General Solution Of Homogeneous Differential Equation - The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root. If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set of n n linearly independent functions (i.e.
Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root. So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set of n n linearly independent functions (i.e.
So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set of n n linearly independent functions (i.e. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree.
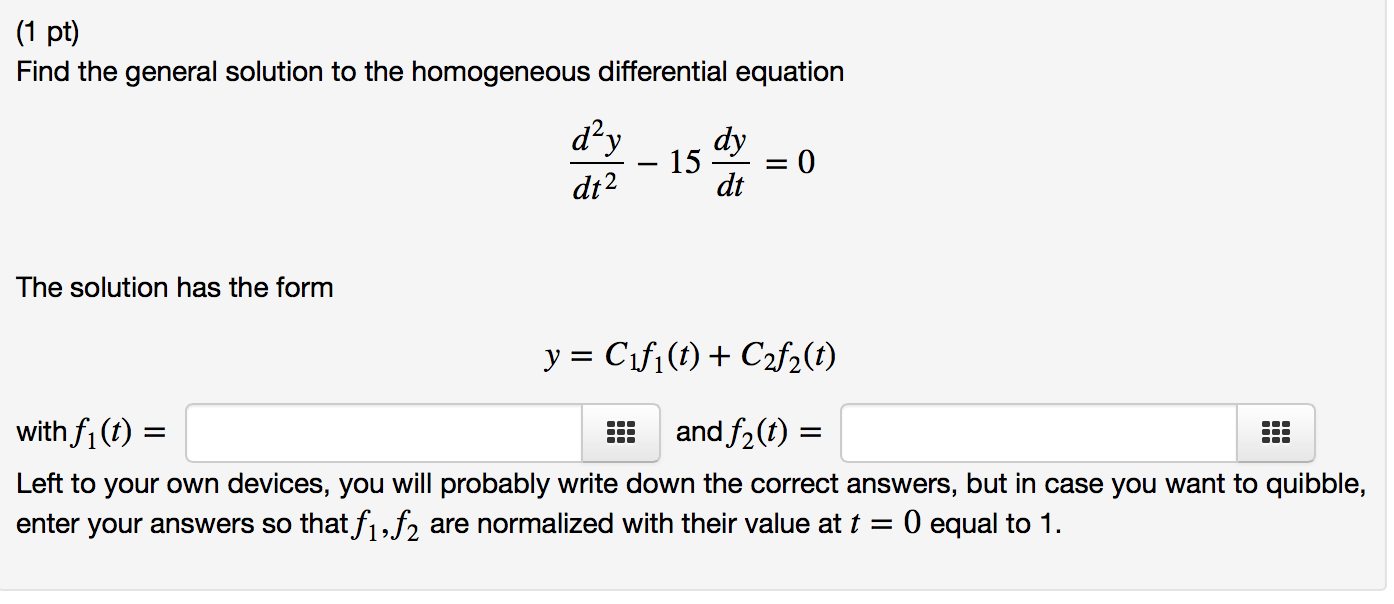
Solved Find the general solution to the homogeneous
Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set of n n linearly independent functions (i.e. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. If \(y_1\).
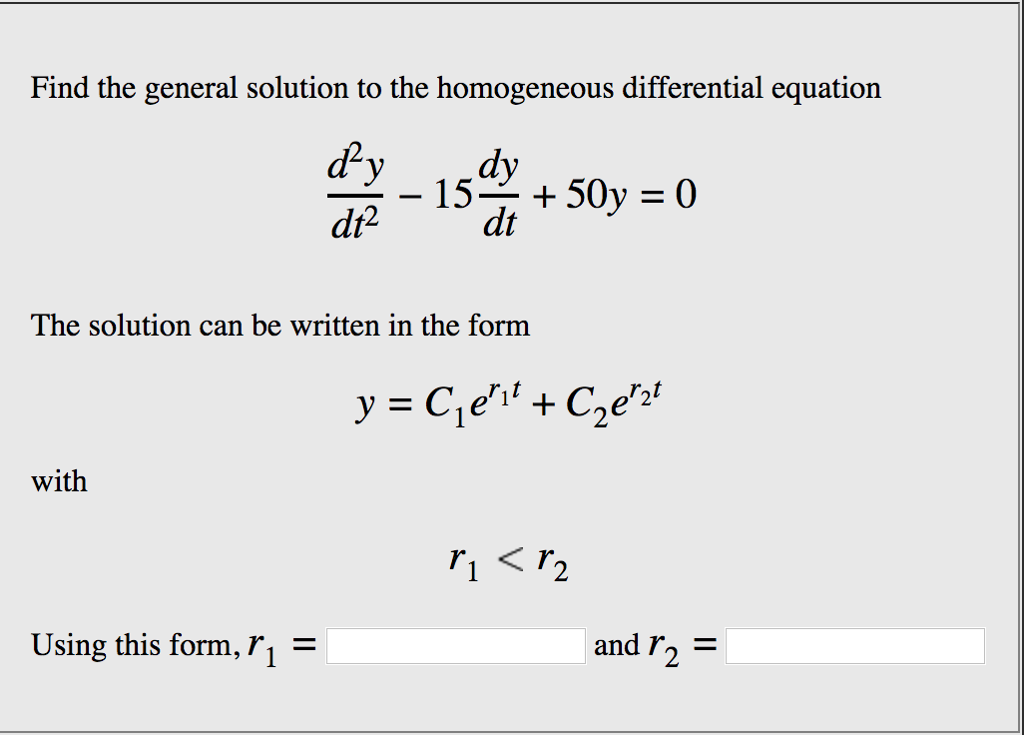
[Solved] Find the general solution to the homogeneous differential
The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set of n n linearly independent functions (i.e. If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. Homogeneous differential equation are the.
Solved The general solution of the homogeneous differential
The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree.
[Solved] find the general solution of this homogeneous differential
The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree.
Solved Find the general solution to the homogeneous
Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root.
[Solved] find the general solution of this homogeneous differential
If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential.
Solved Differential Equation Find the general solution to
The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set.
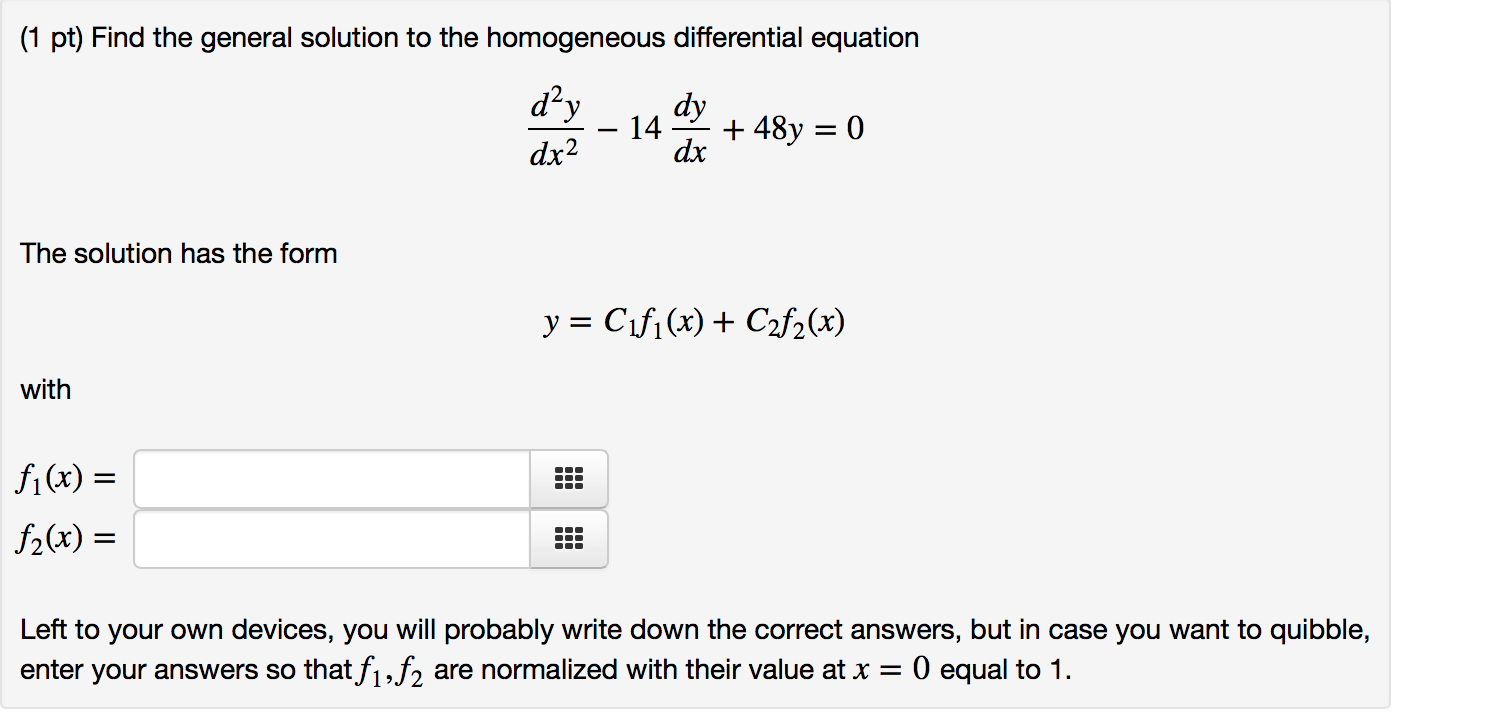
[Solved] ( 1 point) Find the general solution to the homo
Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root. So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set of n n linearly independent.
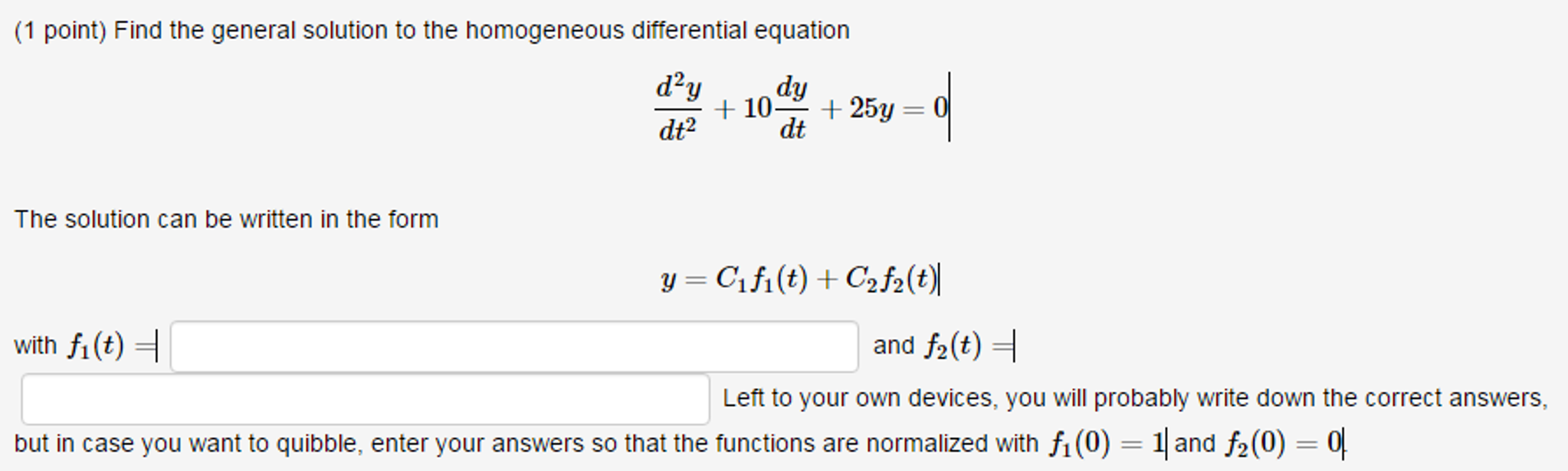
[Solved] Find the general solution to the homogeneous differential
The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set of n n linearly independent functions (i.e. If \(y_1\) and.
Solved Find the general solution to the homogeneous
If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval. Learn to solve the homogeneous equation of. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set of n n linearly independent functions (i.e. Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree.
If \(Y_1\) And \(Y_2\) Are Defined On An Interval.
Homogeneous differential equation are the equations having functions of the same degree. Let us learn more about the homogeneous differential. The general form of a homogeneous differential equation is f(x, y).dy + g(x, y).dx = 0. So, for each n n th order differential equation we’ll need to form a set of n n linearly independent functions (i.e.
Learn To Solve The Homogeneous Equation Of.
The characteristic equation is \[\begin{aligned}r^2+2r+1&=(r+1)^2 \\ &=0,\end{aligned}\] which has a repeated root.

![[Solved] ( 1 point) Find the general solution to the homo](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/335/335da5e9-34ec-4b22-8068-6fd8a60eb996/phpxlWnqN)