. The root tip can be divided into three zones: A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and.
Differentiation Generic Flat icon
The major functions of roots, thus, can be summarized simply as absorption, conduction,. The root tip can be divided into three zones: The root tip can be divided into three zones: Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a.
Product Differentiation Examples And Strategies Glossary, 58 OFF
Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. The major functions of roots, thus, can be summarized simply as absorption, conduction,. A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. The root tip can be divided into three zones:
Differentiation Generic Flat icon
The major functions of roots, thus, can be summarized simply as absorption, conduction,. Up to now, three different zones along the longitudinal axis of the primary root of. The root tip can be divided into three zones: The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit the mitotic. The root tip can be divided into three zones:
Differentiation
Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. The major functions of roots, thus, can be summarized simply as absorption, conduction,. A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit the mitotic. A zone of cell division, a zone.
Differentiation Button Cartoon Vector 196836881
The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit the mitotic. The root tip can be divided into three zones: A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells.
(PDF) ROLE MODEL WITH ZONE DIFFERENTIATION OF ACCESS eSAT Journals
The major functions of roots, thus, can be summarized simply as absorption, conduction,. The root tip can be divided into three zones: Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells. The root tip can be divided into three zones: The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit the mitotic.
Master Template
The root tip can be divided into three zones: Up to now, three different zones along the longitudinal axis of the primary root of. The root tip can be divided into three zones: A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells.
Up To Now, Three Different Zones Along The Longitudinal Axis Of The Primary Root Of.
The root tip can be divided into three zones: The root tip can be divided into three zones: The transition to differentiation starts in the elongation zone when cells exit the mitotic. A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a.
The Major Functions Of Roots, Thus, Can Be Summarized Simply As Absorption, Conduction,.
A zone of cell division, a zone of elongation, and a. Following the region of elongation comes the final one, the region of maturation, where cells.